In calculus, integration and differentiation are the two most important concepts. Integration originated during the course of finding the area of a plane figure, whereas differentiation is a process of finding a function that outputs the rate of change of one variable with respect to another variable. Integration is the reverse of differentiation. It is also called the antiderivative. In this section, students will learn about the list of definite and indefinite integration important formulas, how to use integral properties to solve integration problems, integration methods and much more.
Indefinite Integration
The indefinite integral is defined as a function that describes an area under the function’s curve from an undefined point to another arbitrary point. Read more.
Standard Formulas for Indefinite Integration
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{{{x}^{n}}dx=\frac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}}+c\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{{{a}^{x}}dx}=\frac{{{a}^{x}}}{\ell n\,a}+c\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{{{e}^{x}}}dx={{e}^{x}}+c\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{1}{x}}dx=\ell n\,x+c\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\sin x\,dx=-\cos x+c}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\cos x\,dx=\sin x+c}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{{{\sec }^{2}}x\,\,dx=\tan x+c}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\cos e{{c}^{2}}x\,\,dx=-\cot x\,+c}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\sec x\tan xdx=\sec x+c}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\cos ec\,\,x\,\,}\cot x\,dx=-\cos ec\,x+c\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-{{x}^{2}}}}dx\begin{matrix} = \\ = \\ \end{matrix}}\left\{ \begin{matrix} {{\sin }^{-1}}x+c \\ -{{\cos }^{-1}}x+c \\ \end{matrix} \right.\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{1}{1+{{x}^{2}}}}dx\begin{matrix} = \\ = \\ \end{matrix}\left\{ \begin{matrix} {{\tan }^{-1}}x+c \\ -{{\cot }^{-1}}x+c \\ \end{matrix} \right.\end{array} \)
.\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{1}{x\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}}=\left\{ \begin{matrix} {{\sec }^{-1}}x+c \\ -\cos e{{c}^{-1}}x+c \\ \end{matrix} \right.\end{array} \)
⇒ Also Read – Introduction to Integration
Methods of Integration
- Substitution method
- Integration by partial fractions
- By parts
- Euler substitution
- Reduction method
Properties of Indefinite Integration
\(\begin{array}{l}k\int{f\left( x \right)dx=k\int{f\left( x \right)}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\left( f\left( x \right)+g\left( x \right) \right)dx=\int{f\left( x \right)dx+\int{g\left( x \right)dx}}}\end{array} \)
Below are some Illustrations based on integration properties and the substitution method:
Illustration 1: Solve
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{{{\left( 1+x \right)}^{3}}}{\sqrt[3]{{{x}^{2}}}}}dx\end{array} \)
.
Solution:
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{{{\left( 1+x \right)}^{3}}}{\sqrt[3]{{{x}^{2}}}}}dx=\int{\frac{1+3x+3{{x}^{2}}+{{x}^{3}}}{{{x}^{2/3}}}}dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\int({{{x}^{-2/3}}+3{{x}^{1/3}}+3{{x}^{4/3}}}+{{x}^{7/3}})dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=3{{x}^{1/3}}+\frac{9}{4}{{x}^{4/3}}+\frac{9}{7}{{x}^{7/3}}+\frac{3}{10}{{x}^{10/3}}+c\end{array} \)
Illustration 2: Solve
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{{\sec }^{2}}x\cos e{{c}^{2}}x\,\,dx\end{array} \)
.
Solution:
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{{{\sec }^{2}}x\cos e{{c}^{2}}x\,\,dx=\int{\frac{{{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x}{{{\sin }^{2}}x\,{{\cos }^{2}}x}}dx}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\int{{{\sec }^{2}}x+\cos e{{c}^{2}}x\,\,dx}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\tan x-\cot x+c\end{array} \)
Illustration 3. Solve
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{2x\,\,\sin \left( {{x}^{2}} \right)dx}\end{array} \)
.
Solution: Put x2 = t.
Then, 2x dx = dt
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\sin t\,\,dt=-\cos t+c}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=-\cos {{x}^{2}}+c\end{array} \)
Illustration 4.
