NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines is an essential study material for students who are seriously preparing for CBSE Class 12 board exam as well as graduate entrance examinations. Practising these exemplar solutions will help them in grasping the topics covered in Chapter 13 Amines completely and also will assist them in preparing notes which will come in handy during revision.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 are prepared by subject experts at BYJU’S. These exemplar solutions contain questions from NCERT Class 12 Exemplar book along with important questions, questions from sample papers and previous years’ question papers.
Download the PDF of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
1. Which of the following is a 3° amine?
(i) 1-methylcyclohexylamine
(ii) Triethylamine
(iii) tert-butylamine
(iv) N-methyl aniline
Solution:
Option (ii) is the answer.
2. The correct IUPAC name for CH2==CHCH2 NHCH3 is
(i) Allylmethylamine
(ii) 2-amino-4-pentene
(iii) 4-aminopent-1-ene
(iv) N-methylprop-2-en-1-amine
Solution:
Option (iv) is the answer.
3. Amongst the following, the strongest base in aqueous medium is ____________.
(i) CH3NH2
(ii) NCCH2NH2
(iii) (CH3)2 NH
(iv) C6H5NHCH3
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
4. Which of the following is the weakest Brönsted base?

Solution:
Option (A) is the answer.
5. Benzylamine may be alkylated as shown in the following equation :
C6H5CH2NH2 + R—X → C6H5CH2NHR
Which of the following alkyl halides is best suited for this reaction through
SN1 mechanism?
(i) CH3Br
(ii) C6H5Br
(iii) C6H5CH2Br
(iv) C2H5 Br
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
6. Which of the following reagents would not be a good choice for reducing an
aryl nitro compound to an amine?
(i) H2 (excess)/Pt
(ii) LiAlH4 in ether
(iii) Fe and HCl
(iv) Sn and HCl
Solution:
Option (ii) is the answer.
7. To prepare a 1° amine from an alkyl halide with simultaneous addition
of one CH2 group in the carbon chain, the reagent used as a source of nitrogen
is ___________.
(i) Sodium amide, NaNH2
(ii) Sodium azide, NaN3
(iii) Potassium cyanide, KCN
(iv) Potassium phthalimide, C6H4(CO)2N–K+
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
8. The source of nitrogen in Gabriel synthesis of amines is _____________.
(i) Sodium azide, NaN3
(ii) Sodium nitrite, NaNO2
(iii) Potassium cyanide, KCN
(iv) Potassium phthalimide, C6H4(CO)2N–K+Solution:
Option (iv) is the answer.
9. Amongst the given set of reactants, the most appropriate for preparing 2°
amine is _____.
(i) 2° R—Br + NH3
(ii) 2° R—Br + NaCN followed by H2/Pt
(iii) 1° R—NH2 + RCHO followed by H2/Pt
(iv) 1° R—Br (2 mol) + potassium phthalimide followed by H3O+/heat
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
10. The best reagent for converting 2–phenylpropanamide into
2-phenylpropanolamine is _____.
(i) excess H2
(ii) Br2 in aqueous NaOH
(iii) iodine in the presence of red phosphorus
(iv) LiAlH4 in ether
Solution:
Option (iv) is the answer.
11. The best reagent for converting 2-phenylpropanamide into 1- phenylethanamine is ____.
(i) excess H2/Pt
(ii) NaOH/Br2
(iii) NaBH4/methanol
(iv) LiAlH4/ether
Solution:
Option (ii) is the answer.
12. Hoffmann Bromamide Degradation reaction is shown by __________.
(i) ArNH2
(ii) ArCONH2
(iii) ArNO2
(iv) ArCH2NH2Solution:
Option (ii) is the answer.
13. The correct increasing order of basic strength for the following compounds is
_________.

(i) II < III < I
(ii) III < I < II
(iii) III < II < I
(iv) II < I < III
Solution:
Option (iv) is the answer.
14. Methylamine reacts with HNO2
to form _________.
(i) CH3—O—N==O
(ii) CH3—O—CH3
(iii) CH3OH
(iv) CH3CHO
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
15. The gas evolved when methylamine reacts with nitrous acid is __________.
(i) NH3
(ii) N2
(iii) H2
(iv) C2H6
Solution:
Option (ii) is the answer.
16. In the nitration of benzene using a mixture of conc. H2SO4
and conc. HNO3, the species which initiates the reaction is __________.
(i) NO2
(ii) NO+
(iii) NO2+
(iv) NO2–
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
17. Reduction of aromatic nitro compounds using Fe and HCl gives __________.
(i) aromatic oxime
(ii) aromatic hydrocarbon
(iii) aromatic primary amine
(iv) aromatic amide
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
18. The most reactive amine towards dilute hydrochloric acid is ___________.
Solution:

