With the continuous rise in the global population, the demand for food has also increased at an alarming rate. The conventional practices of agriculture and animal husbandry have been unable to fulfil the nutritional requirements of the present population. This has resulted in malnutrition owing to deficiency of protein in food.
What is Single Cell Protein -SCP?
Single-cell protein refers to the crude, a refined or edible protein extracted from pure microbial cultures, dead, or dried cell biomass. They can be used as a protein supplement for both humans or animals.
Microorganisms like algae, fungi, yeast, and bacteria have very high protein content in their biomass. These microbes can be grown using inexpensive substrates like agricultural waste viz. wood shavings, sawdust, corn cobs etc. and even human and animal waste.
Also Refer: Biomass
The microorganisms utilize the carbon and nitrogen present in these materials and convert them into high-quality proteins which can be used as a supplement in both human and animal feed. The single-cell proteins can be readily used as fodder for achieving fattening of calves, pigs, in breeding fish and even in Animal Husbandry – Poultry and Cattle Farming.
Single Cell Protein (SCP) offers an unconventional but plausible solution to this problem of protein deficiency being faced by the entire humanity.
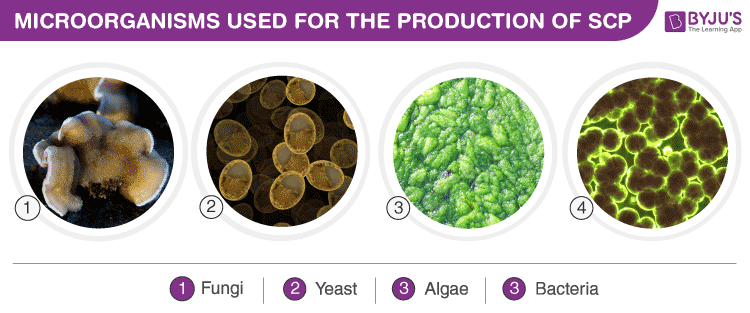
Sources of Single Cell Protein
A list of the microorganisms used for the production of Single Cell Protein is as follows:
Fungi
- Aspergillus fumigatus
- Aspergillus niger
- Rhizopus cyclopean
Yeast
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Candida tropicalis
- Candida utilis
Algae
- Spirulina (spa)
- Chlorella pyrenoidosa
- Chondrus crispus
Bacteria
- Pseudomonas fluorescens
- Lactobacillus
- Bacillus megaterium
Here are the average compositions of the different microorganisms present in the % dry weight of Single-cell protein.
| Composition | Fungi | Algae | Yeast | Bacteria |
| Protein | 30-45 | 40-60 | 45-55 | 50-65 |
| Fat | 2-8 | 7-20 | 2-6 | 1-3 |
| Ash | 9-14 | 8-10 | 5-10 | 3-7 |
| Nucleic Acid | 7-10 | 3-8 | 6-12 | 8-12 |
Production of Single-Cell Protein
The production is carried out in the following steps:
- Selection of suitable strain.
- Fermentation.
- Harvesting.
- Post-harvest treatment.
- SCP processing for food.
Like any other microbial culture, production of pure microbial cultures for desired protein products requires a nitrogen source, sources of carbohydrates and other nutrients like phosphorus to support optimal growth of the culture. Contamination is prevented by maintaining strict sterile conditions throughout the process. The components of the culture media are either heat sterilized or filtered through microporous membranes. The selected microorganism is then inoculated in pure conditions. Most of the processes are highly aerobic, except algal fermentation; hence a good supply of oxygen is an indispensable requirement. After the multiplication of the biomass, it is recovered from the medium and purified further for enhanced usefulness and or storability.
Advantages of Single-Cell Protein
Large-scale Single-Cell Protein production has multiple advantages over conventional food production practices such as:
- Microorganisms have a high rate of multiplication, which means a large quantity of biomass can be produced in a comparatively shorter duration.
- The microbes can be easily genetically modified to vary the amino acid composition.
- A broad variety of raw materials, including waste materials, can be used as a substrate. This also helps in decreasing the number of pollutants.
- Production is independent of climatic conditions.
Disadvantages of Single-Cell Protein
In spite of many advantages, there are few drawbacks. Single-Cell Protein has not been widely accepted for human consumption owing to certain problems as follows:
- High level of nucleic acid in biomass makes it difficult for consumption as it may lead to gastrointestinal problems.
- The biomass may trigger an allergic reaction if the digestive system recognizes it as a foreign product.
- The presence of nucleic acids in high content leads to elevated levels of uric acid.
- In certain cases, the development of kidney stone and gout if consumed in high quality.
- Possibility of the presence of secondary toxic metabolites which results in Hypersensitivity and other skin reactions.
- The capital cost of production is high as sophisticated machinery is required.
Applications of Single-Cell Protein
- Provides instant energy.
- It is extremely good for healthy eyes and skin.
- Provides the best protein supplemented food for undernourished children.
- Serves as a good source of vitamins, amino acids, minerals, crude fibres, etc.
- Used in therapeutic and natural medicines for:
- Controlling obesity.
- Lowers blood sugar level in diabetic patients.
- Reducing body weight, cholesterol and stress.
- Prevents accumulation of cholesterol in the body.
- Used in Cosmetics products for:
- Maintaining healthy hair.
- Production of different herbal beauty products, like- Biolipstics, herbal face cream, etc.
- Used in Poultry:
- As it serves as an excellent and convenient source of proteins and other nutrients, it is widely used for feeding cattle, birds, fishes etc.
Frequently Asked Questions on Single cell protein
Single cell protein can be obtained from?
Single cell proteins are obtained by the culturing of single-celled entities. Typically, these proteins are consumed as dietary supplements. Fungi, Bacteria, algae either are single-celled structures or the clusters have one or more forms that are single-celled. Consequently, all these form the different sources of single-celled proteins.

thanks. it was helpful. thanks for sharing such a nice note.
is there any factor that impair the usefullness of SCP?