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{{{\sin }^{3}}x{{\cos }^{5}}x\,\,dx}\end{array} \)
Solution:
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{{{\sin }^{2}}x{{\cos }^{5}}x\sin x\,\,dx}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\int{\left( 1-{{\cos }^{2}}x \right)}{{\cos }^{5}}x\,\,\sin x\,\,dx\end{array} \)
put cos x = t
Therefore, -sin x dx = dt
So, the new equation is:
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\left( 1-{{t}^{2}} \right)}{{t}^{5}}\left( -dt \right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\int{{{t}^{5}}-{{t}^{7}}}dt\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=-\left( \frac{{{t}^{6}}}{6}-\frac{{{t}^{8}}}{8} \right)\end{array} \)
Resubstituting the value, we get
\(\begin{array}{l}-\frac{{{\cos }^{6}}x}{6}+\frac{{{\cos }^{8}}x}{8}+c\end{array} \)
.
Important Formulae Set for Indefinite Integration
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{dx}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}}}={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \frac{x}{a} \right)+c\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{dx}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}}=\ell n\left| x+\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}} \right|}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{dx}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}}=\ell n\left| x+\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}} \right|}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{1}{{{a}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}}}dx=\frac{1}{a}{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \frac{x}{a} \right).\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{1}{{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}}dx=\frac{1}{2a}\ell n\left| \frac{a+x}{a-x} \right|.\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{1}{{{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}}dx=\frac{1}{2a}\ell n\left| \frac{x-a}{x+a} \right|.\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}}dx=\frac{x}{2}\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}+\frac{{{a}^{2}}}{2}{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \frac{x}{a} \right).\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}}}dx=\frac{x}{2}\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}+\frac{{{a}^{2}}}{2}\ell n\left| x+\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}} \right|\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}}dx=\frac{x}{2}\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}+\frac{{{a}^{2}}}{2}\ell n\left| x+\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}} \right|\end{array} \)
Types of Substitutions
Type I
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{{{\sin }^{m}}x{{\cos }^{n}}x\,\,dx}\end{array} \)
Rule:
- If from either m and n, one of them is odd, then substitute for even power.
- If both are odd, then substitute either of them.
- If both even use trigonometric identities.
Type II: Substitution of Trigonometric Functions.
\(\begin{array}{l}\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}\rightarrow{{}}x=a\sin \theta\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}\rightarrow{{}}x=a\tan \theta\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}\rightarrow{{}}x=a\sec \theta\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\sqrt{\frac{x-a}{b-x}}\rightarrow{{}}x=a{{\cos }^{2}}\theta +b{{\sin }^{2}}\theta\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\sqrt{\frac{x-a}{x-b}}\rightarrow{{}}x=a{{\sec }^{2}}\theta -b\end{array} \)
Type III:
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{px+q}{a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c}}dx\And \int{\frac{px+q}{\sqrt{a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c}}}\,dx\And \int{\left( px+q \right)}\sqrt{a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c}\,dx\end{array} \)
We express px + q as:
\(\begin{array}{l}m{{\left( a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c \right)}^{1}}+n\end{array} \)
Then, this gets changed to standard integral.
Biquadratic Substitutions
\(\begin{array}{l}I=\int{f\left( x+\frac{1}{x} \right)}\left( 1-\frac{1}{{{x}^{2}}} \right)dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Put}\ x+\frac{1}{x}=t\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}I=\int{f\left( x-\frac{1}{x} \right)}\left( 1+\frac{1}{{{x}^{2}}} \right)dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Put}\ \left( x-\frac{1}{x} \right)=t\end{array} \)
Solved Problems
Problem 1: Solve
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{dx}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+2x+2}}}\end{array} \)
Solution:
