Reproduction Definition
Reproduction is a life process which enables an organism to reproduce its own offspring. Thus, they continue their species without extinction.
Refer more: Reproduction
Table of Contents
Types of Reproduction
Reproduction can take place by the participation of a single parent or two parents. Based on this, reproduction can be classified into two types.
- Asexual reproduction: A type of reproduction where a single parent is divided by itself and reproduce its offspring.
- Sexual reproduction: A process where two parents participate in producing their offspring.
Let us study about sexual reproduction.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a natural way of reproduction in humans, animals and the majority of plants also choose to reproduce sexually. This type of reproduction is more complex and lengthy as compared to asexual reproduction. Moreover, reproducing sexually gives the benefit of variation and offsprings are unique. Sexual reproduction consists of a set of events and can be divided into three stages: Pre-fertilization, Fertilization, and Post-fertilization.
Also Read: Sexual reproduction
Stages of Sexual Reproduction
Pre-Fertilization
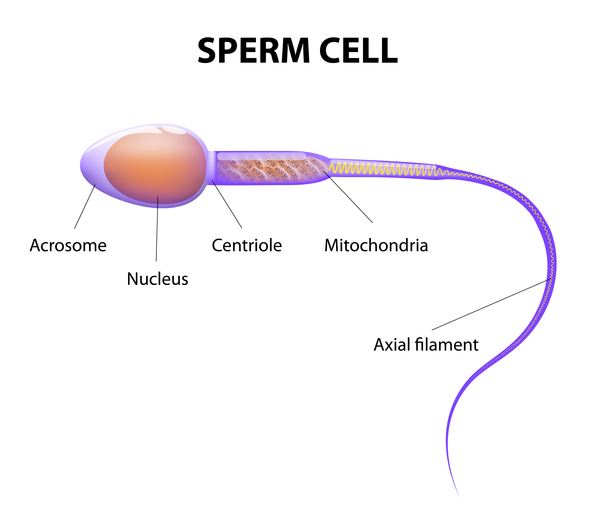
This stage involves the events prior to fertilization. Gamete formation (gametogenesis) and transfer of gamete are the two processes that take place during this stage. Gametes are sex cells, which are haploid (23 chromosomes) in nature and are distinct in males and females. The male gamete is called sperm whereas female gamete is called ovum or egg. In every organism, these gametes are formed within special structures. Since female gamete is immobile, male gametes need to be transferred for fertilization.
In plants, this is attained by pollination. Unisexual animals transfer gametes by sexual intercourse.
Fertilization
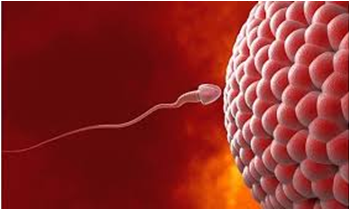
Once the haploid male and female gametes meet and fuse together to form a zygote, this is known as fertilization or syngamy. This can occur either outside the body called external fertilization or inside the body called internal fertilization.
Refer more: Internal And External Fertilization
Post-Fertilization
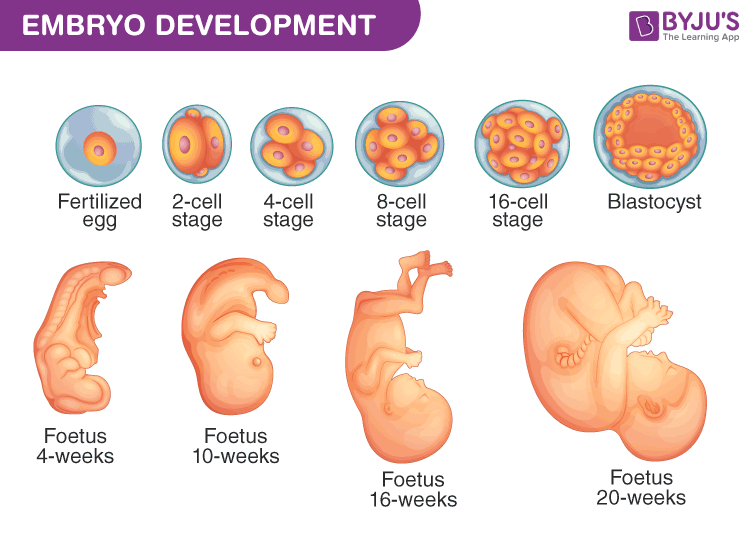
Fertilization results in diploid zygote formation. Eventually, the zygote divides mitotically and develops as an embryo. This process is called embryogenesis. During embryogenesis, cell differentiates and modifies accordingly. Zygote development depends on the organism and its life cycle.

Animals are classified into oviparous and viviparous based on whether the zygote develops outside or inside the body respectively. In angiosperms, the zygote develops into the ovary and ovary transforms into the fruit while ovules develop into seeds.
Explore more: Oviparous and Viviparous Animals
Learn more in detail about sexual reproduction, its stages, and other related topics at BYJU’S Biology
Recommended Videos:

I love this page
I also love this page
Awesome