Literally, replication means the process of duplication. In molecular biology, DNA replication is the primary stage of inheritance. Central dogma explains how the DNA makes its own copies through DNA replication, which then codes for the RNA in transcription and further, RNA codes for the proteins by the translation.
Let’s go through Meselson and Stahl Experiment and DNA replication.
Meselson and Stahl Experiment
Meselson and Stahl Experiment was an experimental proof for semiconservative DNA replication. In 1958, Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl conducted an experiment on E.coli which divides in 20 minutes, to study the replication of DNA.
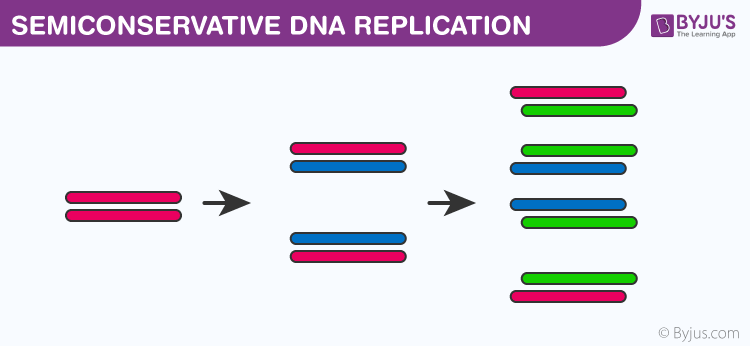
Semi conservative DNA Replication through Meselson and Stahl’s Experiment
Experiment
15N (heavy) and 14N (normal) are two isotopes of nitrogen, which can be distinguished based on their densities by centrifugation in Ca,esium chloride (CsCl). Meselson and Stahl cultured E.coli in a medium constituting 15NH4Cl over many generations. As a result, 15N was integrated into the bacterial DNA. Later, they revised the 15NH4Cl medium to normal 14NH4Cl. At a regular interval of time, they took the sample and checked for the density of DNA.
Observation
Sample no. 1 (after 20 minutes): The sample had bacterial DNA with an intermediate density. Sample no. 2 (after 40 minutes): The sample contained DNA with both intermediate and light densities in the same proportion.
Conclusion
Based on observations and experimental results, Meselson and Stahl concluded that DNA molecules can replicate semi-conservatively. Investigation of semi-conservative nature of replication of DNA or the copying of the cells, DNA didn’t end there. Followed by Meselson and Stahl experiment, Taylor and colleagues conducted another experiment on Vicia faba (fava beans) which again proved that replication of DNA is semi-conservative.
Also Read: DNA Structure
DNA Replication
DNA is the genetic material in the majority of the organisms. Structurally, it is a double-stranded helical structure which can replicate.
DNA replication is the process by which the DNA makes multiple copies of itself. It was originally proposed by Watson and Crick. DNA replication proceeds as follows:
- Primarily during this process, two DNA strands will open and separate.
- As the strands are separated, the enzymes start synthesizing the complementary sequence in each of the strands. That is, each parental strand will act as a template for the newly synthesized daughter strands.
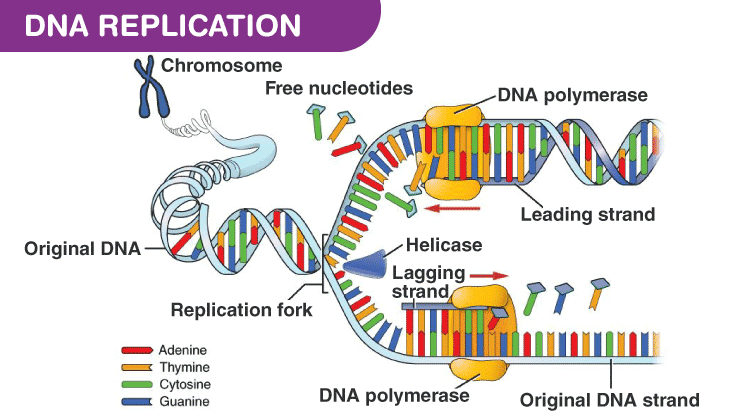
DNA Replication
Since the new DNA strands thus formed have one strand of the parent DNA and the other is newly synthesized, the process is called semiconservative DNA replication.
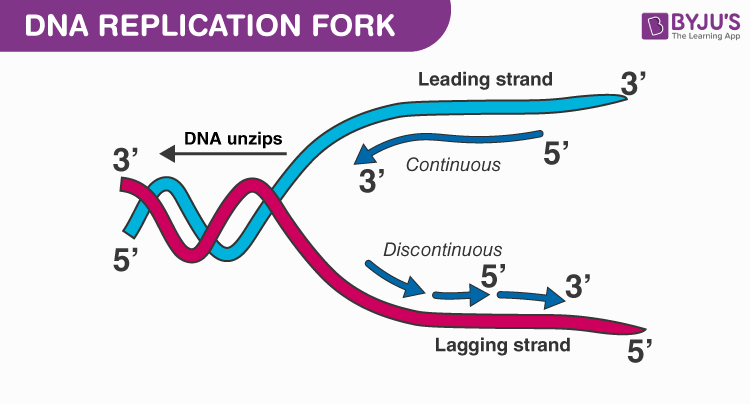
DNA Replication Fork
Also Read: DNA Replication
For more information on DNA Replication and Messelson and Stahl experiment, keep visiting BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S app for further reference.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which mode of replication did the Messelson and Stahl’s experiment support?
Messelson and Stahl’s experiment supported the semi-conservative mode of replication. The DNA was first replicated in 14N medium which produced a band of 14N and 15N hybrid DNA. This eliminated the conservative mode of replication.
What are the different modes of replication of DNA?
The different modes of replication of DNA are:
- Semiconservative
- Dispersive
- Conservative
How are semi-conservative and conservative modes of replication different?
Semi-conservative mode of replication produces two copies, each containing one original strand and one new strand. On the contrary, conservative replication produces two new strands and would leave two original template DNA strands in a double helix.
What is the result of DNA replication?
The result of DNA replication is one original strand and one new strand of nucleotides.
What happens if DNA replication goes wrong?
If DNA replication goes wrong, a mutation occurs. However, if any mismatch happens, it can be corrected during proofreading by DNA Polymerase.
I FOUND IT VERY USEFUL AND THE WAY EVERYTHING IS EXPLAINED IS VERY HELPFUL.
THANK YOU
This is awesome and straight to the point