NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 – Electricity and Circuits aid students in effective preparation for the annual exams. The solutions are prepared by expert faculty having vast knowledge in their respective field. Students aspiring to secure high marks in the final examination are advised to practise the solutions on a regular basis. To learn the concepts in a better way, students can download the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions PDF for free and practise offline as well.
Chapter 12 – Electricity and Circuits, deals with circuits and direction, in which the current flows, and provides answers to all the questions related to each and every concept covered in this chapter. The solutions have been designed in a unique and simple manner so that students can understand the concepts clearly. NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions are provided in PDF in the link below for students to download easily.
Download the PDF of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 – Electricity and Circuits
Access Answers to NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 – Electricity and Circuits
Multiple Choice Questions:
1. Choose from the options a, b, c and d given in fig 12.1, which shows the correct direction of the current.

Solution:
(b): In an electric circuit, the direction of current flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the electric cell.
2. Choose the incorrect statement.
(a) A switch is the source of electric current in a circuit.
(b) A switch helps to complete or break the circuit.
(c) A switch helps us to use electricity as per our requirement.
(d) When the switch is open, there is an air gap between its terminals.
Solution:
(a): A switch is the source of electric current in a circuit.
An electric cell is the source of electric current in a circuit, not the switch.
3. In an electric bulb, light is produced due to the glowing of
(a) the glass case of the bulb
(b) the thin filament
(c) the thick wires supporting the filament
(d) gases inside the glass case of the bulb.
Solution:
(b): the thin filament
4. In the following arrangement shown in fig 12.2, the bulb will not glow if the ends A and B are connected with

(a) A steel spoon
(b) A metal clip
(c) A plastic clip
(d) A copper wire
Solution:
(c): A plastic clip
A plastic clip is a poor conductor of electricity; it is an insulator.
5. In the circuit shown in fig 12.3, when the switch is moved to the ‘ON’ position,

(a) bulb A will glow first
(b) bulb B will glow first
(c) bulb C will glow first
(d) all bulbs will glow together
Solution:
(d): all bulbs will glow together
As soon as the circuit gets completed, the current is found at every point in the circuit instantly.
6. Filament of a torch bulb is
(a) a metal case
(b) metal tip at the centre of the base
(c) two thick wires
(d) a thin wire
Solution:
(d): a thin wire
7. Paheli is running short of connecting wires. To complete an electric circuit, she may use a
(a) glass bangle
(b) thick thread
(c) rubber pipe
(d) steel spoon
Solution:
(d): steel spoon
Steel spoon is a good conductor of electricity. Hence, we use a steel spoon to complete an electric circuit.
8. In which of the following circuits, A, B and C, given in fig 12.4, will the cell be used up very rapidly?

Solution:
In circuit A, the cell will be used up very rapidly.
9. Fig. 12.5 shows a bulb with its different parts marked as 1,2,3,4, and 5. Which of them labels the terminals of the bulb?

Solution:
Labels 3 and 4 are the terminals of the bulb.
Short Answer Questions:
10. You are provided with a bulb, a cell, a switch and some connecting wires. Draw a diagram to show the connections between them to make the bulb glow.
Solution:

11. Will the bulb glow in the circuit shown in fig 12.6? Explain.

Solution:
No, the bulb will not glow in this circuit because the switch is open, and the circuit is broken. Current flows only in a closed circuit.
12. An electric bulb is connected to a cell through a switch, as shown in fig 12.7. When the switch is brought in the ‘ON’ position, the bulb does not glow. What could be the possible reason/s for it? Mention any two of them.

