Cinnamic acid is a white crystalline acid with a molecular formula C9H8O2. It is a crystalline compound that is white in colour and is slightly soluble in water. It is collected from the oil of cinnamon and is also found in shea butter. It has a honey-like odour. In this short piece of article, we shall be discussing more about the cinnamic acid formula along with its chemical structure and properties.
Cinnamic Acid Properties
| Properties of Cinnamic Acid | |
| Name | Cinnamic Acid |
| Other Names | Cinnamylic acid, Isocinnamic acid, Benzenepropenoic acid,
trans-Cinnamic acid, Phenylacrylic acid, 3-Phenylacrylic acid |
| Appearance | White monoclinic crystals |
| Molecular Formula | C9H8O2 |
| Melting Point | 133 °C |
| Boiling Point | 300 °C |
| Density | 1.2475 g/cm3 |
| Molar Mass | 148.161 g.mol–1 |
| Solubility in Water | Slightly soluble |
Cinnamic Acid Structure
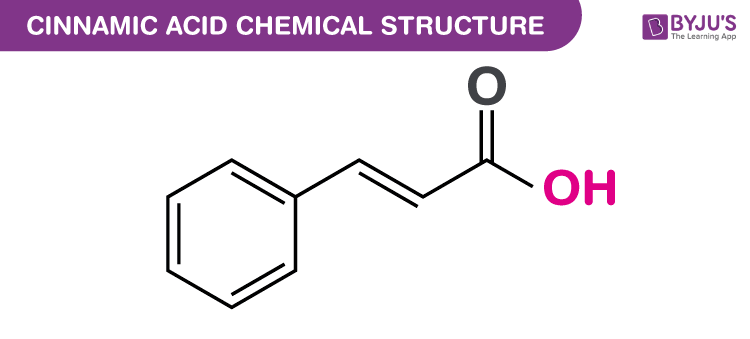
Cinnamic Acid Uses
- Used in flavourings and certain pharmaceuticals
- Used in the perfume industry
- Used as a precursor to the sweetener aspartame
To learn more about such chemistry topics register to BYJU’S now!
Comments