Solution:
Option (ii) is the answer.
19. Acid anhydrides on reaction with primary amines give ____________.
(i) amide
(ii) imide
(iii) secondary amine
(iv) imine
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer
20. The reaction Ar + N2Cl– → )Cu/HCl)– ArCl + N2 + CuCl is named as _________.
(i) Sandmeyer reaction
(ii) Gatterman reaction
(iii) Claisen reaction
(iv) Carbylamine reaction
Solution:
Option (ii) is the answer.
21. The best method for preparing primary amines from alkyl halides without
changing the number of carbon atoms in the chain is
(i) Hoffmann Bromamide reaction
(ii) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
(iii) Sandmeyer reaction
(iv) Reaction with NH3
Solution:
Option (ii) is the answer.
22. Which of the following compound will not undergo an azo coupling reaction
with benzene diazonium chloride.
(i) Aniline
(ii) Phenol
(iii) Anisole
(iv) NitrobenzeneSolution:
Option (iv) is the answer.
23. Which of the following compounds is the weakest Brönsted base?
Solution:

Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
24. Among the following amines, the strongest Brönsted base is __________.

Solution;
Option (iv) is the answer.
25. The correct decreasing order of basic strength of the following species is _______. H2O, NH3, OH–, NH2–
(i) NH2– > OH – > NH3 > H2O
(ii) OH– > NH2– > H2O > NH3
(iii) NH3 > H2O > NH2– > OH–
(iv) H2O > NH3> OH– > NH2–
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
26. Which of the following should be most volatile?

(i) II
(ii) IV
(iii) I
(iv) III
Solution:
Option (ii) is the answer.
27. Which of the following methods of preparation of amines will not give the same number
of carbon atoms in the chain of amines as in the reactant?
(i) The reaction of nitrite with LiAlH4.
(ii) The reaction of the amide with LiAlH4
followed by treatment with water.
(iii) Heating alkyl halide with potassium salt of phthalimide followed by
hydrolysis.
(iv) Treatment of amide with bromine in the aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide.
Solution:
Option (iv) is the answer.
II. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-II)
Note: In the following questions, two or more options may be correct.
28. Which of the following cannot be prepared by Sandmeyer’s reaction?
(i) Chlorobenzene
(ii) Bromobenzene
(iii) Iodobenzene
(iv) Fluorobenzene
Solution:
Option (iii) and (iv) are the answers.
29. Reduction of nitrobenzene by which of the following reagent gives aniline?
(i) Sn/HCl
(ii) Fe/HCl
(iii) H2-Pd
(iv) Sn/NH4OH
Solution;
Option (i), (ii) and (iii) are the answers.
30. Which of the following species are involved in the carbylamine test?
(i) R—NC
(ii) CHCl3
(iii) COCl2
(iv) NaNO2 + HCl
Solution:
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers.
31. The reagents that can be used to convert benzene diazonium chloride to
benzene are __________.
(i) SnCl2/HCl
(ii) CH3CH2OH
(iii) H3PO2
(iv) LiAlH4
Solution:
Option (ii) and (iii) are the answers.
32. The product of the following reaction is __________.

Solution:
Option (A) and (B) is the answer.
33. Arenium ion involved in the bromination of aniline is __________.

