What is the Ullmann Reaction?
The Ullmann reaction (also known as Ullmann coupling) is an organic named reaction that involves the coupling of two aryl halides in the presence of copper to yield a biaryl as the product.
Ullmann coupling reaction is named after the German chemist Fritz Ullmann.
Table of Contents
- General Ullmann Reaction
- Ullmann Reaction Mechanism
- Applications of the Ullmann Reaction
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
General Ullmann Reaction
The general format of the Ullmann reaction is illustrated below.
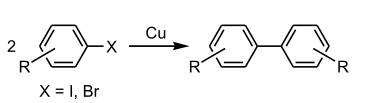
An illustration of the Ullmann reaction undergone by ortho-chloronitrobenzene in the presence of a copper-bronze alloy at a temperature of approximately 500 K to afford 2,2’-dinitrobiphenyl is provided below.
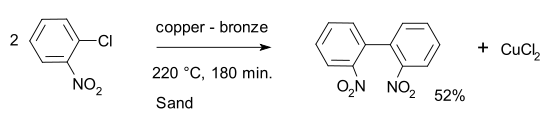
It can be noted that the Ullmann reaction is known to have relatively low yields, which is why palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions (such as the Heck reaction) are preferred over this reaction. Also, the reaction conditions for the Ullmann reaction are quite harsh.
Ullmann Reaction Mechanism
Step 1
The mechanism of the Ullmann reaction involves the formation of an active copper(I) species upon the introduction of the aryl halide to an excess of metallic copper under relatively high temperatures (>200oC).
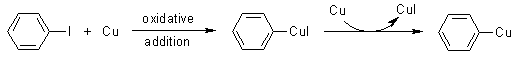
Step 2
This copper(I) species undergoes further oxidative addition with another haloarene molecule, linking the two molecules (as illustrated below).
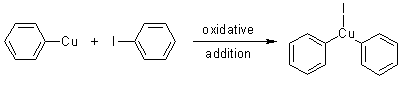
Step 3
In the final step of the Ullmann reaction mechanism, the copper compound formed by the two aryl halide molecules undergoes reductive elimination, resulting in the formation of a new carbon-carbon bond between the two aryl compounds (as illustrated below).
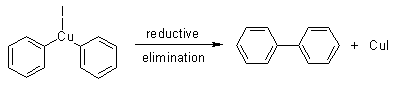
Applications of the Ullmann Reaction
- Biphenylenes can be obtained from 2,2-diiodobiphenyl via the Ullmann reaction.
- This reaction can also be employed for the closure of five-membered rings.
- An unsymmetrical reaction can also be achieved given that one of the reactants is provided in excess.
- Chiral reactants can be coupled into a chiral product via this reaction.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is Ullmann reaction? Explain with an example.
The Ullmann reaction or Ullmann coupling is a coupling reaction between aryl halides. Traditionally this reaction is affected by copper, but palladium and nickel are also effective catalysts.
What is Ullmann synthesis?
The “classic” Ullmann Reaction is the synthesis of symmetric bi aryls via copper-catalyzed coupling. The “Ullmann-type” Reactions include copper-catalyzed Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution between various nucleophiles (e.g. substituted phenoxides) with aryl halides.
Why copper is used in Ullmann reaction?
Catalysts, like copper, provide an alternative pathway by which the reaction can proceed, in which the activation energy is lower. It thus increases the rate at which the reaction comes to equilibrium.
What is difference between Wurtz reaction and Ullmann reaction?
The Wurtz–Fittig reaction is the chemical reaction of aryl halides with alkyl halides and sodium metal in the presence of dry ether to give substituted aromatic compounds as their products. The Ullmann reaction or Ullmann coupling is a coupling reaction between aryl halides and copper.
What are the reagents involved in Ullmann reaction?
Ullmann reaction, also known as Ullmann biaryl synthesis or Ullmann coupling, is an organic reaction which couples two molecules of aryl halide to produce a biaryl employing copper metal in the presence of thermal conditions.
To learn more about the Ullmann reaction and other important named reactions in organic chemistry (such as the Fries rearrangement reaction), register with BYJU’S and download the mobile application on your smartphone).

Comments