Table of Contents
Introduction
Gregor Mendel worked on the principles of inheritance in genetics a long time ago. His work helped form the fundamentals of genetics and inheritance patterns in living organisms. Later, scientists developed another approach to help us understand the inheritance of genes in living organisms. This approach is known as the pedigree analysis. Let’s now learn about pedigree analysis and how it helps predict genetic diseases.
What is Pedigree Analysis?
Pedigree analysis was developed to understand the inheritance of genes from parents to offspring. It was developed as a chart that can represent a family tree along with the family members and their genetic traits, respectively.
Gregor Mendel’s experiments showed that the “factors” that we now know as “genes”, are the factors which are responsible for the inheritance of traits from parents to offspring.
Therefore, genes are the hereditary unit of organisms which are responsible for carrying the information from the parents to their offspring. These genes are responsible for the characteristics of a living organism and can also be the reason for some disorders present in them.
These conclusions are based on the evidence provided by the controlled cross experiments in pea plants and other organisms. Since we can’t perform similar experiments on human populations due to ethical reasons, we formed pedigree analysis to study the pattern of the inheritance even when we have limited data.
Mendelian disorders are genetic diseases which follow a Mendelian inheritance pattern, and their inheritance is controlled by Mendelian genetics. Therefore, by studying the family history of an individual through pedigree analysis, we can predict whether an individual is at risk of a genetic disorder.
Pedigree Analysis – Diagram
A family tree can be represented by a pedigree chart with all the members of a family. They may be having a genetic disorder or maybe a carrier of the disease. In the pedigree analysis, standard symbols are used to distinguish between different families.
Here is a diagrammatic representation of a pedigree chart.
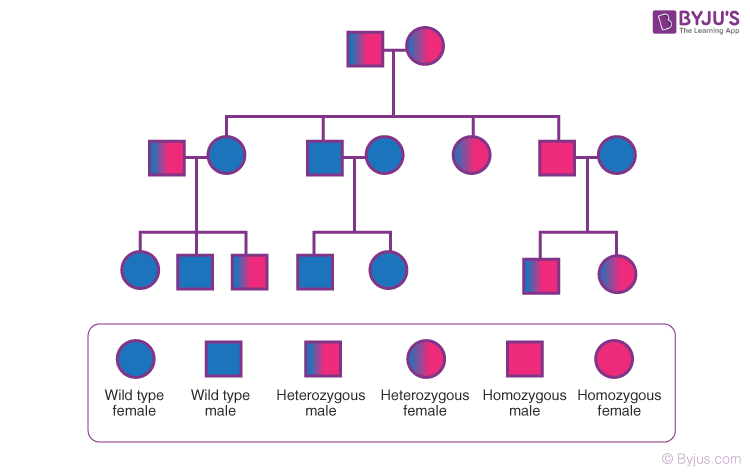
- Here, the rows represent the generations of a family, squares represent males, and circles represent females. Individuals on the same row belong to the same generation.
- A marriage or mating is represented as a horizontal bar between the square and the circle. Likewise, a double bar between the symbols indicates a consanguineous mating or marriage.
- The offsprings are indicated by a suspending vertical line drawn perpendicular to the horizontal bar or marriage bar.
- The homozygous individuals are represented as fully shaded symbols. Whereas heterozygous individuals are just carriers and are represented by half-shaded symbols.
- A normal or natural genotype is denoted as wild type. Unshaded squares and circles indicate the normal or “unaffected” individuals.
- Usually, the carrier of a sex-linked recessive gene is represented by a black spot in the middle of the symbol.
- Sometimes, a particular affected individual who is being interviewed or who bought the trait to the geneticists is indicated by a pointing arrow. Such members are termed, propositus.
Also Read:
| Heredity |
| Genetics: Principles of Heredity |
For more details on the Pedigree analysis or any other related topic, login to BYJU’S-The Learning App.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do you mean by a pedigree chart?
A pedigree chart is a diagrammatic flow chart that is prepared to exhibit a person’s hereditary information in an easily readable form. The chart usually displays the members of the family who are affected by a particular genetic trait.
What are the main goals of a pedigree analysis?
Pedigree analysis is done to determine if the mode of inheritance is recessive, dominant, partial dominant, autosomal, mitochondrial or sex-linked. Moreover, it also determines the probability of an individual or offspring being affected in the given cross.

Comments