Solution:
Option (i), (ii) and (iii) are the answers.
34. Which of the following amines can be prepared by Gabriel synthesis?
(i) Isobutyl amine
(ii) 2-Phenylethylamine
(iii) N-methyl benzylamine
(iv) Aniline
Solution:
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers.
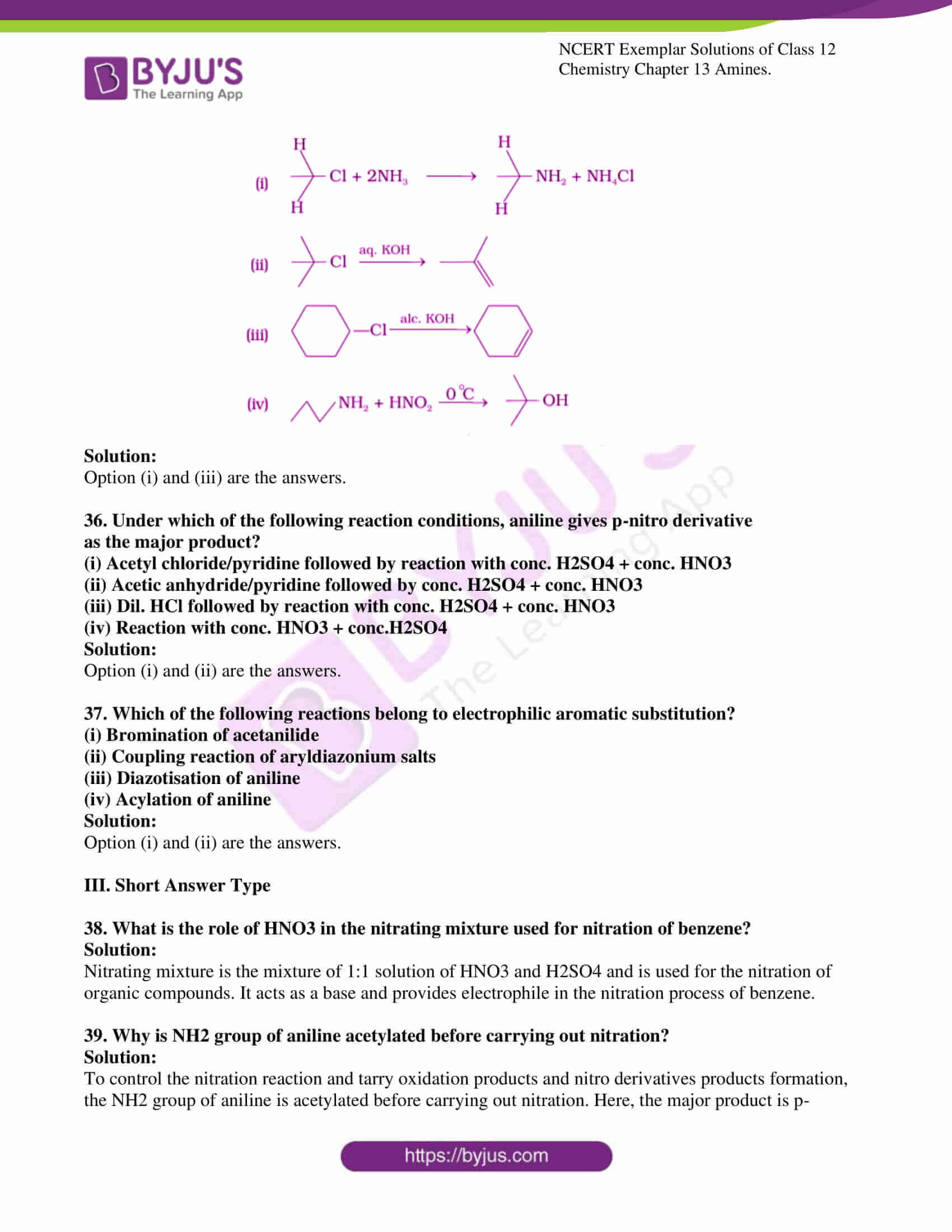
35. Which of the following reactions is correct?

Solution:
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers.
36. Under which of the following reaction conditions aniline gives p-nitro derivative
as the major product?
(i) Acetyl chloride/pyridine followed by reaction with conc. H2SO4 + conc. HNO3
(ii) Acetic anhydride/pyridine followed by conc. H2SO4 + conc. HNO3
(iii) Dil. HCl followed by reaction with conc. H2SO4 + conc. HNO3
(iv) Reaction with conc. HNO3 + conc.H2SO4
Solution:
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers.
37. Which of the following reactions belong to electrophilic aromatic substitution?
(i) Bromination of acetanilide
(ii) Coupling reaction of aryldiazonium salts
(iii) Diazotisation of aniline
(iv) Acylation of aniline
Solution:
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers.
III. Short Answer Type
38. What is the role of HNO3 in the nitrating mixture used for nitration of benzene?
Solution:
The nitrating mixture is the mixture of a 1:1 solution of HNO3 and H2SO4 and is used for the nitration of organic compounds. It acts as a base and provides electrophile in the nitration process of benzene.
39. Why is the NH2 group of aniline acetylated before carrying out nitration?
Solution:
To control the nitration reaction and tarry oxidation products and nitro derivatives products formation, the NH2 group of aniline is acetylated before carrying out nitration. Here, the major product is p-nitroaniline.
40. What is the product when C6H5CH2NH2 reacts with HNO2?
Solution:
C6H5CH2NH2 reacts with HNO2 to form unstable diazonium salt, which in turn gives alcohol.
C6H5CH2NH2 + HNO2 → C6H5CH2OH + N2 + H2O
41. What is the best reagent to convert nitrile to primary amine?
Solution:
The best reagents for the conversion of nitrile to primary amine are LiAlH4 and Sodium/Alcohol. By reduction, the nitriles can be converted into a corresponding primary amine.
42. Give the structure of ‘A’ in the following reaction.

