What is Acetate?
Acetate is a chemical compound with formula C2H3O2−. It is also known as Acetate Ion or Monoacetate. It is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with alkaline, metallic, earthy, nonmetallic or other bases.
Table of Contents
- Structure Of Acetate
- Fermentation of Acetate
- Properties of Acetate
- Chemical Properties of Acetate
- Uses Of Acetate
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-coenzyme A is carried out with the help of an enzyme called pyruvate dehydrogenase. The acetyl-CoA is further converted to acetate in E. coli and simultaneously produces ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation. The entire process requires two enzymes viz acetate kinase and phosphate acetyltransferase.
acetyl-CoA + Phospate → acetyl-Phospate+CoA
acetyl-Phospate+ADP → acetate + ATP
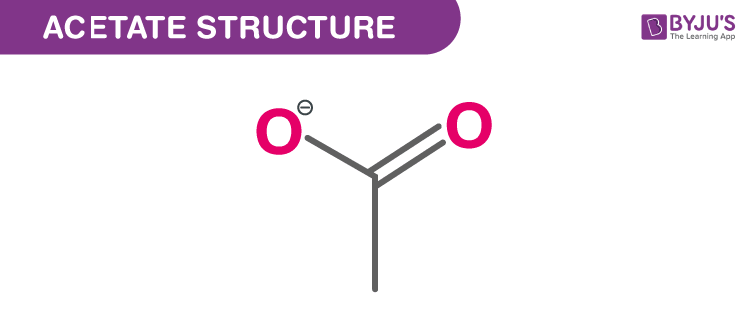
Structure Of Acetate (C2H3O2−)
Fermentation of Acetate
Acetic acid undergoes dismutation reaction to generate carbon dioxide and methane.
CH3COO− + H+ → CH4 + CO2 ΔG° = −36 kJ/mol
The reaction is carried out in the presence of catalyst methanogen archaea. One electron is transferred from the carboxylic group to the methyl group of acetic acid to generate carbon dioxide and methane gas.
Properties of Acetate (C2H3O2−)
| Acetate | C2H3O2− |
| Molecular Weight of Acetate | 59.044 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass of Acetate | 59.013 g/mol |
| Complexity | 25.5 |
| Conjugate acid | Acetic acid |
Chemical Properties of Acetate – (C2H3O2−)
1. Acetate reacts with sodium hydroxide
Sodium acetate and soda lime(NaOH + CaO), on reaction give methane and sodium carbonate. This reaction is called decarboxylation and is one of the general methods to prepare alkanes.
CH3COONa + NaOH → CH4 + Na2CO3
2. Acetate reacts with Water
Water spontaneously ionizes into hydroxide anions and hydrogen cations. Sodium acetate dissociates in water into sodium and acetate ions. Sodium ions react very little with the hydroxide ions whereas the acetate ions combine with hydrogen ions to produce acetic acid.
The solution is not neutral but slightly alkaline.
Uses Of Acetate (C2H3O2−)
-
- Acetate is used as a solvent in paints, inks, coatings.
- Cellulose acetate is used eyeglass frame.
- It is used in diapers.
- Potassium acetate is used as a food preservative.
- It is used in laboratories.
- Aluminium acetate is used as an anti stringent.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What elements are in acetate?
Both metallic acetates are inorganic salts of a metal cation and acetate anion, a polyatomic ion consisting of two carbon atoms ionically bound to three hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms (Symbol: CH3COO) with a total formula weight of 59.05.
What is the difference between acetate and acetic acid?
The main distinction between acetate and acetic acid is that acetic acid is a neutral compound, while acetate is an anion with a net negative electric charge. Acetic acid is an organic compound that helps create vinegar while acetate ion is the acetic acid’s conjugate base.
Is Acetate a base or acid?
Sodium acetate is a basic salt; the acetate ion will deprotonate water, thereby increasing the pH of the solution. The basic salt are formed in the neutralization reaction between a strong base and a weak acid.
What are the advantages of acetate?
This is among the most flexible fabrics and can resist wrinkling. ADVANTAGES: Has a silky appearance, a luxurious feel to it. DISADVANTAGES: The dyes can fade or bleed, are prone to heat, and are relatively poor fibres. Hand wash acetate clothes with warm water, and just a light-duty detergent.
How is acetate produced?
The acetate fiber is developed by using acetic anhydride to react with high purity wood pulp. The acetate flakes formed by this chemical reaction are dissolved in a solvent, filtered, and modified to obtain a solution for spinning stock.
Learn more about the chemical behaviour and importance of acetate (C2H3O2−) with the expert faculties at BYJU’S.

Comments