Table of Contents
What is Copper (II) Chloride?
CuCl2 is an inorganic compound with chemical name Copper (II) chloride.
Copper (II) chloride is also called Cupric chloride, or Copper dichloride, or Cupric dichloride. Copper dichloride occurs naturally as an anhydrous mineral called tolbachite and dehydrated eriochalcite. Both are mostly obtained from fumaroles areas.
Cupric chloride, in its anhydrous form, appears as a yellowish-brown powder whereas in its dihydrate form it appears as a green crystalline solid. It is corrosive to aluminium and the oxidation state of the metal is +2. It is widely used in printing, dyeing, as a wood preservative and in fungicides.
Properties of Copper (II) Chloride – CuCl2
| CuCl2 | Copper (II) chloride |
| Molecular weight of CuCl2 | 134.45 g/mol (anhydrous) |
| Density of Copper (II) chloride | 3.386 g/cm3 (anhydrous) |
| Boiling point of Copper (II) chloride | 993 °C |
| Melting point of Copper (II) chloride | 498 °C |
Copper (II) Chloride Structure – CuCl2
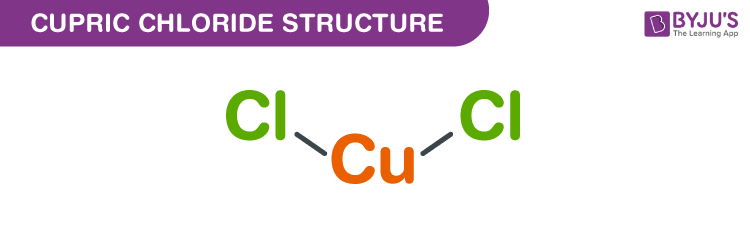
Copper (II) Chloride Structure – CuCl2
The exact mass and the monoisotopic mass of Cupric chloride is 132.867 g/mol. The number of hydrogen bond acceptors equals to zero and the number of hydrogen bond donors equals to zero. This compound is canonicalized and has one covalently bonded unit.
CuCl2 Uses
-
-
-
- Copper (II) chloride is used as deodorizing in the petroleum industry.
- Used as an oxidizing agent.
- Used as a purifying agent.
- Used as mordant in dyeing.
- Used as a disinfectant.
- Used in water treatment.
- Used in the manufacturing of agricultural chemicals.
- Used as a fixer in photography.
- Used in laundry marking inks.
- Used in electrotype baths.
-
-
Production of Copper (II) Chloride
Cupric dichloride is commercially obtained by chlorination of copper:
Cu + Cl2 + 2 H2O → CuCl2 (H2O)2
Health hazards:
Inhaling cupric dichloride causes sneezing and coughing. Swallowing it causes vomiting and pain. When liquid comes in contact with eyes and skin, it causes irritation in eyes and on the skin. It is non-combustible but when heated, it liberates irritating hydrogen chloride gas.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is copper (II) chloride used for?
Copper (II) chloride is used as a catalyst for organic and inorganic reactions, textile dyeing and printing mordant, glass and ceramic pigment, wood preservative, disinfectant, insecticide, fungicide, and herbicide, and as a catalyst for hydrogen chlorine processing.
How dangerous is copper chloride?
Copper chloride, when breathed in, will impact you. Touch can seriously irritate and burn with potential damage to the eyes and skin. Repeated exposure can cause skin to thicken. Copper chloride breathing can irritate the nose, throat, and lungs which cause coughing and wheezing.
Is Copper (II) chloride a solid?
Copper (II) is the chemical compound that contains the chemical formula CuCl2. It is a light brown solid, gradually absorbing moisture to form a green-blue dihydrate.
Why is CuCl2 blue?
As the electrons pass from the t2 energy level to the e energy level, photons that have the wavelength of yellow light are absorbed so that hydrated copper chloride becomes violet.
What is the charge of copper chloride?
For copper chloride, the copper charge is 1. This forms either CuCl or CuCl2 as the copper binds to chlorine. In the case of CuCl, the chloride ion has a charge of -1, so to make the compound stable the copper must have a charge of +1. Therefore, copper(I) chloride is called CuCl.
Learn more about the Structure, physical and chemical properties of CuCl2 from the experts at BYJU’S.


Comments