Carbonous acid, commonly known as formic acid, is a colourless liquid with a pungent odour. Naturally, carbonous acid is found in ants and in stingless bees. Carbonous acid, comparatively has low toxicity because of which it is used as a food additive. In this short piece of article, learn more about carbonous acid formula, its chemical structure, properties and uses.
Carbonous Acid Properties
| Properties of Carbonous Acid | |
| Name | Carbonous Acid |
| Other Names | Formic Acid, Hydrogen carboxylic acid |
| Appearance | Colourless fuming liquid |
| Chemical Formula | CH2O2 |
| Melting Point | 8.4 °C |
| Boiling Point | 100.8 °C |
| Density | 1.220 g/mL |
| Molar Mass | 46.025 g.mol–1 |
| Solubility in Water | Miscible |
Carbonous Acid Structure
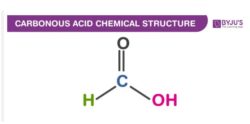
Carbonous Acid Uses
- Used as an antibacterial and preservative agent in livestock feed
- Used as a coagulant in the production of rubber
- Used in the production of leather
- Effective in treating warts
To learn more about such chemistry topics register to BYJU’S now!
Comments