
Silkworm
Introduction
A material which is composed of thin and continuous strands is known as fibre. Fibre can be of two types: natural fibre and synthetic fibre. The fibres which are obtained from plants and animals are known as natural fibres whereas synthetic fibres are man-made fibres. Examples of natural fibres are cotton and silk whereas examples of synthetic fibres are: nylon, polyester, etc. Silk is a type of natural fibre or animal fibre. Silkworm is responsible for spinning of silk and it is reared to obtain silk.
Table of Contents
- History of silk
- The life cycle of silkworm
- Processing of silk
- Recommended Videos
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
History of silk
Silk was discovered around 3500 BC in China. For a long period of time, silk was shipped to other parts of the world through trade. Technological advancement and new developments have enabled manufacturers to produce different types of silk from different silkworms on the basis of lustre and texture. Mulberry silk is the most common silk moth that is used for producing silk. Rearing of the silkworm is known as sericulture.

History of silk
The life cycle of silkworm
The life cycle of silk moth starts when a female silk moth lays eggs. The caterpillar or larvae are hatched from the eggs of the silk moth. The silkworms feed on mulberry leaves and give rise to pupa. In the pupa stage, a weave is netted around by the silkworm to hold itself. After that it swings its head, spinning a fibre made of a protein and becomes a silk fibre. Several caterpillars form a protective layer around pupa and this covering is known as the cocoon. The silk thread (yarn) is obtained from the silk moth’s cocoon. The life cycle of the silkworm is explained below in detail.
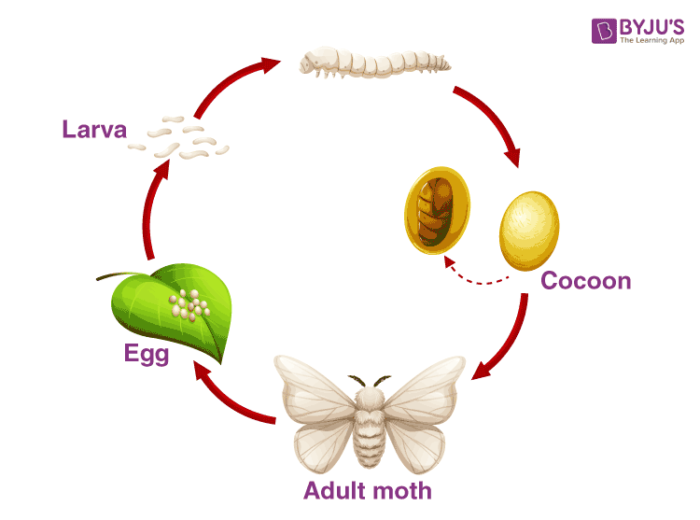
Stage 1: Egg
An egg is the first stage of the life cycle of the silkworm. The egg is laid by a female moth which is mostly the size of small dots. A female moth lays more than 350 eggs at a time. In the springtime, the eggs hatch due to the warmth in the air. This procedure happens once in every year.
Stage 2: Silkworm
A hairy silkworm arises after the eggs crack. In this stage of silkworms, the growth happens. they feed on mulberry leaves and consume a large amount of these leaves for around 30 days before going to the next stage.
Stage 3: Cocoon
In this stage, silkworms spin a protective cocoon around itself. It is the size of a small cotton ball and is made of a single thread of silk.
Stage 4: Pupa
The pupa stage is a motionless stage. In this stage, people kill the pupa by plunging the cocoon into boiling water and unwind the silk thread.
Stage 5: Moth
In this stage, the pupa changes into an adult moth. The female moth lays eggs after mating and thus the life cycle of silkworm begins again.
Processing of silk
Extracting silk from the cocoon is known as the processing of silk. Silk is separated from the cocoon by exposing it to sunlight. After the reeling of silk is done, the process of unwinding silk from a cocoon takes place. Silk thread is then bleached. The silk fibre is then spun into silk threads.
Recommended Videos
The Story of the Silk Worm

Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more interesting topics in Chemistry. Also, get various engaging video lessons to learn more effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions on Silkworm
How long can silkworms live without food?
We can stop feeding the silkworms every day once they’ve moulted a couple of times. It is possible for them to go a week or longer without eating (depending on temperature and size). However, feeding them every couple of days will keep them hydrated and healthy, extending the “hold” period.
Does a silkworm turn into a butterfly?
We can’t see what happens within the cocoon, but the larva’s body undergoes changes for two or three weeks, during which it transforms into a pupa, and then into a white butterfly. The butterfly secretes a yellowish liquid despite the cocoon being constructed of a strong silk thread.
How long does a silkworm take to complete its life cycle?
The silkworm’s life cycle is approximately 6-8 weeks long. The silkworm’s life cycle begins when the female silk moth produces eggs.
What happens to silkworms after silk is extracted?
Peace silk is silk that has been farmed ethically. This means the silkworms will be permitted to mature into full-fledged Bombyx mori moths. They naturally emerge from their cocoons and die a natural death.
Which stage of silkworm produces silk?
Silkworms produce pupa by feeding on mulberry leaves. To keep itself alive during the pupa stage, the silkworm weaves a net around itself. After that, it swings its head, spinning a protein fibre that eventually turns into silk.

Very useful. Good answer👍👍👍👍👍👍
Thank u . Because I now understood the life cycle of silkworms
Thanks shreya Hiwarkear
Super Answer . It is right to the question.
It is right answer for my project
Very nice answer will understand more faster
Very useful. thank you
It was helpful for me to understand. Thanks for your efforts👍👍👍🙏🙏🙏
very useful answer. Now l understood the concept clearly. thank you so much.
very useful thank you
thank you I understood it easily
AMAZING ANSWER!!! IT ABSOLUTELY FITS MY HOLIDAY HOMEWORK
very useful thanks
Thank u very much. Now I can answer any question related to the life cycle of silkworm.
Thank you. it’s really usefull.
Thank you . It’s very useful . I can understand it very well
this is awesome!!
Its help full. Keep it up and keep going forward.
It is useful information about silk moth.
Thank you, very useful for my Project.
Thank you so much sir. It really help me in my exam. I had practise this question and wrote in my exam i got really good marks.
Thanks for the answer its perfect for my project 😊😊😊
Thanks alot 🙏🤞 for this great answers I love all answers 😁😊🙂
I love the answer , I will use them in my assignment