What are Acids, Bases, and Salts?
Many acids and bases occur naturally in nature, such as citric acid in fruits like orange, lemon, etc, tartaric acid in tamarind, malic acid in apples, and lactic acid in milk and milk products, hydrochloric acid in gastric juices.
Similarly, many bases are found such as lime water. We use many of these acids in our day-to-day life, such as vinegar or acetic acid in the kitchen, boric acid for laundry, baking soda for the purpose of cooking, washing soda for cleaning, etc.
Table of Content
Many of the acids that we do not consume in the household are used in the laboratories and industries, which include an acid such as HCl, H2SO4 etc, and bases such as NaOH, KOH etc. When these acids and bases are mixed in the right proportions, the neutralization reaction thus results in the formation of salt and water. Some naturally occurring salts found in nature include NaCl and KCl etc in seawater and natural rock deposits. In this section, we will read more about acid, base, and salt and their properties.
Definitions
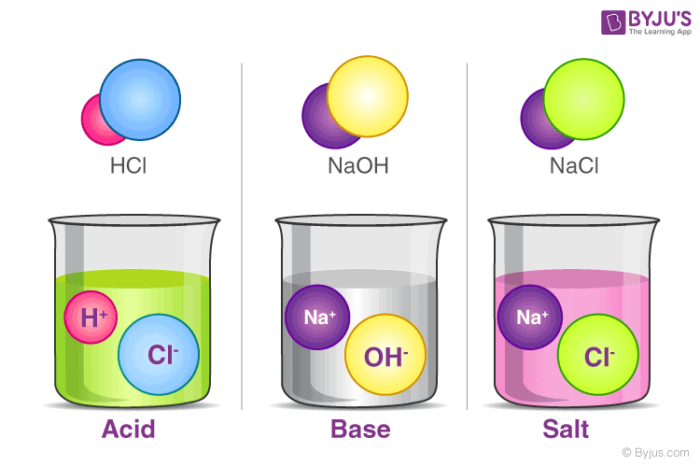
- Acid:- An acid is defined as a substance whose water solution tastes sour, turns blue litmus red, and neutralizes bases.
- Base:- A substance is called base if its aqueous solution tastes bitter, turns red litmus blue, or neutralizes acids.
- Salt:- Salt is a neutral substance whose aqueous solution does not affect litmus.
Recommended Videos
Acids and Bases

Acids
The term acid is derived from a Latin word ‘acidus’ or ‘acere’, which means sour. The most common characteristic is their sour taste. An acid is a substance that renders ionizable hydronium ion (H3O+) in its aqueous solution. It turns blue litmus paper red. These dissociate in their aqueous solution to form their constituent ions, as given by the following examples.
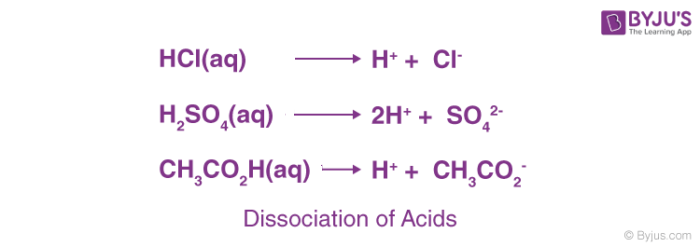

Based on their occurrence, they are divided into two types- Natural and mineral acids.
Natural Acids: These are obtained from natural sources, such as fruits and animal products. For e.g. lactic, citric, and tartaric acid etc.
Mineral Acids: Mineral acids are acids prepared from minerals. Examples are Hydrochloric acid (HCl), Sulphuric Acid (H2SO4), and nitric acid (HNO3), etc.
Also, Check ⇒ Dilute Acids
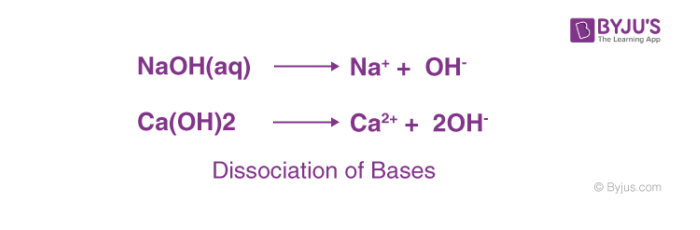
Bases
The most common characteristic of bases is their bitter taste and soapy feel. A base is a substance that renders hydroxyl ion(OH–) in their aqueous solution. Bases turn the colour of red litmus paper to blue.

The bases dissociate in their aqueous solution to form their constituent ions, given in the following examples.
Salts
Salt is an ionic compound that results from the neutralization reaction of acids and bases. Salts are constituted of positively charged ions, known as cations, and negatively charged ions, known as anions, which can either be organic or inorganic in nature. These ions are present in a relative amount, thus rendering the nature of the salt neutral.

The formation of salt can be seen from the chemical reactions shown in the equations below.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is salt in acids, bases and, salts?
In chemistry, a salt is a substance obtained by the reaction of an acid and a base. Salts are composed of positive ions (cations) of bases and negative ions (anions) of acids. The reaction of acid and base is called the neutralization reaction.
Is NH4Cl a basic salt?
Ammonium chloride (chemical formula NH4Cl) is an acid salt because it is a salt of a strong acid (i.e. hydrochloric acid) and a weak base (i.e. ammonium hydroxide).
What are the 2 types of acids?
There are two basic types of acids organic and inorganic acids. Inorganic acids are sometimes referred to as mineral acids. As a group, organic acids are generally not as strong as inorganic acids. The main difference between the two is the presence of carbon in the compound; inorganic acids do not contain carbon.
Inorganic acids – Inorganic acids are often termed mineral acids. The anhydrous form may be gaseous or solid. An inorganic anhydride is an oxide of metalloid which can combine with water to form an inorganic acid.
Example:
Sulphuric acid (H2SO4)
Phosphoric acid (H3PO4)
Nitric acid (HNO3)
Organic acids – Organic acids are corrosive and toxic. Corrosivity is a form of toxicity to the tissues that the acid contacts. Organic acids and their derivatives cover a wide range of substances. They are used in nearly every type of chemical manufacture. Because of the variety in the chemical structure of the members of the organic acid group.
Example:
Acetic acid
Citric acid
Formic acid
Is salt basic or acidic?
The salt is basic only when it contains a weak acid conjugate base. For example, sodium chloride contains chloride (Cl-), the conjugate base of HCl.
What happens when salt reacts with HCl?
When an acid reacts with metal, a salt and hydrogen are produced:
acid + metal → salt + hydrogen
The salt that is produced depends upon which acid and which metal react.
Sodium metal reacts with hydrochloric acid which produces hydrogen gas and sodium chloride.
2Na(s)+2HCl(aq)→2NaCl(aq)+H2(g)
To learn more about acids and bases and neutralization reactions, the pH scale and other related topics, come register with BYJU’S and download BYJU’S – The Learning App.


Nice
good
Very informative ,thank you
Byjus is the best learning app ever . It helps me to solve my doubts regarding maths and science. I love byjus . I fall in love with learning
ur answers r very accurate and to the point.
Pretty cool teaching I have learnt a lot.
It’s very informative and excellent
But plz provide some related points about it
Thanks u have thought us a good thing
Very informative and ur answers r very accurate and to the point thank you 👍