Solution:

The product formed in this chemical reaction is 3-Methylnitrobenzene.
43. What is Hinsberg reagent?
Solution:
Benzenesulphonyl chloride, or C6H5SOCl, is commonly known as Hinsberg’s reagent. Hinsberg’s reagent is be used to distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
44. Why is benzene diazonium chloride not stored and used immediately after its preparation?
Solution:
Benzene diazonium chloride is highly soluble in water at high temperature and is itself very stable at low temperature. It should be used immediately after its preparation as it is unstable.
45. Why does the acetylation of —NH2 group of aniline reduce its activating effect?
Solution:
The acetylation of —NH2 group of aniline reduces its activating effect because the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen of acetanilide interacts with the oxygen atom due to resonance.
46. Explain why MeNH2 is a stronger base than MeOH?
Solution:
MeNH2 is a stronger base than MeOH because of the lower electronegativity and the presence of the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom in MeNH2.
47. What is the role of pyridine in the acylation reaction of amines?
Solution:
The activating effect of –NH2 group can be controlled by protecting the -NH2 group by acetylation with acetic anhydride in the presence of pyridine and then carrying out the desired substitution followed by hydrolysis of the substituted amide to the substituted amine. Pyridine is a base that is used to get rid of HCl as a side product from the reaction.
48. Under what reaction conditions (acidic/basic), the coupling reaction of aryldiazonium chloride with aniline is carried out?
Solution:
This reaction is carried out in a mild basic medium. This is an electrophilic substitution reaction. Aryldiazonium chloride reacts with aniline to form a yellow dye of p-Aminoazobenzene.
49. Predict the product of the reaction of aniline with bromine in a non-polar solvent such as CS2.
Solution:
The products formed in the reaction of aniline with bromine in a non-polar solvent such as CS2 are 4-Bromoaniline and 2-Bromoaniline, where 4-Bromoaniline is the major product.
50. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of dipole moment.
CH3CH2CH3, CH3CH2NH2, CH3CH2OH
Solution:
CH3CH2CH3 < CH3CH2NH2 < CH3CH2OH
The dipole moment of CH3CH2OH is greater than that of CH3CH2NH2. CH3CH2CH3 has the least dipole moment among the three given compounds because it is almost a non-polar molecule.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines
In this chapter, students will learn about a functional group called Amines. An amine contains a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. After studying this chapter, students will get familiar with how to classify amines as primary, secondary and tertiary.
Important Concepts Covered in NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines
- Structure of Amines
- Classification
- Nomenclature
- Preparation of Amines
- Physical Properties
- Chemical Reactions
- Method of Preparation of Diazonium Salts
- Physical Properties
- Chemical Reactions
- Importance of Diazonium Salts in the Synthesis of Aromatic Compounds.
In order to solve higher-order thinking questions from this chapter, students are advised to solve the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines provided in this article.
Why Opt for BYJU’S?
With BYJU’S NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry, students can easily plan their studies and understand the concepts at their own pace. Additionally, as we believe that students should be supported extensively in their education journey, we provide the assistance of some of the best subject experts in the country who can constantly help and guide them to learn the subject in a more simplified and conceptual manner.
As part of an overall package, we also keep track of the progress that each student makes. After assessing their performance, regular feedback will be given. Also, we have a responsive support team in place to clear their doubts. Students can drop in queries regarding not only Chemistry but also other subjects, including Physics, Biology and Maths.
Watch videos on Class 12 Chapter 13 Amines for comprehensive learning of this chapter. For more interesting study materials for Class 12, subscribe to BYJU’S YouTube channel or download BYJU’S – The Learning App.











Comments