Force of attraction is a force that pulls the body near due to its attraction. There are numerous attractive forces prevailing in nature. Some of them are magnetic force, electric force, electrostatic force and gravitational force. Gravitational force is very well-identified instance force of attraction as it draws objects towards itself regardless of its distance. Newton’s universal law of gravitation clarifies a lot more about how this force performs. It states that every mass that occurs in the universe attracts some or the other mass in the universe. It validates the fact that anyone thrown up comes down.
Let’s take two masses m1 and m2 parted by a spaced.
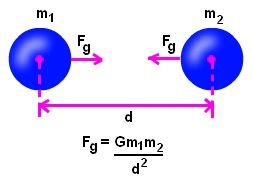
The formula for the force of attraction is articulated as,
Where,
F is the force of attraction
G is the gravitational constant (6.67 × 10-11 Nm2/kg2),
the mass of object 1 is m1,
the mass of object 2 is m2,
the distance between two objects is d.
This formula aids out in calculating the force acting amongst any two bodies having a greater mass since in smaller masses this force is insignificant.
Solved Examples
Example 1: Compute the gravitational force acts amongst two bodies of masses 20,000 kg and 50,000 kg parted by a distance of 50 m.
Answer:
Known:
mass m1 = 20000 kg,
mass m2 = 50000 kg,
radius r = 50 m,
Gravitational constant G = 6.67 × 10-11 Nm2/kg2
The force due to gravity is articulated as,
Therefore, the gravitational force is
Example 2: A body of weight 80 kg is 2 m far away from the body of weight 50 kg. Calculate the gravitational force acting between them.
Answer:
Known:
mass m1 = 80 kg,
mass m2 = 50 kg,
radius r = 2 m,
Gravitational constant G = 6.67 × 10-11 Nm2/kg2
Therefore,
Stay tuned with BYJU’S for more such interesting articles. Also, register to “BYJU’S – The Learning App” for loads of interactive, engaging Physics-related videos and unlimited academic assist.
Comments