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{dx}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+2x+2}}}=\int{\frac{dx}{\sqrt{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}+1}}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\log \left| \left( x+1 \right)+\sqrt{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}+1} \right|.\end{array} \)
Problem 2: Solve
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\sqrt{5{{x}^{2}}+2x+3}}\,\,dx\end{array} \)
Solution:
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\sqrt{5{{x}^{2}}+2x+3}}\,\,dx\end{array} \)
here
\(\begin{array}{l}5{{x}^{2}}+2x+3=5\left[ {{\left( x+\frac{1}{5} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{\frac{14}{25}} \right)}^{2}} \right]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\sqrt{5{{x}^{2}}+2x+3}\,dx}=\sqrt{5}\int{\sqrt{{{\left( x+\frac{1}{5} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{\frac{14}{25}} \right)}^{2}}}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\sqrt{5}\frac{\left( x+\frac{1}{5} \right)}{2}\sqrt{{{\left( x+\frac{1}{5} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{\frac{14}{15}} \right)}^{2}}}+\frac{14}{25.2}\log \left| \left( x+\frac{1}{5} \right)+\sqrt{{{\left( x+\frac{1}{5} \right)}^{2}}+\frac{14}{15}} \right|\end{array} \)
Problem 3: Evaluate
\(\begin{array}{l}I=\int{\frac{x+1}{{{x}^{2}}+3x+4}}dx\end{array} \)
Solution:
\(\begin{array}{l}I=\int{\frac{x+1}{{{x}^{2}}+3x+4}}dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}x+1=a{{\left( {{x}^{2}}+3x+4 \right)}^{1}}+b\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=2ax+\left( 3a+b \right)\end{array} \)
[Using Type III (mentioned above)]
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore a=\frac{1}{2}\,\,\,\,b=\frac{-1}{2}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow I=\int{\frac{1}{2}}\frac{{{\left( {{x}^{2}}+3x+4 \right)}^{1}}}{{{x}^{2}}+3x+4}-\frac{1}{2}\left( \frac{1}{{{x}^{2}}+3x+4} \right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{1}{2}\log \left( {{x}^{2}}+3x+4 \right)-\frac{1}{2}\int{\frac{1}{{{\left( x+\frac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}+\frac{7}{4}}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{1}{2}\log \left( {{x}^{2}}+3x+4 \right)-\frac{1}{2}\frac{1}{\sqrt{\frac{7}{4}}}{{\tan }^{-1}}\frac{\left( x+\frac{3}{2} \right)}{\sqrt{\frac{7}{4}}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{1}{2}\log \left| {{x}^{2}}+3x+4 \right|-\frac{1}{\sqrt{7}}{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \frac{2x+3}{\sqrt{7}} \right)\end{array} \)
Problem 4: Solve
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{1+{{x}^{2}}}{1+{{x}^{4}}}}\,dx\end{array} \)
Solution:
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{1+{{x}^{2}}}{1+{{x}^{4}}}}\,dx=\int{\frac{\left( 1+\frac{1}{{{x}^{2}}} \right)}{\left( \frac{1}{{{x}^{2}}}+{{x}^{2}} \right)}}\,dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\int{\frac{\left( 1+\frac{1}{{{x}^{2}}} \right)dx}{{{\left( x-\frac{1}{x} \right)}^{2}}+2}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\int{\frac{d\left( x-\frac{1}{x} \right)}{{{\left( x-\frac{1}{x} \right)}^{2}}+2}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \frac{\left( x-\frac{1}{x} \right)}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\end{array} \)
Integration by Partial Fraction
Integrals of rational functions can be evaluated by splitting them into partial fractions.
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{f\left( x \right)}{g\left( x \right)}\end{array} \)
Where, f and g are polynomials is called a rational function.
If the degree of f < the degree of g, it is called a proper fraction.
Otherwise, it is an improper fraction.
Then
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{f\left( x \right)}{g\left( x \right)}=h\left( x \right)+\frac{d\left( x \right)}{g\left( x \right)},\end{array} \)
degree of d < degree of g.
Cases:
1. When g(x) is expressed as the product of non-repeating linear factors,
\(\begin{array}{l}g\left( x \right)=\left( x-{{a}_{1}} \right)\left( x-{{a}_{2}} \right)….\left( x-{{a}_{n}} \right)\end{array} \)
then
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{f}{g}=\frac{{{A}_{1}}}{x-{{a}_{1}}}+\frac{{{A}_{2}}}{x-{{a}_{2}}}+….\frac{{{A}_{n}}}{x-{{a}_{n}}}.\end{array} \)
2. Some factors of g are repeating, then
\(\begin{array}{l}g\left( x \right)={{\left( x-a \right)}^{k}}\left( x-{{a}_{1}} \right)\left( x-{{a}_{2}} \right)…\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{f}{g}=\frac{{{A}_{1}}}{\left( x-a \right)}+\frac{{{A}_{2}}}{{{\left( x-a \right)}^{2}}}+…..\frac{{{A}_{k}}}{{{\left( x-a \right)}^{n}}}+…\end{array} \)
3. If g(x) has a quadratic term, then
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{f}{g}=\frac{Ax+B}{a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c}\end{array} \)
Where, A & B are constants determined by comparing coefficients.
