What is Mannitol (C6H14O6)?
C6H14O6 is a type of sugar alcohol with the chemical name Mannitol.
It is a diuretic and renal diagnostic aid which is related to sorbitol. It is also called D-mannitol, Osmitrol, or mannite. It is a naturally occurring alcohol found in vegetables and fruits. It is the most effective and safe medicine in the health system which is listed on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines. It is a prescribed drug used to reduce elevated pressure in the brain.
Also, Since it is poorly absorbed by the intestine it is often used in diabetic food as a sweetener. It is widely used as a research tool in cell biological studies, to control osmolarity. It appears as crystalline solid white in color or free-flowing granules. It is odorless and has a sweet taste. It has a flashpoint greater than 300° F. When decomposed it emits acrid smoke and fumes.
Properties of Mannitol – C6H14O6
| C6H14O6 | Mannitol |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 182.172 g/mol |
| Density | 1.489 at 68° F |
| Boiling Point | 563° F at 3.5 mm Hg |
| Melting Point | 331 to 334° F |
Mannitol Structure (C6H14O6 Structure)
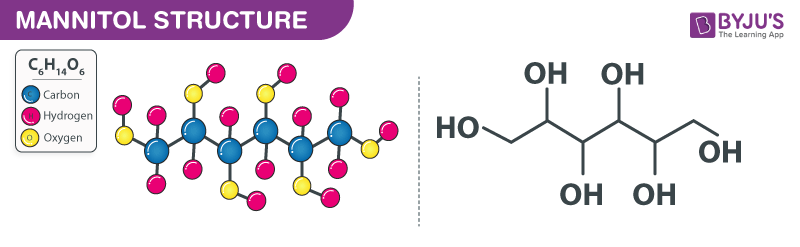
Mannitol Structure – C6H14O6
Mannitol (C6H14O6 ) Uses
- It is used in cyanide poisoning as an antidote.
- It is used to measure extracellular body fluid as well as to measure the renal glomerular filtration rate.
- Used as treatment of calciphylaxis in hemodialysis.
- It is used during cardiopulmonary bypass.
- It is used to decrease pressure in the eyes, such as in the case of glaucoma.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is mannitol composed of?
Mannitol, also known as manna sugar, is an alcohol which is colourless and sweet. A sweetener made from plants, the name comes from the word manna, which was the heavenly bread that God created for the Israelites. Mannitol is made of fructose and hydrogen, and it can also be artificially produced.
What is the function of mannitol?
Mannitol is a diuretic used either inside the eye or around the brain to minimize swelling and pain. Mannitol is used to help the body produce more urine, too.
Does mannitol cause hypokalemia?
Mannitol results in increased serum osmolality, osmotic water movement out of cells and secondary hyponatremia through dilution. Mannitol also causes hypokalemic, hypochloremic alkalosis. This alkalosis is typically associated with contraction of the volume and with diuresis.
What happens after mannitol administration?
More frequently recorded adverse reactions during or after mannitol infusion (mannitol injection) include pulmonary swelling, fluid and electrolyte imbalance, acidosis, electrolyte loss, mouth dryness, fatigue, marked diuresis, urinary retention, oedema, headache.
Is mannitol hypertonic or hypotonic?
Mannitol, given as a hypertonic solution, is commonly used in cerebral edema and glaucoma treatments. Although generally well-tolerated, a number of fluid, electrolyte, and renal problems may occur when the patient is not closely monitored.
Other related links:
| Types Of Alcohol | Classification Of Crystalline Solids |

Comments