Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is the Differentiation Process in Plants?
- What are the Developmental Processes in Plants?
Introduction
Plants are different, and special living organisms belong to the kingdom Plantae. They display many distinctive characters from animals. They have different cell structures and organelles, which make them self-sufficient. They are also unique in their life cycle and development processes which are discussed below.
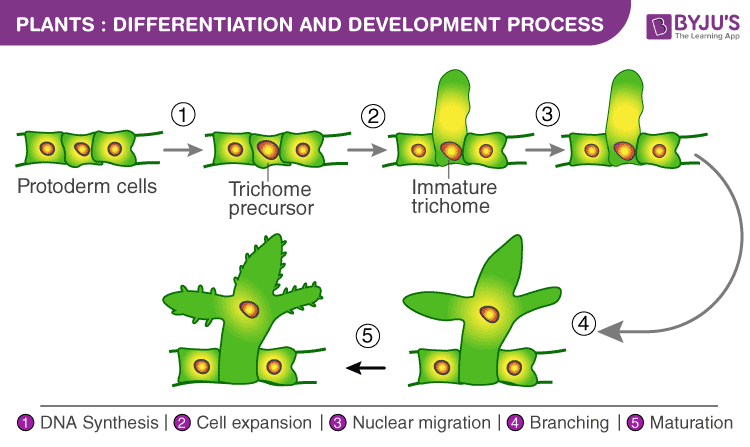
What is the Differentiation Process in Plants?
Differentiation is a process through which meristematic tissues undergo permanent change to form specialized cells in the plant body. Differentiation leads to the formation of permanent tissues which have specialized structures for specific functions.
For instance, The protoplasm is lost during the formation of tracheary elements.
There are two types of differentiation process:
Dedifferentiation process: Through the dedifferentiation process, permanent cells that have lost their ability to divide, regain their ability to divide under certain special conditions.
For example, under special circumstances, parenchymal cells undergo dedifferentiation to form meristematic cells.
Redifferentiation process: – Redifferentiation is the process through which cells, which had regained their ability to divide, again lose that ability and mature into permanent tissue to perform their specialized functions.
What are the Developmental Processes in Plants?
This includes all the changes that an organism goes through during its life cycle. In the case of seeds, their life cycle starts with germination and ends with senescence. This process includes all the steps – cell division, elongation of cells, differentiation, maturation etc.
Cell division occurs in the meristematic tissues due to which cell elongation or expansion might occur. These cells undergo the process of differentiation and form mature cells which undergo senescence (ageing) and ultimately die. This is the whole developmental process in plants.
The developmental process is considered the sum total of growth and differentiation. This process in plants is controlled by various factors which might be intrinsic, such as genetic factors and chemical factors or extrinsic factors, including the light, temperature, nutrients, water, oxygen, etc.
Plants follow different types of pathways in response to their environment in different phases of life and show different kinds of structures. This is known as plasticity. For instance, a condition known as heterophily in which the shapes of leaves in young plants are different from that of the leaves of mature plants. This is found in plants like cotton, coriander etc.
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about the Differentiation and Developmental process in Plants.

Comments