Solution:
When the switch is brought in ‘ON’ position, the bulb does not glow. There could be the following reasons for it:
(i) Loose connections.
(ii) Connecting wires are broken.
(iii) The cell is a used one.
(iv) The bulb is fused.
13. A torch requires 3 cells. Show the arrangement of the cells, with a diagram, inside the torch so that the bulb glows.
Solution:

14. When the chemicals in the electric cell are used up, the electric cell stops producing electricity. The electric cell is then replaced with a new one. In the case of rechargeable batteries (such – as the type used in mobile phones, cameras and inverters), they are used again and again. How?
Solution:
Rechargeable batteries can be recharged by providing them with appropriate current through secondary cells or storage cells.
15. Paheli connected two bulbs to a cell, as shown in fig 12.8,

She found that the filament of bulb B is broken. Will the bulb A glow in this circuit? Give reason.
Solution:
No, the bulb will not glow in this circuit as the filament of bulb B is broken. Due to the breakage in the circuit current does not flow.
16. Why do bulbs have two terminals?
Solution:
A bulb has a tiny thin wire called filament which consists of two terminals to connect the filament within the circuit so that current can pass through it.
17. Which of the following arrangement, A, B, C and D, given in fig 12.9, should not be set up? Explain why.
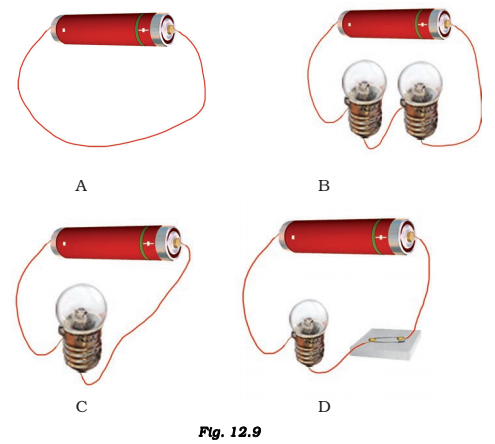
Solution:
Arrangement A should not be set up since the current flows from a negative terminal to the positive terminal, which will exhaust the cell very quickly as the large current will flow through it.
18. A fused bulb does not glow. Why?
Solution:
A fused bulb does not glow since the filament inside it is broken, and the circuit is incomplete.
19. Paheli wanted to glow a torch bulb using a cell. She could not get connecting wires; instead, she got two strips of aluminium foil. Will she succeed? Explain how.
Solution:
Yes, Paheli will succeed. Aluminium foil being a good conductor of electricity, it can be used as connecting wires for the supply of electricity.
Long Answer Questions:
20. Boojho has a cell and a single piece of connecting wire. Without cutting the wire in two, will he be able to make the bulb glow? Explain with the help of a circuit diagram.
Solution:
Yes, he can succeed in getting the bulb to glow by using the given arrangements.
He can connect by connecting to a positive terminal of the cell directly from the second terminal of the bulb, as given in the figure. In this way, the circuit will get completed without using another piece of connecting wire.

21. Fig 12.10 A and B show a bulb connected to a cell in two different ways.

(i) What will be the direction of the current through the bulb in both cases (Q to P or P to Q)?
(ii) Will the bulb glow in both cases?
(iii) Does the brightness of the glowing bulb depend on the direction of current through it?
Solution:
(i) In the case of Q to P: the current flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal.
In the case of P to Q: the current flows from the negative terminal to the positive terminal.
(ii) Yes, the bulb will glow in both cases as the current is flowing and the circuit is complete.
(iii) No, the brightness of the glowing bulb does not depend on the direction of the current through it. The amount of current and voltage in the circuit decides the brightness of the glowing blub.
22. Think of six activities which use electric current. Also, name the devices used to perform the activity.

Solution:
| Activity you perform | Device | |
| Example | Get light | Torch |
| Make toast | Toaster | |
| Heat water | Geyser | |
| Listen to music | CD player | |
| Watch movies | Laptop/TV | |
| Cook food | Microwave/Heater |
23. A torch is not functioning, though contact points in the torch are in working condition. What can be the possible reasons for this? Mention any three.
Solution:
The possible reasons for the torch, not functioning could be
(i) The switch may be faulty.
(ii) The cells may not be placed in the correct order.
(iii) The cells may have been used up.
(iv) The filament may be fused in the bulb.










Comments