Let us understand with the help of examples:
Example 1: Solve
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{dx}{\left( x+1 \right)\left( x-2 \right)}}\end{array} \)
Solution:
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{dx}{\left( x+1 \right)\left( x-2 \right)}}=\int{\frac{a}{x+1}+\frac{b}{x-2}}\,dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\int{\frac{-\frac{1}{3}}{x+1}}+\int{\frac{\frac{1}{2}}{x-2}}\,dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=-\frac{1}{3}\ell n\left| x+1 \right|+\frac{1}{2}\ell n\left| x-2 \right|\end{array} \)
Example 2: Solve
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{2{{x}^{2}}-1}{\left( x-1 \right){{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}}dx\end{array} \)
Solution:
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{2{{x}^{2}}-1}{\left( x-1 \right){{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}dx=\int{\frac{A}{x-1}+\frac{B}{\left( x+1 \right)}}+\frac{C}{{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}2{{x}^{2}}-1=A{{\left( x+1 \right)}^{2}}+B\left( x+1 \right)\left( x+1 \right)+C\left( x-1 \right)\end{array} \)
Put x = 1 ⇒ A = 1/2
x = -1 ⇒ C – -1/2
B = 3/2.
\(\begin{array}{l}I=\int{\frac{\frac{1}{2}}{\left( x-1 \right)}}dx+\frac{3}{2}\int{\frac{dx}{\left( x+1 \right)}}+\left( \frac{-1}{2} \right)\int{\frac{dx}{{{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}}}\end{array} \)
,
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{1}{2}\ell n\left| x-1 \right|+\frac{3}{2}\left( ln\left| x+1 \right| \right)+\frac{1}{2\left( x+2 \right)}+c\end{array} \)
,
Example 3: Solve
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{dx}{\left( x+2 \right)\left( {{x}^{2}}+1 \right)}}\end{array} \)
Solution:
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{dx}{\left( x+2 \right)\left( {{x}^{2}}+1 \right)}}=\frac{A}{x+2}+\frac{Bx+C}{{{x}^{2}}+1}\end{array} \)
Comparing by x = -2 ⇒ A = 1/5
And by x2 coefficient B = -1/2 and C = 2/5,
On substituting the values and integrating, we have
\(\begin{array}{l}I=\frac{1}{5}\ell n\left| x+2 \right|-\frac{1}{10}\ell n\left( {{x}^{2}}+1 \right)+\frac{2}{5}{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\end{array} \)
Integration of Trigonometric Functions
Type 1:
\(\begin{array}{l}I=\int{{{\sin }^{m}}x{{\cos }^{n}}xdx}\end{array} \)
1. If m –odd, put cos x = t
2. If n odd, put sin x = t
3. If m and n rationales, then put tan x = t
4. If both are even, then use the reduction method.
Let us understand with the help of an example:
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{{{\cos }^{3}}x}{{{\sin }^{6}}x}dx=\int{\frac{1-{{t}^{2}}}{{{t}^{6}}}dt}}\end{array} \)
Where, t = sin x
\(\begin{array}{l}=\int{{{t}^{-6}}-{{t}^{-4}}dt}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=-\frac{1}{5si{{n}^{5}}x}+\frac{1}{3{{\sin }^{3}}x}+c\end{array} \)
Type 2:
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{dx}{a\cos x+b\sin x+c}}\end{array} \)
Put t = tan (x/2)
Illustration:
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{dx}{2+\sin x}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow t=\tan \left( \frac{x}{2} \right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}dx=\frac{2dt}{1+{{t}^{2}}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\int{\frac{\frac{2dt}{1+{{t}^{2}}}}{2+\frac{2t}{1+{{t}^{2}}}}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow \int{\frac{dt}{{{t}^{2}}+t+1}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \frac{2t+1}{\sqrt{3}} \right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \frac{2\tan \frac{x}{2}+1}{\sqrt{3}} \right)+c\end{array} \)
Type 3
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{dx}{a{{\cos }^{2}}x+b{{\sin }^{2}}x}},\int{\frac{dx}{a+b{{\sin }^{2}}x}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{1}{a+b{{\cos }^{2}}x}}\,dx,\int{\frac{1}{{{\left( a\sin x+b\cos x \right)}^{2}}}}\,dx\end{array} \)
or \(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{1}{a+b{{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x}}\,dx\end{array} \)
Rule:
Divide both the numerator & denominator by cos2x.
