Table of Contents
Experiment 2A – Reaction of Acid and Base
In this article, we have given step by step procedure to perform an experiment which will help you understand the different properties of acids. Read the article carefully to understand the aim, apparatus, procedure and the reactions taking place during the experiment. You can conduct the experiment and try to match the result with this.
|
Also Read: |
Aim:
To study the properties of acids (dilute HCl) and bases (dilute NaOH) by their reactions with the following:
- Litmus solution (red/blue)
- Zinc metal
- Solid sodium carbonate
Materials required:
- Test tube
- Test tube stand
- Cork
- Test tube holder
- Boiling tube
- Droppers
- Flat bottom flask
- Burner
- Matchbox
- Beaker
- Thistle funnel
- Litmus paper/solution
- Fresh lime water
- Glass rod
- Dilute HCl
- Dilute NaOH
- Zinc granules
- Solid sodium carbonate
Theory:
What is acid?
Chemical species which donate protons or release H+ ions when dissolved in water are called acid. They turn blue litmus solution to red colour.
Hydrochloric acid reacts with zinc metal to produce zinc chloride and hydrogen gas. The reaction is given below:
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Hydrochloric acid reacts with Na2CO3 to produce carbon dioxide and turns the lime water milky as it forms calcium carbonate. The milkiness formed disappears when more than necessary carbon dioxide is passed through the solution. The reaction is as follows:
Na2CO3(s/aq) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) → Ca(HCO3)2(aq)
Experimental Setup for Litmus Test Procedure:
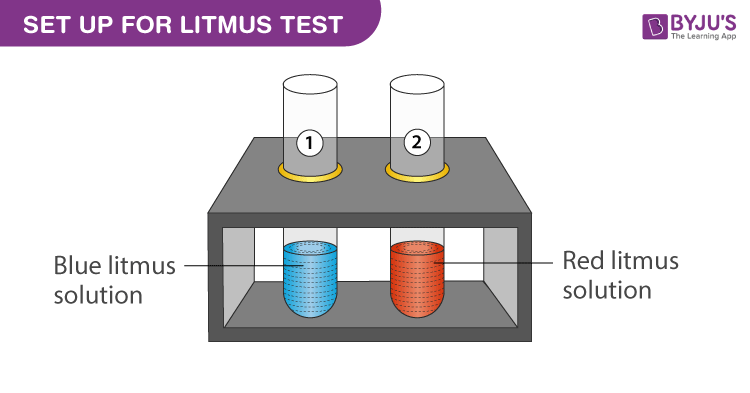
- Take a test tube stand and place two test tubes in it.
- Label the test tube as test tube 1 and test tube 2.
- Add 5 ml of blue litmus solution to test tube 1.
- Add 5 ml of red litmus solution to test tube 2.
- Use a dropper and add equal drops of hydrochloric acid in the both test tubes.
- Wait and observe the colour change.
Experimental Setup for Reaction with Zinc metal:
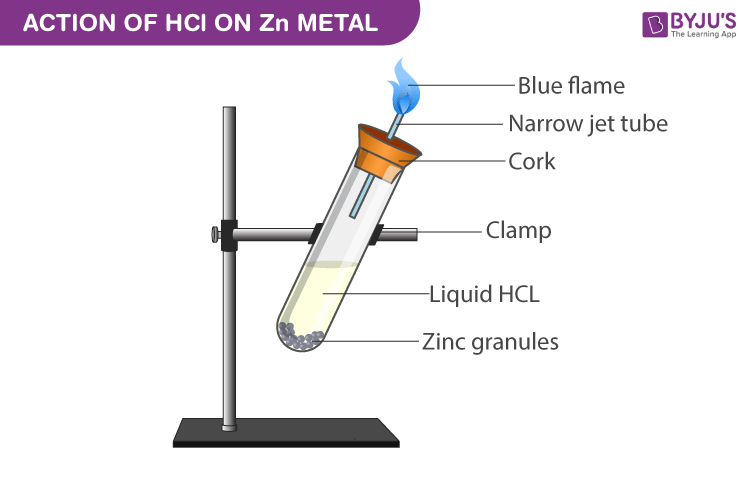
Procedure
- Take a clean and dry test tube.
- Add zinc granules to it.
- Submerge the zinc granules in the test tube by adding hydrochloric acid to it.
- Close the mouth of the test tube with cork which has a glass delivery.
- A robust explosion takes place between 2-3 minutes liberating colourless and odourless gas.
- When a burning match stick is got near the glass tube mouth the gas burns with a pale blue flame with a pop sound.
