What is Metabolism?
Metabolism is defined as the total amount of the biochemical reactions involved in maintaining the living conditions of the cells in an organism. All living organisms require energy for different essential processes and for producing new organic substances.
The entire process of nutrition has two main parts- ingestion of food and utilization of food for energy. In every living organism, let it be a simple prokaryotic bacterial cell or a eukaryotic cell, the process of nutrition is the same. The concept of metabolic reactions concentrates on the utilization of food for energy. Ingested food needs to be utilized for the turnover. The nutrition is the key and energy extraction is the target of metabolism. The dynamic state of body constituents and the concept of metabolism are discussed below in detail.
Concept of Metabolism
How does a cell extract energy and how does it synthesize the building blocks of its macromolecules?
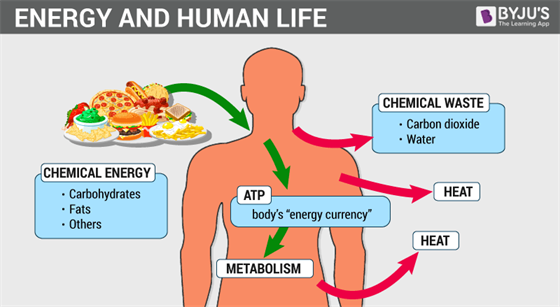
Here comes the concept of metabolism. Metabolism is the sum total of all the chemical reactions taking place in the cells of the living organisms. This involves both breaking and making of biomolecules. Catabolism and anabolism are two types of metabolism. Catabolism (breaking of bonds) involves the breaking of biomolecules while anabolism (making of bonds) is the building of new compounds required by the cells.
The food which we eat happens to be useless until and unless it undergoes metabolic changes. During metabolism, biomolecules present in the food get utilized to extract the energy from the cell. In addition, conversion and formation of the biomolecules take place. In other words, the transformation of one compound results in the formation of another molecule. For example, the proteins we obtained from the food are metabolized into amino acids, which are later utilized to synthesize another protein required by the cell.
All metabolic changes take place in multiple reactions and follow a particular pathway called the metabolic pathway. The metabolic pathway includes a series of reactions. The metabolite flow, the rate, and direction at which metabolism takes place are called the dynamic state of body constituents. All metabolic reactions are catalyzed by a set of proteinaceous compounds called enzymes.
Hence, metabolism is an enzyme-catalyzed reaction which provides biomolecules, needed by the cells for growth, maintenance, and repair etc. Let us summarize the purposes of metabolic pathways in the below three points:
- To extract energy from the food for cellular activities.
- To convert food to building blocks, to synthesize biomolecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids.
- To eliminate waste and toxic products.
To know more about Metabolism, its types and Metabolic Pathways, visit BYJU’S.

Comments