Table of Content:
| What is Buccal Cavity | Parts of the Buccal Cavity | Frequently Asked Questions |
What is Buccal Cavity?
The mouth is also called the buccal cavity or the oral cavity. In the human digestive system, the mouth is the upper end, or the beginning of the alimentary canal, which leads to the pharynx and to the oesophagus. In humans, both the mouth or the buccal cavity and the nasal cavity are separated by the palate.
The buccal cavity mainly comprises the primary organ of the digestive system including the teeth, tongue and salivary glands.
Also, read Digestive System In Humans
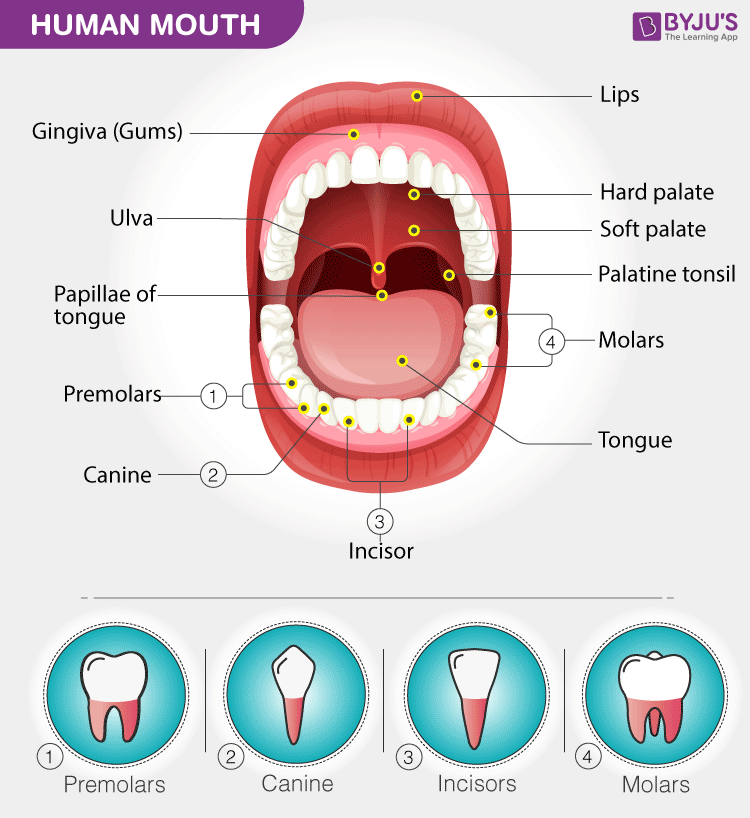
The mouth is an opening through which the food is taken inside the body. It is bounded by lips and its inner parts comprise the cheeks, tongue, upper jaw and lower jaw.
The upper jaw is fixed, which forms the roof of the mouth cavity and consists of the palate, teeth, and gums surrounding the teeth. The lower jaw is movable and forms the floor of the mouth cavity, which consists of the tongue along with the teeth and gums surrounding them. The parts of the mouth play an important role in speech and helps in breathing in certain cases, when the nose is blocked and during strenuous exercise. It is also the most important part of the human body, which permits us to enjoy the food we eat and also to communicate with the rest of the world.
The mouth or the oral cavity comprises two parts:
- The oral cavity proper — It mainly comprises the tongue.
- The oral vestibule – It is the slit-like space between the teeth and the buccal cavity and between the lips and cheeks.
Let us learn in detail about the main parts of the buccal cavity or oral cavity.
Parts of the Buccal Cavity
The parts of the mouth include lips, teeth, gums, mouth cavity with buccal mucosa, salivary glands and tongue. Let’s have a look at each structure.
Lips
Lips are soft, muscular and movable structures, which are formed by the complex of orbicularis oris muscles. The reddish-pink appearance of the lips is mainly because of the underlying blood vessels which are covered by the thin and transparent epithelium tissues.
Buccal mucosa
It is the inner lining of the cheeks and the back of the lips. It provides a round shape to the cheeks.
Tongue
It is a large, muscular organ, which occupies most of the oral cavity and can take up a variety of shapes and positions. There are 50 to 100 taste receptor cells in each taste bud, which are located in the lining of the mouth. It is the main sense organ of human beings and is involved in:
- Sense of Taste
- A major organ of speech
- Oral cleansing of the mouth
- Squeezing food into the oropharynx while swallowing
- Formation of clear and distinct sounds during the speech.
Teeth
The teeth are the strongest and most rigid substances in the human body. A normal adult has 32 teeth and is divided into incisor, canine, molars and premolars. There is a third molar, which is called the wisdom teeth, which appear in a person’s late teens or early twenties.
Each tooth consists of a crown with one or more tips, a neck, and a root. The Pulp cavity is the centre part of the tooth, filled with blood vessels, nerves and connective tissues and is surrounded by an enamel, which protects the tooth against scratch, cut and the invasion of bacteria present in the mouth.
Also, read Teeth – Different Types in Humans
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main parts of the mouth?
The mouth, also called the oral cavity includes teeth, tongue, salivary glands, tonsils, back of the throat and the epiglottis. The mouth is an important part as it is helpful for speech and communication, eating and digestion, and can also be used for breathing.
What is the function of the buccal cavity?
The buccal cavity or oral cavity is the beginning of the alimentary canal, which leads from the pharynx to the oesophagus. It is separated by the palate and functions as an entrance to the digestive system and is composed of the teeth, tongue, and palate.
What are the 4 types of teeth?
The four types of teeth are – incisors, canines, premolars and molars.
This was a brief introduction to the parts of the mouth. Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about the mouth, digestive system and other related topics at BYJU’S Biology

thanks for good matter