Reaction:
2HCl(aq) + Zn(s) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2↑
Experimental Setup for Reaction with solid sodium carbonate:
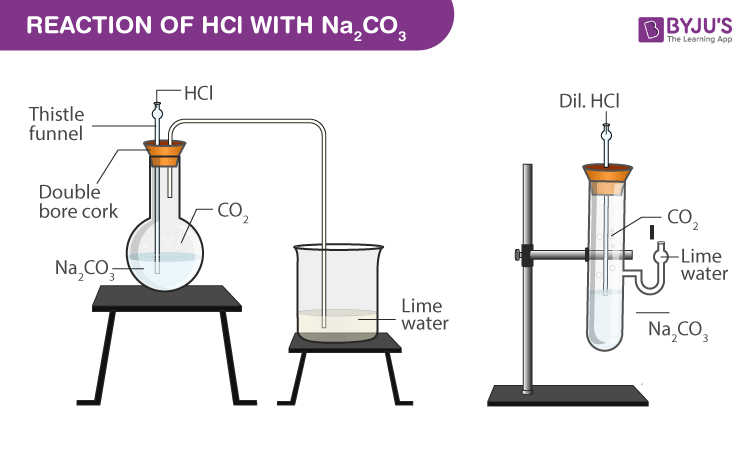
Procedure
- Take a flat bottom flask with 1 gm of solid sodium carbonate and some distilled water.
- Take a clean and dry double bore cork and thistle funnel which has a delivery tube fitted to it.
- Close the mouth of the flat flask with the double bore cork.
- Add 2 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid.
- Colourless and odourless gas is liberated which is passed through the lime water using the delivery tube.
- The colour of the lime water changes to milky.
Reaction:
Na2CO3(s/aq) + 2HCl(aq) –→ 2NaCl(aq) + CO2↑+ H2O(l)
Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2↑ –→ CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) –→ Ca(HCO3)2(aq)
Observation:
| Experiment | Observation |
| Litmus test | The blue litmus solution in test tube 1 turns red whereas there is no change in colour observed in the test tube 2 containing red litmus solution. |
| Reaction with Zinc metal | Acids such as hydrochloric acid (HCl) liberate hydrogen gas when reacted with active metals such as zinc and burns with a pop sound when burning splinter is got near it. |
| Reaction with Na2CO3 | Sodium carbonate and hydrochloric acid react to produce carbon dioxide gas and turns lime water milky. When excess gas is passed the milkiness is disappeared. |
Result and Conclusion:
- In the litmus test experiment the blue litmus solution turns red when hydrochloric is added. Therefore, acids such as HCl show acidic character.
- Hydrochloric acid reacts with active metals such as zinc to form zinc chloride and liberate hydrogen gas.
- HCl reacts with sodium carbonate to liberate carbon dioxide gas.
Therefore, from the above three points we can conclude that HCl (Hydrochloric acid) is acidic in nature.
Precautions to be taken during the experiment:
- Conduct the experiment in clean test tubes.
- HCl is corrosive in nature and should be handled with great care.
- Take a small amount of chemicals to perform the experiments.
- While shaking the solution and reaction mixture do not spill.
- Whenever you conduct a test for hydrogen, conduct it with the least amount of gas.
- To get quick results for lime water test, pass carbon dioxide gas through the solution and shake the test tube by placing your thumb on its mouth.
Recommended Videos
Acids and Bases

Neutralization Of Acids And Bases

Viva Voce:
- When bases dissolve in water which ion do they release?Ans: OH– ions.
- Can you name a metal that reacts with base as well as acid and liberates H2 gas?. Ans: Zinc metal.
- X releases OH– ions when it dissolves in water. Then X is?Ans: Base.
- Can you write the chemical formula for Zinc chloride?Ans: ZnCl2.
- What is the colour of zinc granules when it reacts with HCl?Ans: Black.
Experiment 2B – Reaction of Base with a Metal
Theory:
What is Base?
Chemical species which release OH– ions when dissolved in water are called bases. Sodium hydroxide is a powerful base and has a pH value greater than 7. Therefore, it turns the red litmus solution into the blue.
Sodium chloride reacts with zinc metal to produce sodium zincate and hydrogen gas. The reaction is given below:
Zn(s) + 2NaOH(aq) → Na2ZnO2(aq) + H2(g)
Sodium hydroxide does not react with solid sodium carbonate as both are basic in characteristic.
