Flashcards for NEET Chemistry are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for the chapter “Equilibrium”. These flashcards are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. These are helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams during last-minute revision. It covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Chemistry.
Download PDF of NEET Chemistry Flashcards for Equilibrium
|
Name of the NEET Sub-section |
Topic |
Flashcards Helpful for |
|
Chemistry |
Equilibrium |
NEET Exams |
|
Equilibrium |
|
|
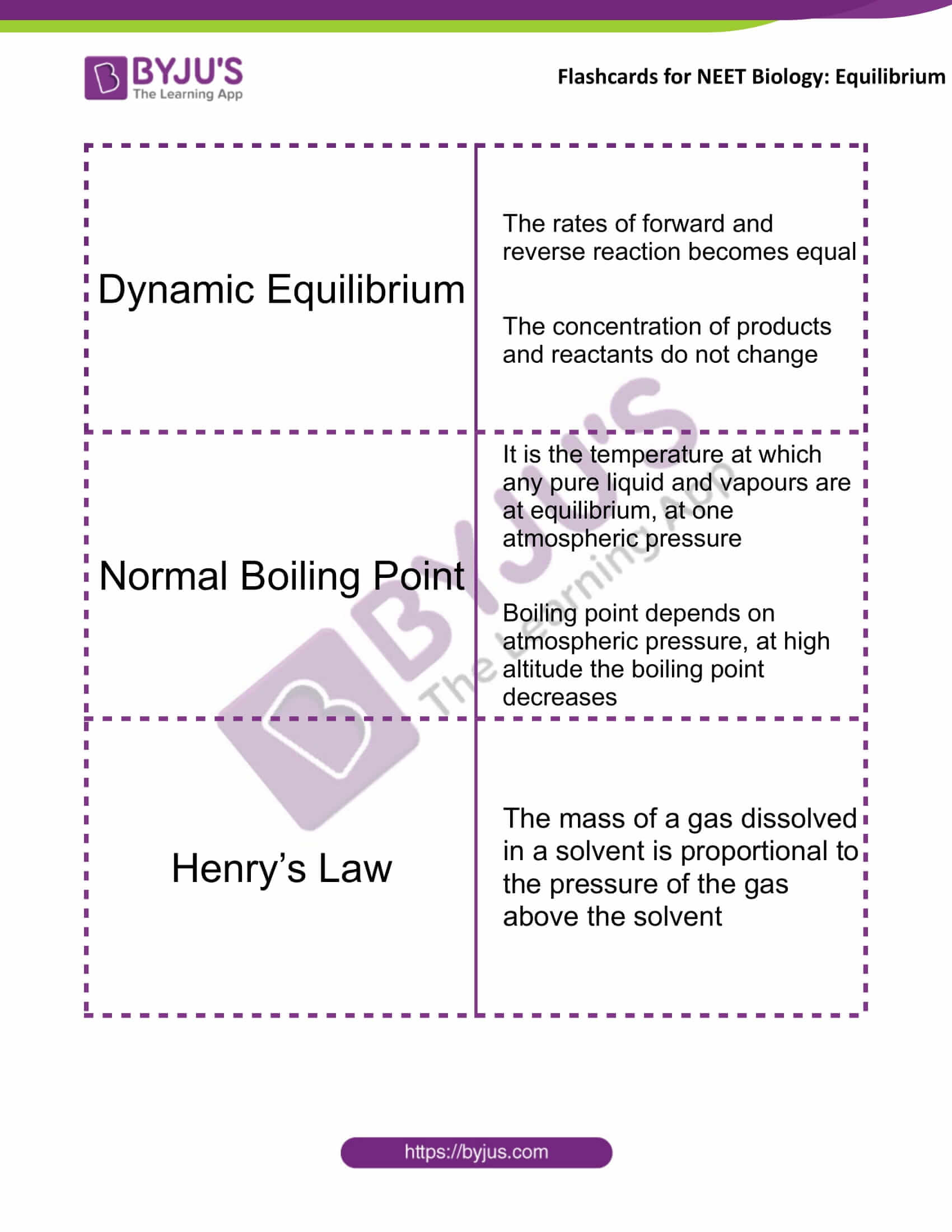
Dynamic Equilibrium |
The rates of forward and reverse reaction become equal The concentration of products and reactants do not change |
