What is Thiourea?
Thiourea is an organosulphur compound similar to urea in which the oxygen atom is replaced by a sulphur atom.
Thiourea is the sulphur analogue of urea. Thiourea is used for its synthetic equivalence to hydrogen sulphide. It plays an important role in the construction of heterocycles. It appears as white crystals, which are combustible and, in contact with fire give off irritating or toxic fumes. It acts as a precursor to sulphide to produce metal sulphides like mercury sulphide.
Other names – Thiocarbamide, Pseudothiourea
Table of Contents
- Structure Of Thiourea
- Chemical Information On Thiourea
- Physical Properties Of Thiourea
- Chemical Properties Of Thiourea
- Uses Of Thiourea
- Health Hazard Of Thiourea
- Faqs
Thiourea Structure – CH4N2S
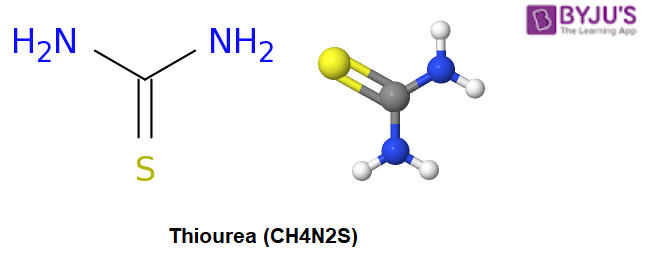
Chemical information on thiourea
| CH4N2S | Thiourea |
| Density | 1.4 g/cm³ |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 76.12 g/mol |
| Boiling Point | 150 – 160oC |
| Melting Point | 176 – 178oC |
| Chemical Formula | CS(NH2)2 |
Physical Properties of Thiourea – CH4N2S
| Odour | odourless |
| Appearance | White solid |
| pH | > 3 |
| Surface tension | 1.0404 X 10-2 N/m |
| Solubility | soluble in water (137 g/litre at 20 °C) |
Chemical Properties of Thiourea – CH4N2S
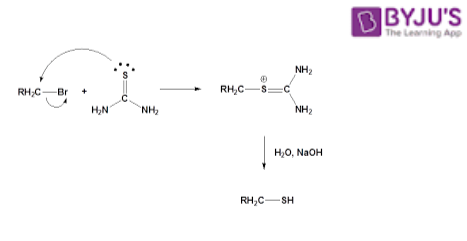
- Thiourea reacts with alkyl halides and gives isothiouronium salt on further hydrolysis reaction of this salt results in the formation of thiol and urea.
Uses of Thiourea – CH4N2S
- It is used in industries for the production of flame retardant resins and vulcanisation accelerators.
- Used as a chemical intermediate or catalyst in metal processing and plating and in photo processing.
- Used as a contaminant in the ethylene bisdithiocarbanate fungicides and can also be formed when food containing the fungicides is cooked.
Health Hazard
Exposure to thiourea causes adverse health effects and poisoning. It is absorbed into the body by inhalation of its aerosol and by ingestion. Repeated or prolonged contact of thiourea is known to cause skin sensitization and diverse health effects on the thyroid.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is thiourea used for?
Thiourea’s industrial uses include the manufacture of flame retardant resins and accelerators for vulcanization. Thiourea is used in the diazo paper as an auxiliary agent (light-sensitive photocopy paper) and almost every other form of copy paper. This is also used to colour the photographic prints in silver-gelatin.
Which functional group is present in urea?
In urea, the functional group is the carbonyl group. A functional group with a carbonyl group bound to two atoms of nitrogen, or a molecule containing the functional group. This family’s simplest member is also called urea.
Is urea acidic or basic?
It is neither acidic nor alkaline when urea dissolves in water. This is used by the body in many ways, most importantly for the excretion of nitrogen. In the urea cycle, the liver shapes it by mixing two ammonia molecules (NH3) with a molecule of carbon dioxide (CO2).
What type of inhibitor is thiourea?
Thiourea-containing drugs exhibit non-competitive kinetics inhibiton. Enzyme inhibition kinetics listed all drugs containing thiourea as non-competitive inhibitors, whereas the reference molecules (PTU and kojic acid) were designated as competitive inhibitors.

Comments