Lithium oxide, also known as Lithia, is a white inorganic chemical compound. Lithium oxide is produced by thermal dehydration of lithium hydroxide. Although not explicitly important, many materials are evaluated based on the lithium oxide content in them. Lithium oxide has a molecular formula as Li2O. In this short piece of article, let us learn more about the lithium oxide formula, its properties, its chemical structure and uses.
Lithium Oxide Properties
| Lithium Oxide Properties | |
| Name | Lithium Oxide |
| Also Known as | Lithia |
| Appearance | White Solid |
| Molecular Formula | Li2O |
| Melting Point | 1570 °C |
| Boiling Point | 2,600 °C |
| Density | 2.013 g/cm3 |
| Molar Mass | 29.88 g/mol |
| Solubility in Water | Reacts violently with water to form LiOH |
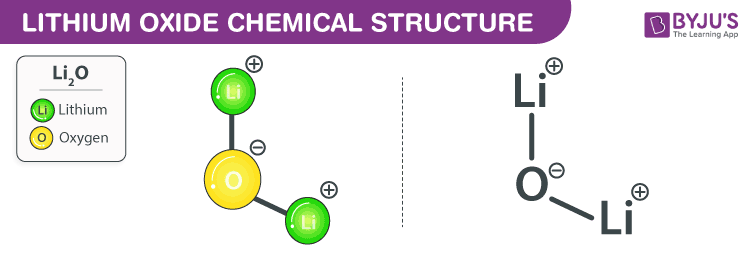
Lithium Oxide Chemical Structure
Lithium Oxide Uses
- Used as a flux in ceramic glazes
- Used as a thickening agent in the manufacture of greases
- Used as a coolant in nuclear reactors
To learn more about such chemistry topics register to BYJU’S now!
Comments