Iodic acid is a conjugate acid and is an iodine oxoacid. It is soluble in water and also exists in a pure state. Iodic acid can be obtained by oxidizing iodine with strong oxidizers like nitric acid, hydrogen peroxide, chloric acid and chlorine. It is also known as monoiodic acid, trioxoiodic acid, hydrogen trioxoiodate, hydroxidodioxidoiodine and iodic(V) acid. The property value of hydrogen bond donor and hydrogen bond acceptor are 1 and 3 respectively.
Following is the table of formulas of iodic acid:
| Molecular formula | HIO3 |
| Linear formula | HIO3 |
Structure Of Iodic Acid
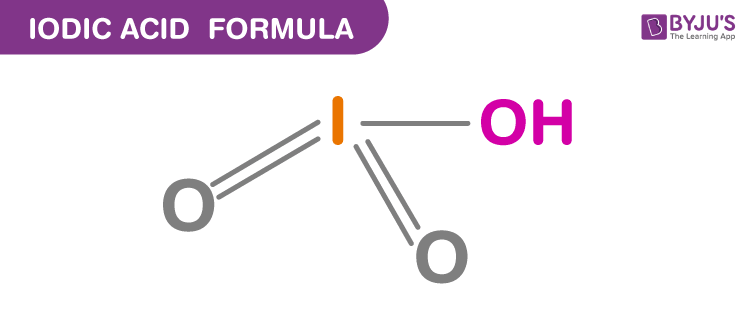
Properties Of Iodic Acid
| IUPAC name | Iodic acid |
| Molecular formula | HIO3 |
| Molecular mass | 175.909 g/mol |
| Melting point | 110℃ |
| Density | 4.629 g/cm3 |
Uses Of Iodic Acid
- It is used in the salt industry to synthesize sodium and potassium iodate to increase the iodine content in the salt.
- In analytical chemistry, it is used as a strong acid.
- It is used as a standardized solution for both weak and the strong acid.
To learn more about concepts related to Chemistry, stay tuned with BYJU’S.
Comments