|
Normal Boiling Point |
It is the temperature at which any pure liquid and vapours are at equilibrium, at one atmospheric pressure Boiling point depends on atmospheric pressure, at high altitudes the boiling point decreases |
|
Henry’s Law |
The mass of a gas dissolved in a solvent is proportional to the pressure of the gas above the solvent |
|
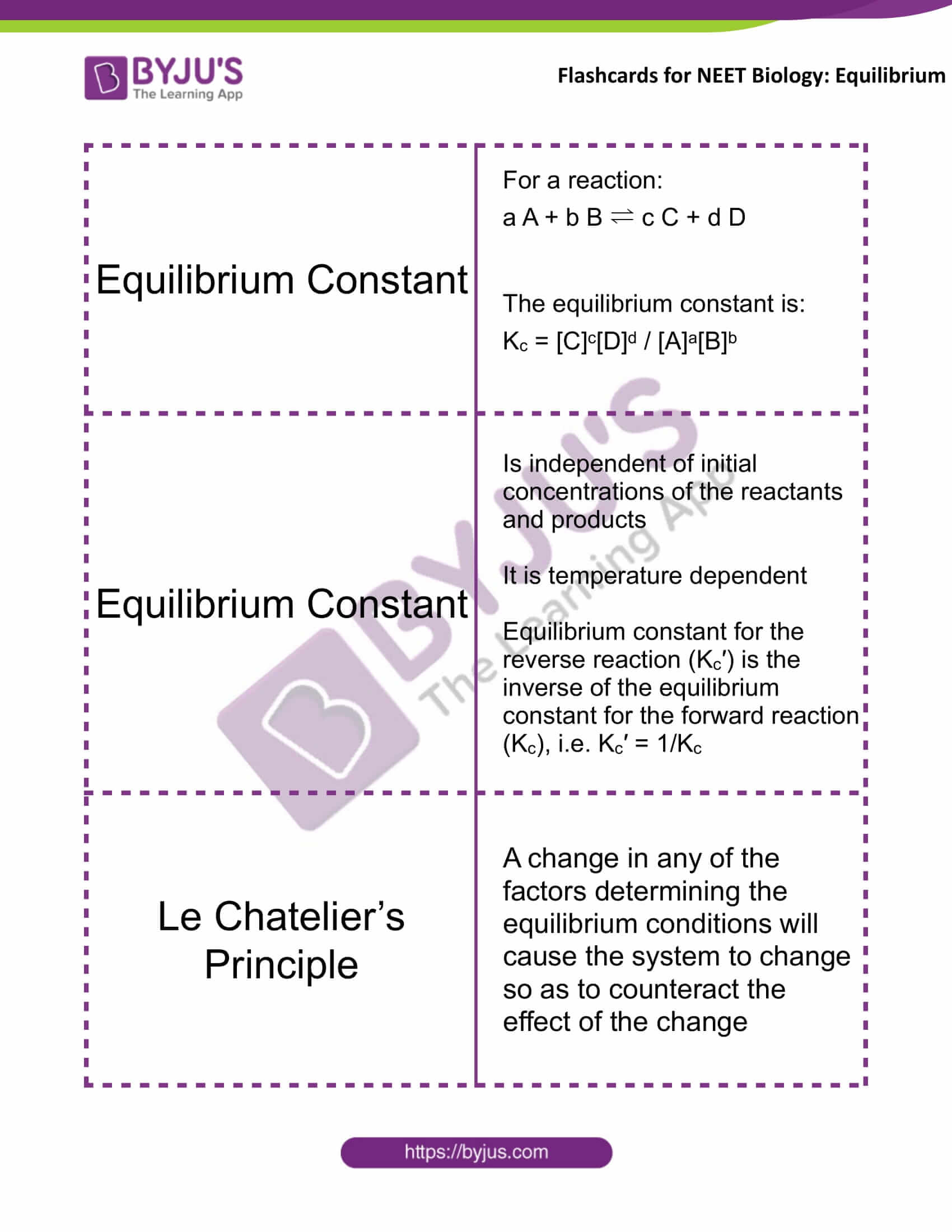
Equilibrium Constant |
For a reaction: a A + b B ⇌ c C + d D The equilibrium constant is: Kc = [C]c[D]d / [A]a[B]b |
|
Equilibrium Constant |
