Table of Contents
- What is Tuberculosis?
- Types of Tuberculosis
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis
- Diagnosis of Tuberculosis
- Symptoms of Tuberculosis
- Causes of Tuberculosis
- Treatment of Tuberculosis
What is Tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis (TB) is a dangerous and highly contagious bacterial disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It primarily affects the lungs, but if left untreated, it might spread to different parts of the body.
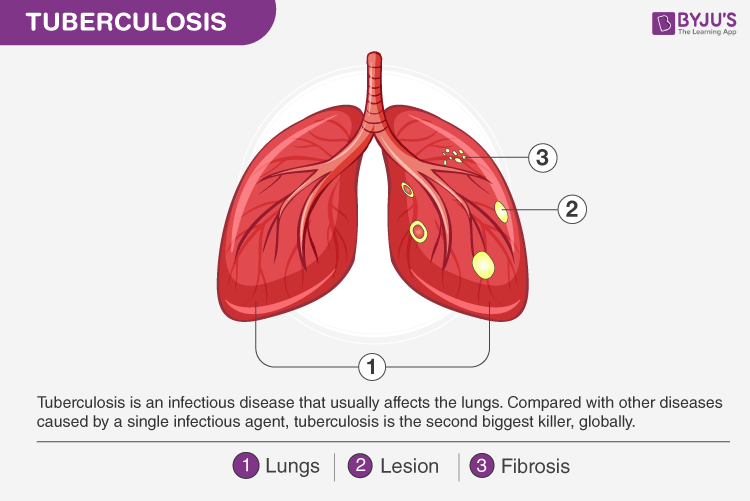
Types of Tuberculosis
There are two different types of tuberculosis:
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis.
- Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis.
Pulmonary Tuberculosis
It is an endemic infection affecting the lungs. It is further classified into:
- Primary Tuberculosis Pneumonia: Associated symptoms include coughing and high fever. It can also arise in patients with HIV/AIDS.
- Miliary Tuberculosis: This form of TB is named so because of a distinctive pattern seen on a chest radiograph, where many small spots are distributed throughout the lung fields, bearing an appearance similar to millet seeds. The infection can eventually spread to the extrapulmonary organs, such as the spleen, liver, and kidneys.
- Latent Tuberculosis Infection: This infection is mainly seen in those patients having the bacteria within their body, but do not display any of the symptoms of the disease. This infection is primarily detected through the tuberculin skin test.
Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis
It is usually seen in immunocompromised patients. There are several types:
- Tuberculosis Meningitis
- Osteal Tuberculosis
- Lymph Node Disease
- Renal Tuberculosis
- Adrenal Tuberculosis
Diagnosis of Tuberculosis
Apart from all the physical tests, other tests are available to diagnose the presence the infectious bacteria. These tests include certain body fluids tests – blood and sputum, skin test and chest X-rays.
Blood Test: In this procedure, Blood samples are collected and tested in the laboratories for the presence or absence of TB germs in the blood cells.
Skin Test: It is the most common type of test. In this procedure, a small sample of Tuberculin – a purified protein is injected under the patient’s skin. If the skin around the site of the injection gets swollen more than five millimetres, then it is a clear indication of TB infection.
Symptoms of Tuberculosis
TB bacteria or Mycobacterium tuberculosis multiply once it gets into the lungs. It can cause severe symptoms such as:
- Coughing up blood and mucus from deep inside the lungs
- A bad cough that lasts three weeks or longer
- Weakness or fatigue
- Sweating at night
- Pain in the chest
- Weight loss
- No appetite
- Chills and Fever
Causes of Tuberculosis
- Infants and senile individuals are at a higher risk of catching TB infections.
- Individuals with a weak immune system are at increased risk.
- Metabolic diseases such as diabetes can also increase the risk of contracting TB.
- Tuberculosis is a contagious airborne disease, which can be acquired from close contact with an infected person.
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis is one of the leading causes of this dreadful infectious disease. It is a pathogenic bacterial species and mainly comprises four other types of TB-causing bacteria, namely:
- Mycobacterium bovis,
- Mycobacterium canettii,
- Mycobacterium microti,
- Mycobacterium africanum.
These bacteria could be cultured even in laboratories.
Treatment of Tuberculosis
Drug treatment is one of the most efficient ways to treat this infectious disease. For patients with Latent TB infections, doctors generally prescribe an antibiotic called isoniazid for preventing the latent infection from becoming active.
Active TB Diseases will be deadly if left untreated. The procedure involved is taking a combination of ethambutol, INH, Priftin and Pyrazinamide for a term of three months, followed by a mix of INH and pyrazinamide for 12 months.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Tuberculosis (TB)?
Tuberculosis (TB) is a highly contagious bacterial infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It generally affects the lungs, and later it might spread to different parts of the body.
2. What are the types of tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is of two different types and is mainly categorized based on the risk factors:- Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis.
3. What are the symptoms of tuberculosis?
Following are some of the common symptoms of TB:
- Coughing with blood
- Cough that lasts three weeks or longer
- Weakness/ fatigue
- Night sweat
- Chest pain
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Chills and Fever
For more information about tuberculosis, visit BYJU’S.

Notes are very good