We have learned about different types of microbes and their benefits to humans. We have also learnt about the various diseases they cause and their repercussions.
Of the many types of microbes, bacteria and virus cause a majority of the diseases. These can range from mild illness such as the common cold to severe medical conditions such as necrotising fasciitis (also called flesh-eating disease).

However, they are vastly different from each other in terms of physiology, morphology, and anatomy. Therefore, it is essential to learn the difference between virus and bacteria.
Table of Contents
Difference Between Virus And Bacteria
Bacteria and viruses differ significantly. Major differences are as follows:
Bacteria |
Virus |
|
Outer Cell Wall |
|
| Bacterial cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan | Viruses do not contain a cell wall. The genetic material is enveloped by a protein coat known as a capsid |
|
Size |
|
| Bacteria are large in size. The size ranges from 900 to 1000nm | Smaller in size. The size ranges from 30 to 50nm |
|
Non-Living/Living |
|
| They are living organisms | They can replicate only within the host cell |
|
Mode of Reproduction |
|
| Reproduce asexually by binary fission | Insert their genome in the host genome and make multiple copies |
|
Host Dependence |
|
| Host independent reproduction | Host dependent reproduction |
|
Ribosomes |
|
| Present | Absent |
|
RNA and DNA |
|
| DNA or RNA is present in the cytoplasm | DNA or RNA are enveloped inside a protein coat known as a capsid |
|
Infections |
|
| Generally localised infection, e.g. Pneumonia | Generally systemic, e.g. flu |
|
Diseases |
|
| Pneumonia, meningitis, food poisoning, typhoid, etc. | Common cold, polio, smallpox, hepatitis, AIDS, etc. |
|
Treatment |
|
| Antibiotics | Vaccines and antiviral drugs |
|
Examples |
|
| Salmonella typheae, Vibrio cholerae, Staphylococcus aureus | Coronavirus, TMV, HIV, Hepatitis A, etc |
What is Bacteria?
Main article: Bacteria
Bacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms. They are found everywhere. They can survive even the harshest of conditions such as hot springs, deep ocean, snow and even in the volcanos. Disease-causing bacteria are known as pathogens.
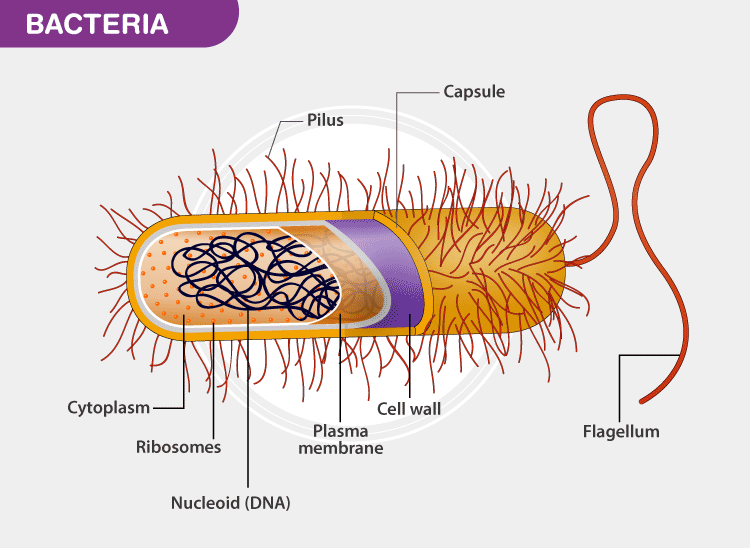
A bacteria
Characteristics Of Bacteria
- Bacteria are unicellular, some of the bacteria form multicellular reproductive structures, e.g. myxobacteria.
- Bacterial cell lacks membrane-bound organelle. Genetic material remains dispersed in nucleoid and the nucleus is absent.
- The bacterial cell has ribosomes, where protein assembly takes place.
Bacteria play a very important role in the ecosystem. They are widely used in the medical and agricultural industries.
What is a Virus?
Virus are extremely small entities which contain either RNA or DNA as the genetic material. They are also smaller than most bacteria.

HIV
Virus are not fully acknowledged as living organisms as they cannot survive outside a host. Anatomically, a typical virus is girdled by a protein coat that is enclosed by a membrane made of proteins. In some virus, this protein coat is covered by a lipid membrane called the viral envelope.
Characteristics Of Virus
- Virus lack cellular organelles and cytoplasm.
- They fail to perform metabolic activities.
- Most of the virus contain RNA or DNA, but not both.
- Virus reproduce at a tremendous pace but only inside the cells of the living hosts. Furthermore, most virus have the capability to mutate.
- They make use of the metabolic machinery of the host cells. Virus cannot grow and divide. They produce and assemble new viral components inside the infected host cell.
Main article: Virus
Learn more about the difference between virus and bacteria, or other related topics only at BYJU’S Biology
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1. Why antibiotics do not work on viruses?
A.1. Antibiotic target cellular structures and proteins present in the bacteria.
E.g. antibiotics target bacterial cell wall, cellular enzymes, metabolic pathways, ribosomes, etc. Since viruses do not contain cellular structure, antibiotics do not affect them.
Q.2. Why viruses are called obligate parasites?
A.2. Viruses cannot live outside the host. They utilise host machinery to perform vital functions.
Q.3. List five diseases caused by virus.
A.3. Polio, Smallpox, Hepatitis, Herpes, Common cold, AIDS
Q.4. Write any five uses of bacteria.
A.4. Bacteria are used in various processes and industries:
- Bacteria are used in baking and brewing industry for the fermentation process.
- Lactobacillus converts milk to curd.
- Bacteria are widely used in the chemical industries for the production of alcohol, enzymes and various organic acids, etc
- They are used in the production of medicines.
- Bacteria play an important role in nitrogen fixation, e.g. Rhizobium.
Q.5. Name the bacteria, which are resistant to antibiotics.
A.5. Most of the bacteria are not resistant to antibiotics, but some of the bacteria such as Neisseria gonorrhoea and Staphylococcus have shown to develop resistance to benzylpenicillin.

Gud explanation
I liked it much
Superb answer😊😊
very nice information
Good explanation of the difference between Virus and Bacteria