Is independent of initial concentrations of the reactants and products It is temperature-dependent The equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction (Kc′) is the inverse of the equilibrium constant for the forward reaction (Kc), i.e. Kc′ = 1/Kc |
|
Le Chatelier’s Principle |
A change in any of the factors determining the equilibrium conditions will cause the system to change so as to counteract the effect of the change |
|
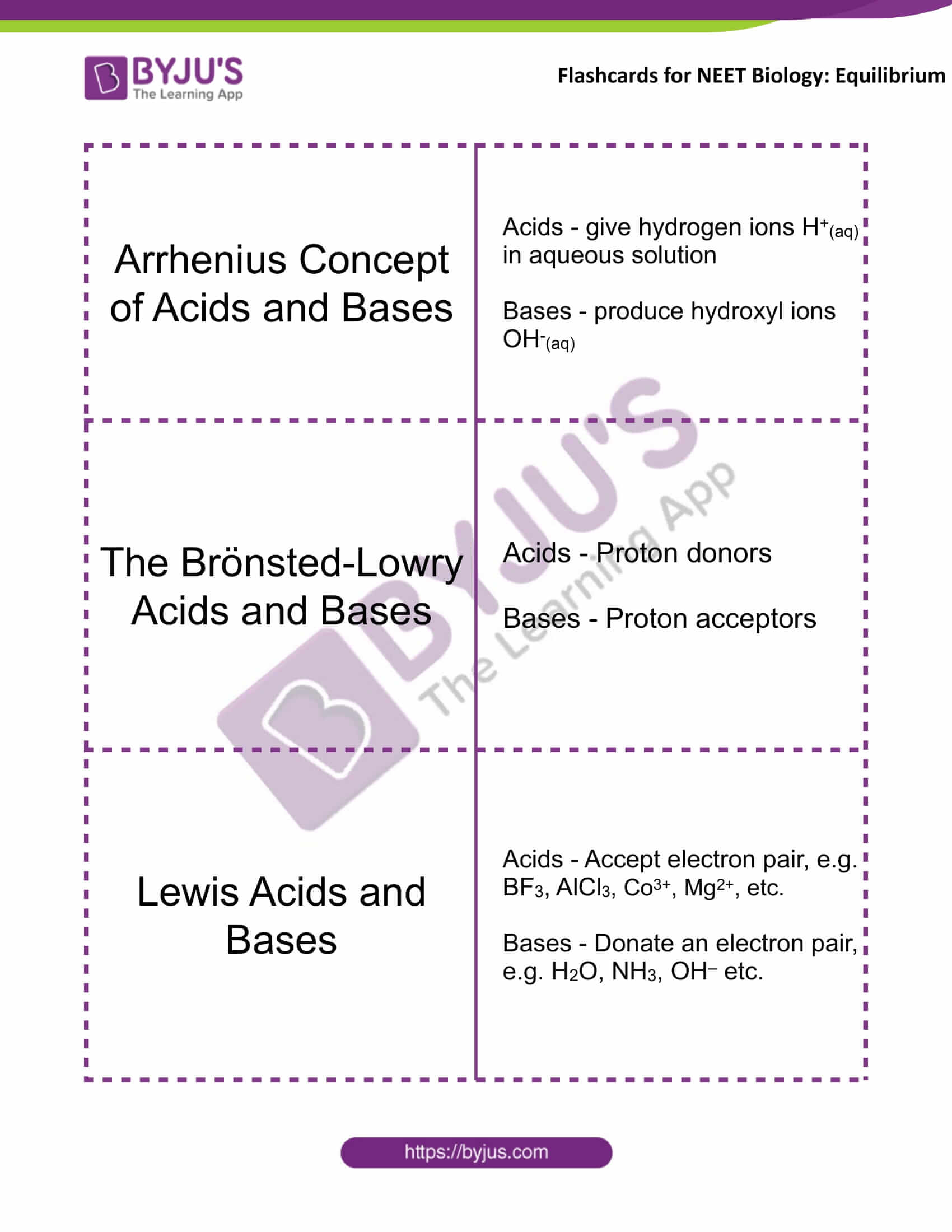
Arrhenius Concept of Acids and Bases |
Acids – give hydrogen ions H+(aq) in an aqueous solution Bases – produce hydroxyl ions OH–(aq) |
|
The Brönsted-Lowry Acids and Bases |
Acids – Proton donors Bases – Proton acceptors |
|
Lewis Acids and Bases |
