What is Methyl acetate?
C3H6O2 is a carboxylate ester with a chemical name Methyl acetate. It is also called Methyl ethanoate or Methylacetate or Methyl ester of acetic acid. It is an acetate ester which results from the condensation of acetic acid and methanol.
Methyl ethanoate is a clear liquid which has no colour and has a fragrant fruity odour. It is moderately toxic and vapours are heavier than air. It is commonly found in apple and various other fruits such as bananas, grapes, etc. As it is an ester it can be synthesized in an esterification reaction by reacting acetic acid with methanol in the presence of sulfuric acid.
Table of Contents
- Properties of Methyl Acetate-C3H6O2
- Methyl Acetate Structure-C3H6O2
- C3H6O2 Uses ( Methyl Acetate)
- Production of Methyl Acetate
- Health Hazards
- Frequently Asked Questions
Properties of Methyl acetate – C3H6O2
| C3H6O2 | Methyl acetate |
| Molecular weight of C3H6O2 | 74.079 g/mol |
| Density of Methyl acetate | 0.932 g/cm3 |
| Melting point of Methyl acetate | −98 °C |
| Boiling point of Methyl acetate | 56.9°C |
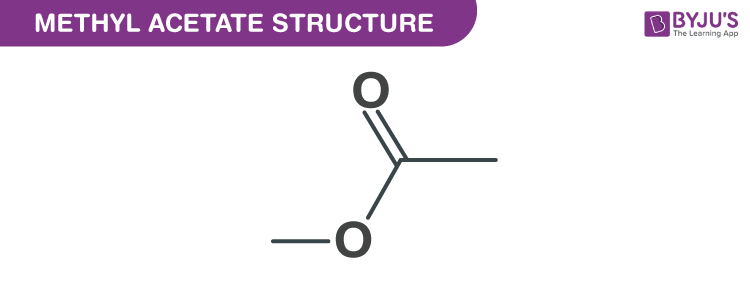
Methyl acetate structure – C3H6O2
C3H6O2 Uses (Methyl acetate)
- Methyl acetate is used as a food additive to enhance the flavour of food.
- Used in the manufacturing of artificial leather.
- Used for the biodegradation of organic materials.
- Used as a plasticizer.
- Used to manufacture Lubricants.
- Used in paint removers.
Production of Methyl acetate
Industrially it is obtained by the carbonylation of methanol as a byproduct of the synthesis of acetic acid. It can also be produced by esterification of acetic acid with methanol along with sulfuric acid (strong acid).
Health hazards
Inhaling Methylacetat can cause headache, drowsiness, and fatigue. Consuming it in high concentrations can result in CNS depression. Swallowing causes dizziness, drowsiness, headache, and fatigue. It can also damage the eyes.
This compound is highly flammable and liberates irritating and toxic gases or fumes when heated.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the uses of methyl acetate?
A significant application of methyl acetate in nail polish removers, glues, and paints is as a volatile low toxicity solvent. Acetic anhydride is generated by methyl acetate carbonylation in a method that was inspired by the synthesis of Monsanto acetic acid.
What is the difference between methyl acetate and acetone?
Unlike Acetone, methyl acetate has a low odour that is ideal for use in furniture and automotive applications. Methyl acetate can also be used in cosmetics such as perfumes and removers of nail polishes, resulting in less damage to nails than acetone.
How is methyl acetate produced?
Methyl acetate can be produced by subjecting methanol and acetic acid to esterification in the presence of an esterification catalyst and subsequently separating the products in the presence of an entrainer with the help of two distillation columns.
Learn more about the Structure, physical and chemical properties of C3H6O2 from the experts at BYJU’S.

Comments