Illustration:
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{1}{3-4{{\sin }^{2}}x}}\,dx=\int{\frac{\frac{1}{{{\cos }^{2}}x}}{\frac{3}{{{\cos }^{2}}x}-\frac{4{{\sin }^{2}}x}{{{\cos }^{2}}x}}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\int{\frac{{{\sec }^{2}}x}{3{{\sec }^{2}}x-4{{\tan }^{2}}x}}\,dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\int{\frac{dt}{3\left( 1+{{t}^{2}} \right)-4{{t}^{2}}}}\end{array} \)
(Since, by tan x = t, sec2x dx = dt)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\int{\frac{dt}{3-{{t}^{2}}}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\int{\frac{1}{{{\left( \sqrt{3} \right)}^{2}}-{{t}^{2}}}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{1}{2\sqrt{3}}\ell n\left| \frac{\sqrt{3}+t}{\sqrt{3}-t} \right|\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{1}{2\sqrt{3}}\log \left| \frac{\sqrt{3}+\tan x}{\sqrt{3}-\tan x} \right|\end{array} \)
Indefinite Integration – Video Lesson
Indefinite-Integration Problems
Definite Integrals
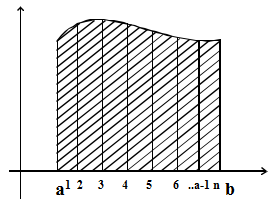
Choose n divide [a, b] in n parts of width h = (b – a)/n partition of the interval, putting (n – 1) parts in between
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)}dx=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,h\,\sum\limits_{n=0}^{n-1}{f\left( a+rh \right)}\end{array} \)
Definition of Definite Integral as the Limit of a Solution
\(\begin{array}{l}=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,h\left[ f\left( a \right)+f\left( a+h \right)+f\left( a+2h \right)+…..+f\left( a+\left( n-1 \right)h \right) \right]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}nh=b-a\end{array} \)
Integrals using limits
Evaluate as the Limit of a Sum
\(\begin{array}{l}I=\int\limits_{a}^{b}{x\,\,dx\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=x\,\,\,so\,h=\frac{b-a}{n}}\end{array} \)
f(a) = a
f(a + h) = a + h
\(\begin{array}{l}I=h\left[ a+\left( a+h \right)+….\left( a+\left( n-1 \right)h \right) \right]\end{array} \)
look for nh
\(\begin{array}{l}=h\left[ \left( na \right)+h+2h+3h….\left( n-1 \right)h \right]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=hna+\frac{{{h}^{2}}n\left( n-1 \right)}{2}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\left( b-a \right)a+\frac{{{h}^{2}}{{n}^{2}}}{2}-\frac{{{\left( b-a \right)}^{2}}}{2}=\frac{{{b}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}{2}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\sum\limits_{r=1}^{n}{n}=\frac{n\left( n+1 \right)}{2}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\sum\limits_{r=1}^{n}{{{n}^{2}}}=\frac{n\left( n+1 \right)\left( 2n+1 \right)}{6}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\sum\limits_{r=1}^{n}{{{n}^{3}}}={{\left[ \frac{n\left( n+1 \right)}{2} \right]}^{2}}\end{array} \)
GP …
\(\begin{array}{l}a+ar+a{{r}^{2}}….a{{r}^{n-1}}=\frac{a\left( 1-{{r}^{n}} \right)}{1-r}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\sin \alpha +\sin \left( \alpha +\beta \right)+\sin \left( \alpha +2\beta \right)….\sin \left( \alpha +\left( n-1 \right)\beta \right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{\sin \left( n\frac{\beta }{2} \right)}{\sin \left( \frac{\beta }{2} \right)}\sin \left[ \frac{\alpha +\alpha +\left( n-1 \right)\beta }{2} \right]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{\sin \left( n\frac{diff}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( \frac{diff}{2} \right)}\sin \left( \frac{1st+last}{2} \right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{\sin \left( \frac{n\,diff}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( \frac{diff}{2} \right)}\cos \left( \frac{1st+last}{2} \right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}1-\frac{1}{{{2}^{2}}}+\frac{1}{{{3}^{2}}}-\frac{1}{{{4}^{2}}}+\frac{1}{{{5}^{2}}}-\frac{1}{{{6}^{2}}}=\frac{{{\pi }^{2}}}{12}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}1+\frac{1}{{{2}^{2}}}+\frac{1}{{{3}^{2}}}+\frac{1}{{{4}^{2}}}+\frac{1}{{{5}^{2}}}….