Acids – Accept electron pair, e.g. BF3, AlCl3, Co3+, Mg2+, etc. Bases – Donate an electron pair, e.g. H2O, NH3, OH– etc. |
|
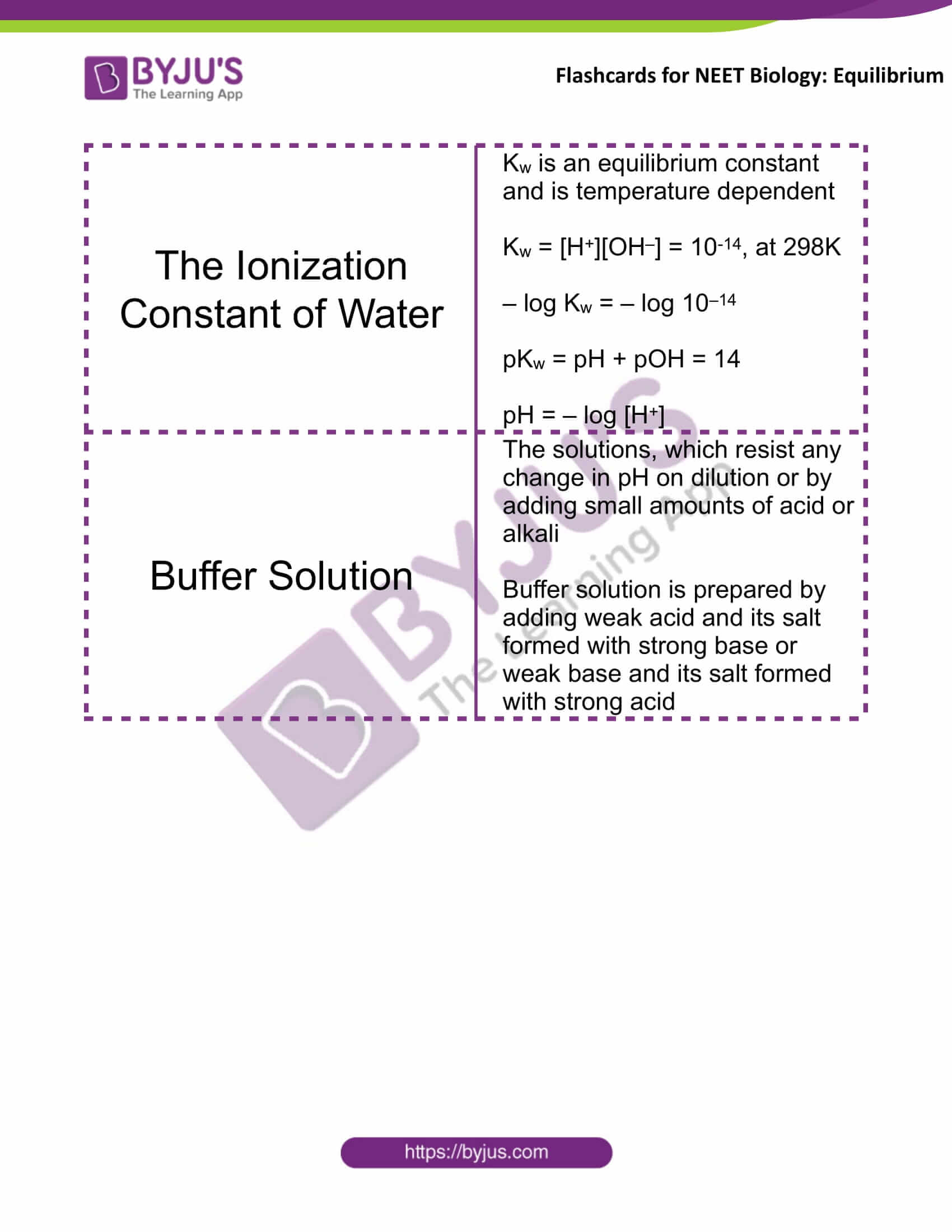
The Ionization Constant of Water |
Kw is an equilibrium constant and is temperature-dependent Kw = [H+][OH–] = 10-14, at 298 K – log Kw = – log 10–14 pKw = pH + pOH = 14 pH = – log [H+] |
|
Buffer Solution |
The solutions, which resist any change in pH on dilution or by adding small amounts of acid or alkali A buffer solution is prepared by adding weak acid and its salt formed with strong base or a weak base and its salt formed with strong acid |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Chemistry, only at BYJU’S.
|
Also Check: |
Comments