Table of Contents
Over thousands and millions of years, a bewildering variety of species have evolved on the earth. Among these, some are known and some are unknown to us. The life forms around us range from, tiny ants to tall trees, colourless worms/insects to brightly coloured flowers and birds. Understanding and tracking all of them in a fraction of the time, one by one is not a wise choice. We need to group them based on certain basic criteria. Let us have a glance at evolution and classification, tracing of evolutionary relationships and the formation of fossils in detail.
Evolution and Classification
Evolution is the successive alteration in inherited characteristics over an extensive span of time, typically over generations. Evolution has created extensive biodiversity. Classification is the way to deal with the immense diversity exhibited by entities.
Living entities are grouped on the basis of traits such as similarities and differences. Characteristics or traits are some attributes such as the form/appearance and function/behaviour of something. These characteristics determine the classification, that is to say, which entity falls into a particular category. For instance, a snake does not have limbs, but a dog does. A dog and a snake could move, but plants are immobile. These are the traits or characteristics of different organisms. These behaviours sort them into different classes.
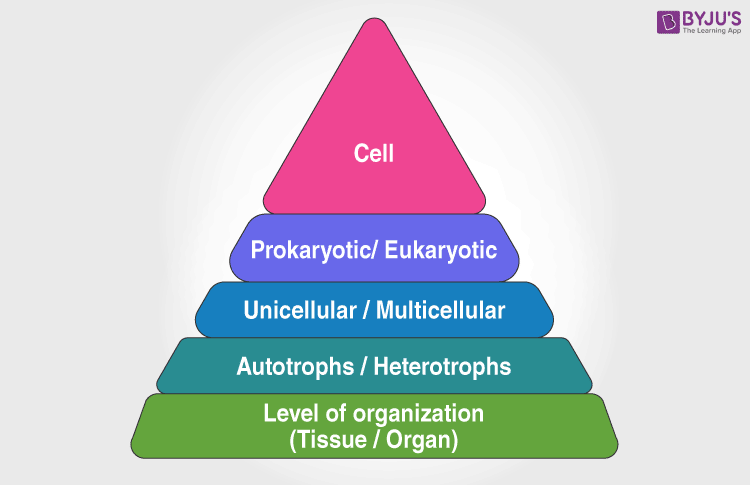
The hierarchy of classification begins with the cell. The cell is the basic unit of every organism. This characteristic is shared by all living organisms. The body design, the level of organization and the development of organs come later. As we move towards the last, the number of entities that share common characteristics becomes lesser. Thus, we could conclude that the greater the number of shared characteristics between two species, the more closely related they are. More recently they have had a common ancestor. This is the same as your relationship with your brother and cousin. Characteristics you share with your brother are more than that with your cousin. Also, the common ancestor of you and your brother is your parents, but the common ancestor of you and your cousin is your grandparents.
Tracing Evolutionary Relationships
Characteristics assist us to trace the evolutionary relationship between organisms. Evolutionary relationships help us to trace who we are closest to and who is our common ancestors.
A group of entities is similar enough to be thought of together by certain characteristics.
For example, reptiles and mammals. All of them have 4 limbs. The basic structure of their organs is more or less the same, although they utilize it for varied functions. These organs are known as homologous organs. This does not mean that they share the same ancestor.
Some entities seem to be similar, however, the basic structure is different.
For instance, the wings of birds and bats. Both of these animals make use of wings for the same purpose, however, their basic structures are different. Such organs are known as analogous organs.
Thus, the analogous and homologous characteristics help in tracking an evolutionary relationship between different species.
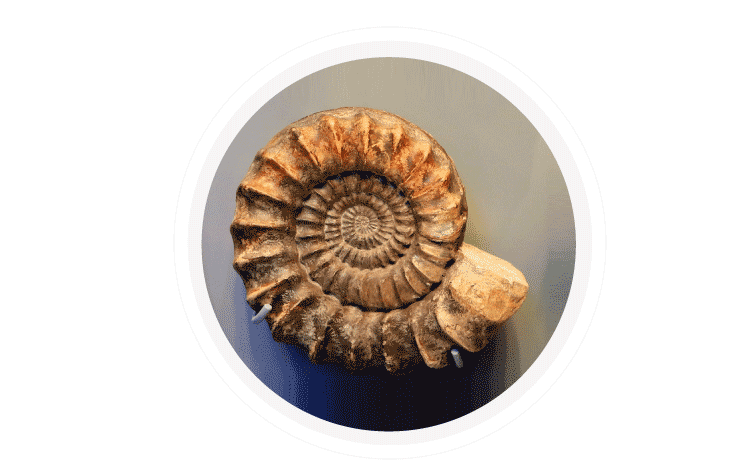

Fossils
We use living species to trace evolutionary relationships. But organisms which once lived and do not exist anymore also have a story to tell about evolution. They can be used for tracing the evolutionary relationship between species. Fossils are the examples of the preserved traces of living entities.
Typically, when living entities die, their body will degrade and gradually decompose. But sometimes, our environment will not decompose them all at once or completely. It will leave some evidence for us. When a body hardens under trapped mud, the body leaves behind impressions in the mud which causes the fossil-formation. One prominent example is the fossils of dinosaurs.
We could estimate the age of fossils in two ways. The first procedure is more relative. In this method, we assume that the fossils which we find at the topmost layers are more recent ones while at a deeper layer, the fossils found are older. In the second approach, an estimation of the ratios of different isotopes of the same element in the fossil is carried out.
To learn more about fossils and evolution with video lessons, visit BYJU’S.
Related Links
Frequently Asked Questions on Fossils – Tracing Evolutionary Relationship
What is carbon dating?
Carbon dating also known as radiocarbon dating, is a method of finding the age of organic materials containing carbon [e.g.: fossils] using radioactive carbon isotope [C-14].
What is considered a living fossil?
The extant living organisms that closely resemble a fossil than any other living thing is known as a living fossil.
How are fossils used in classification?
Fossilized organisms connects the missing links in the phylogenetic tree and are thus helpful in their classification.
What are some examples of fossil records supporting evolution?
The lower jaw of reptiles consists of several bones but mammals have only one. The remaining bones are present in the ears. The intermediate organism in the transition stage was found fossilized. The mammal-like reptiles called therapsids have a double jaw joint.

Comments