The algebraic equations which are valid for all values of variables in them are called algebraic identities. They are also used for the factorization of polynomials. In this way, algebraic identities are used in the computation of algebraic expressions and solving different polynomials. You have already learned about a few of them in the junior grades. In this article, we will recall them and introduce you to some more standard algebraic identities, along with examples.
Standard Algebraic Identities List
All the standard Algebraic Identities are derived from the Binomial Theorem, which is given as:
Some Standard Algebraic Identities list are given below:
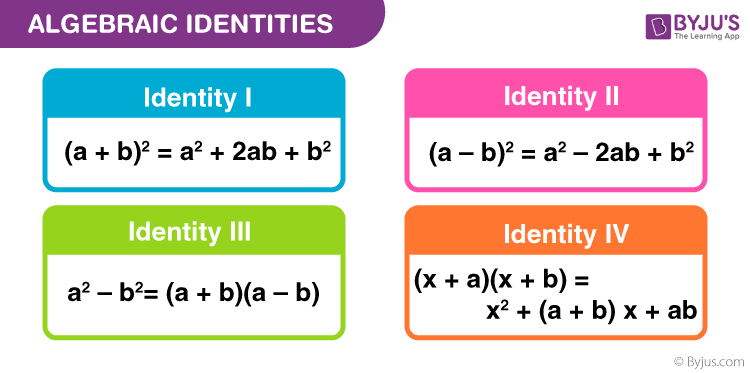
Identity I: (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
Identity II: (a – b)2 = a2 – 2ab + b2
Identity III: a2 – b2= (a + b)(a – b)
Identity IV: (x + a)(x + b) = x2 + (a + b) x + ab
Identity V: (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
Identity VI: (a + b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3ab (a + b)
Identity VII: (a – b)3 = a3 – b3 – 3ab (a – b)
Identity VIII: a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc = (a + b + c)(a2 + b2 + c2 – ab – bc – ca)
Solved Examples of Algebraic Identities
Example 1:
Find the product of (x + 1)(x + 1) using standard algebraic identities.
Solution:
(x + 1)(x + 1) can be written as (x + 1)2. Thus, it is of the form Identity I where a = x and b = 1. So we have,
(x + 1)2 = (x)2 + 2(x)(1) + (1)2 = x2 + 2x + 1
Example 2:
Factorise (x4 – 1) using standard algebraic identities.
Solution:
(x4 – 1) is of the form Identity III where a = x2 and b = 1. So we have,
(x4 – 1) = ((x2)2– 12) = (x2 + 1)(x2 – 1)
The factor (x2 – 1) can be further factorised using the same Identity III where a = x and b = 1. So,
(x4 – 1) = (x2 + 1)((x)2 –(1)2) = (x2 + 1)(x + 1)(x – 1)
Eample 3:
Factorise 16x2 + 4y2 + 9z2 – 16xy + 12yz – 24zx using standard algebraic identities.
Solution:
16x2 + 4y2 + 9z2– 16xy + 12yz – 24zx is of the form Identity V. So we have,
16x2 + 4y2 + 9z2 – 16xy + 12yz – 24zx = (4x)2 + (-2y)2 + (-3z)2 + 2(4x)(-2y) + 2(-2y)(-3z) + 2(-3z)(4x)= (4x – 2y – 3z)2 = (4x – 2y – 3z)(4x – 2y – 3z)
Example 4:
Expand (3x – 4y)3 using standard algebraic identities.
Solution:
(3x– 4y)3 is of the form Identity VII where a = 3x and b = 4y. So we have,
(3x – 4y)3 = (3x)3 – (4y)3– 3(3x)(4y)(3x – 4y) = 27x3 – 64y3 – 108x2y + 144xy2
Example 5:
Factorize (x3 + 8y3 + 27z3 – 18xyz) using standard algebraic identities.
Solution:
(x3 + 8y3 + 27z3 – 18xyz)is of the form Identity VIII where a = x, b = 2y and c = 3z. So we have,
(x3 + 8y3 + 27z3 – 18xyz) = (x)3 + (2y)3 + (3z)3 – 3(x)(2y)(3z)= (x + 2y + 3z)(x2 + 4y2 + 9z2 – 2xy – 6yz – 3zx)
To learn more about algebraic identities, download BYJU’S The Learning App.

Frequently Asked Questions on Algebraic Identities
What are the three algebraic identities in Maths?
The three algebraic identities in Maths are:
Identity 1: (a+b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab
Identity 2: (a-b)2 = a2 + b2 – 2ab
Identity 3: a2 – b2 = (a+b) (a-b)
What is the difference between an algebraic expression and identities?
An algebraic expression is an expression which consists of variables and constants. In expressions, a variable can take any value. Thus, the expression value can change if the variable values are changed. But algebraic identity is equality which is true for all the values of the variables.
How to verify algebraic identity?
The algebraic identities are verified using the substitution method. In this method, substitute the values for the variables and perform the arithmetic operation. Another method to verify the algebraic identity is the activity method. In this method, you would need a prerequisite knowledge of Geometry and some materials are needed to prove the identity.
What is the use of algebraic identities?
Algebraic identities are used to solve the algebraic expression or polynomial faster. It makes the calculation easier.
Give the algebraic identities which help to solve the factorization problems?
The algebraic identities which help to solve the factorization problems are:
(a+b)(a-b) = a2 – b2
(x+a)(x+b) = x2 + x(a+b) + ab.
Is every equation an identity?
The answer is No. Not every equation is considered as an identity. But we can say, every identity is an equation.
Is the equation 2(a+1) = 2a + 2 an identity?
Yes, the equation 2(a+1) = 2a + 2 is an identity. Because, if we substitute any values in the place of “a”, the equation becomes equal.
I.e., 2(1+1) = 2(1) + 2 ⇒ 4 = 4
2(2+1) = 2(2) + 2 ⇒ 6 = 6
2(3+1) = 2(3) + 2 ⇒ 8 = 8, and so on.
Write the expression 103 × 97 in terms of an algebraic identity.
The expression 103 × 97 is written as (100 + 3) (100 – 3)
Here, a = 100 and b = 3.
Hence, 103 × 97 = (100 + 3) (100 – 3) = 1002 – 32.
Therefore, the given expression can also be written as : (100 + 3) (100 – 3) = 1002 – 32.

Hi Team Byjus nice work I love reading with Byjus
this is very good to know that a live chat is very fast and a positive response nice work 👍
I like to read and l hope that the byjus app help me to read
It is very helpful
I also thank to byjus team and I love read with byjus they has excellent method to explain chapter
Thankyou for these “All Algebraic Identities” . It proved very much helpful for me .
I love to read with byjus they has excellent method to explain all concepts .
Thankyou for these “All Algebraic Identities” . It proved very helpful for me .
Thank you for for ‘all the algebraic Identities’ it help me a lot . Thank u again one more time
what is a cube minus b cube
a^3 – b^3 = (a – b)(a^2 + ab + b^2)
It is very helpful to us
Actually it was usful thank you so much
It is very useful for revision during exams
Byjus is best learning app