=\frac{{{\pi }^{2}}}{12}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{a}^{b}{{{e}^{x}}dx=\underset{n\to \infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,}h\left[ {{e}^{a}}+{{e}^{a+h}}+{{e}^{a+2h}}…{{e}^{a+\left( n-1 \right)h}} \right]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=h{{e}^{a}}\left[ 1+{{e}^{n}}+{{e}^{2h}}+…. \right]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}={{e}^{a}}\left[ {{e}^{nh}}-1 \right]\frac{h}{\left( {{e}^{n}}-1 \right)}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}={{e}^{b}}-{{e}^{a}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{a}^{b}{\sin x\,dx=\underset{n\to \infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,}h\left[ \sin a+\sin \left( a+n \right)+…\sin \left( a+\left( n-1 \right)h \right) \right]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\underset{n\to \infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,h\frac{\sin \left( \frac{nh}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( \frac{h}{2} \right)}\left[ \sin \left( \frac{2a+\left( n-1 \right)h}{2} \right) \right]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{\sin \left( \frac{b-a}{2} \right)}{\left( \frac{1}{h} \right)\sin \left( \frac{h}{2} \right)}\left[ \sin \left( a+\frac{nh}{2}-\frac{h}{2} \right) \right]=2\sin \left( \frac{b-a}{2} \right)\sin \left( \frac{a+b}{2} \right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\cos \left( \frac{b-a-\left( a+b \right)}{2} \right)-\cos \left( \frac{\left( b-a \right)+\left( a+b \right)}{2} \right)\end{array} \)
= cos a – cos b
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{0}^{2}{\left( {{x}^{2}}+1 \right)dx=\frac{14}{3}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{0}^{2}{\left( 3{{x}^{2}}+2x+1 \right)dx=3}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{0}^{\frac{\pi }{2}}{\cos x\,dx=1}\end{array} \)
or\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{0}^{\frac{\pi }{2}}{{{\sin }^{2}}x\,dx=h\left[ \frac{1-\cos 2x}{2}+\frac{1-{{\cos }^{\left( 2n+2n \right)}}}{2}…… \right]}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{1}{2}\left( b-a \right)-\frac{1}{4}\left( \sin 2b-\sin 2n \right)\end{array} \)
Limits Using Definite Integration
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)dx=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\sum\limits_{r=1}^{n}{f\left( a+rh \right)}}\end{array} \)
Special case a = 0 and b = 1
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{0}^{1}{f\left( x \right)\,dx=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{1}{n}}\sum\limits_{r=1}^{n}{f\left( \frac{r}{n} \right)}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{0}^{k}{f\left( x \right)\,dx=\underset{h\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{1}{n}}\sum\limits_{r=1}^{kn}{f\left( \frac{r}{n} \right)}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\sum{\rightarrow{Multiple\,\,of\,n}}\int{{}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{1}{n}\to dx\,\,\,\,\frac{r}{n}\Rightarrow x\end{array} \)
How to solve integration with the help of limits?
\(\begin{array}{l}\underset{n\to \infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,\left[ \frac{1}{na}+\frac{1}{na+1}+\frac{1}{na+2}+…\frac{1}{nb} \right]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\underset{n\to \infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,\sum\limits_{r=0}^{\left( b-a \right)}{\frac{1}{na+r}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\sum\limits_{n\to \infty }{\frac{1}{n}\sum\limits_{r=0}^{\left( b-a \right)n}{\frac{1}{a+\frac{r}{n}}}}=\int\limits_{0}^{b-a}{\frac{dx}{a+x}}=\left[ \log \left( a+x \right) \right]_{a}^{b-a}=\log \left( \frac{b}{a} \right)\end{array} \)
Applications of Integrals Videos
Definite Integral & Area Under the Curve – Important Topics
Definite Integral & Area Under the Curve – Important Questions
Most Important Questions from Definite Integration for JEE Advanced
Properties of Definite Integration for JEE Part 1
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1
What do you mean by integration?
Integration is the method of finding the antiderivative of a function.
Q2
What are the rules of integration?
There are many rules of integration, namely the power rule, the sum and difference rules, the exponential rule, the reciprocal rule, the constant rule, the substitution rule, and the rule of integration by parts, etc.
Q3
Why is integration important?
We utilise integration in Mathematics to find areas, volumes, displacement, etc. Integral calculus originated from the concept of integration in calculus.







Comments