Na2CO3(s) + NaOH(aq) → no reaction
Sodium hydroxide neutralizes hydrochloric acid to produce salt (sodium chloride)
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Experimental Setup for NaOH in Litmus Test:
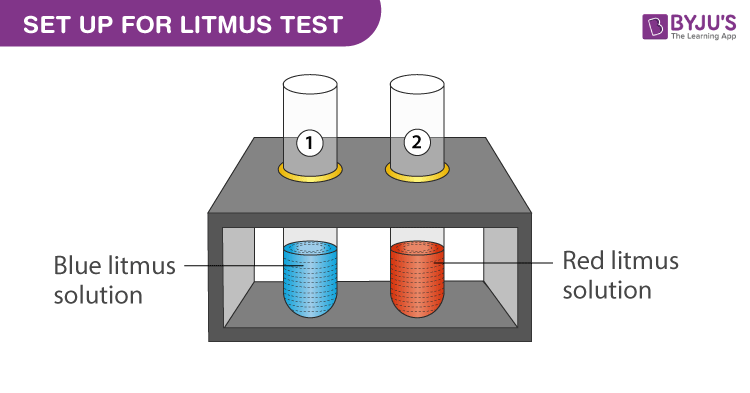
Procedure:
- Take a test tube stand and place two test tubes in it.
- Label the test tube as test tube 1 and test tube 2.
- Add 3 mL of blue litmus solution to test tube 1.
- Add 3 mL of red litmus solution to test tube 2.
- Use a dropper and add equal drops of sodium hydroxide in both the test tubes.
- Wait and observe the colour change.
Experimental Setup for NaOH with Zinc metal:
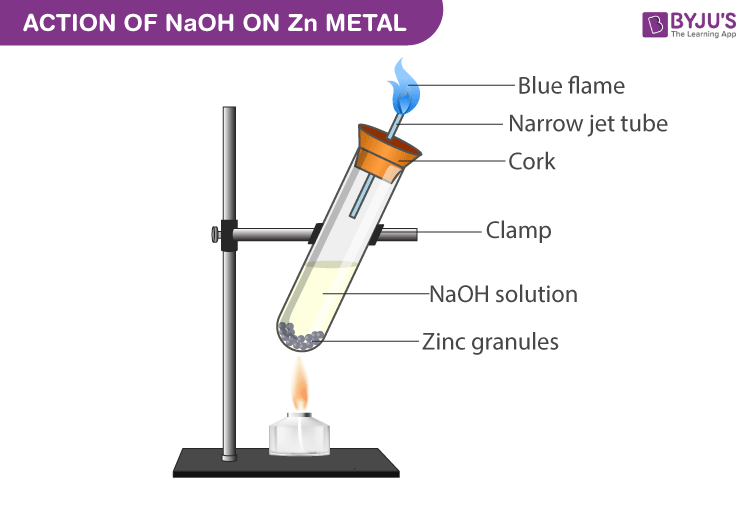
Procedure
- Take a clean and dry test tube.
- Add zinc granules to it.
- Submerge the zinc granules in the test tube by adding sodium hydroxide to it.
- Close the test tube with cork which has a glass delivery tube.
- A robust explosion takes place between 2-3 minutes liberating odourless and colourless gas.
- When a burning match stick is in brought near the glass tube mouth the gas burns with a pale blue flame with a pop sound.
Reaction:
2NaOH(aq) + Zn(s) → Na2ZnO2(aq) + H2↑
Procedure
- Take 1 gm of solid sodium carbonate in a test tube.
- With the help of a dropper, put a few drops of NaOH in the test tube.
- No reactions are observed.
Observation:
| Experiment | Observation |
| Litmus test | The red litmus solution in test tube 2 turns blue whereas there is no change in colour observed in the test tube 1 containing blue litmus solution. |
| Reaction with Zinc metal | Bases such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) liberate hydrogen gas when reacted with active metals such as zinc and burns with a pop sound when burning splinter is brought near it. |
| Reaction with Na2CO3 | No reaction is observed between NaOH and Na2CO3 |
Result and Conclusion:
- In the litmus test experiment the red litmus solution turns into blue when sodium hydroxide is added. Therefore, bases such as NaOH show basic character.
- Sodium hydroxide reacts with active metals such as zinc to form sodium zincate and liberate hydrogen gas.
- NaOH does not react with sodium carbonate.
Therefore, from the above three points we can conclude that NaOH (sodium hydroxide) is basic in nature.
Precautions to be taken during the experiment:
- Conduct the experiment in clean test tubes.
- NaOH is corrosive in nature and do not heat the mixture of zinc and NaOH to boiling point.
- Take a small amount of chemicals to perform the experiments to get the best results.
- Wash the droppers and test tubes with distilled water before and after using them in the experiment.
- Wash your hands thoroughly after the experiment.
Viva Voce:
- What happens NaOH comes in contact with red litmus solution?Ans: The red litmus solution turns into blue.
- Which metal other than aluminium reacts with NaOH to produce hydrogen gas?Ans: Zinc metal.
- When CO2 is passed through the lime water it turns it milky. Why?Ans: The insoluble calcium carbonate makes the solution appear milky..
- Can you write the chemical formula for sodium zincate?Ans: Na2ZnO2.
- Give examples of strong bases.Ans: KOH. NaOH, etc.

it really helped me a lot to undestand the concept