Ketosis Definition
Ketosis means a metabolic state in our body that is characterized by detectable ketone levels. It takes place when the body does lacks sufficient carbohydrates to burn for energy. It instead burns fat, thus making ketones which can be used for fuel. Ketogenesis is the chemical process which generates those ketones.
Download the Complete Guide to NEET UG Prep
Download Now
Here, let’s understand the meaning of ketosis and ketogenesis in detail.
Table of Contents
- Ketogenesis – Definition
- Ketone Bodies
- Ketogenesis Pathway
- Ketogenesis Steps
- Significance of Ketogenesis
- Frequently Asked Questions
Ketogenesis – Definition
Ketogenesis is a catabolic pathway of metabolism. In this process, fatty acids and certain ketogenic amino acids are broken down to derive energy by alternative means. Ketone bodies are produced in the ketogenesis process.
Our body continuously produces ketone bodies in low amounts, but in certain cases like starving, when carbohydrates are present in less amount in diet, ketogenesis is preferred to compensate for the energy requirements.
Ketone bodies accumulated in an excess amount may lead to a condition called ketoacidosis, which may be fatal.
What are Ketone Bodies?
Ketone bodies Meaning
Fatty acids undergo 𝛽-oxidation in the liver mitochondria to generate a high amount of energy and form three compounds, that are known as “ketone bodies”. These ketone bodies are water-soluble and do not require lipoproteins for transportation across the membrane. Ketone bodies are lipid molecules having a carbonyl group attached to two -R groups.
The three ketone bodies formed are – Acetoacetate, D-3-hydroxybutyrate, and Acetone
Utilization of Ketone bodies
Ketone bodies can be transported easily from the liver to different tissues. The ketone bodies β-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate serve as significant sources of energy for outer tissues such as cardiac, skeletal muscle etc.
The tissues lacking mitochondria fail to utilize ketone bodies. Different reactions occur for metabolism to take place –
D-β-hydroxybutyrate gets oxidized to acetoacetate by D-β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase in the extrahepatic tissues. Acetoacetate gets activated to their coenzyme A ester by transfer of CoA from succinyl-CoA which is an intermediate of the citric acid cycle. It is a reaction which is catalyzed by the β-ketoacyl-CoA transferase. Then, thiolase cleaves acetoacetyl-CoA to produce acetyl-CoA that then enters the citric acid cycle. As a result, ketone bodies gets used as fuels in all the tissues. Exception is the liver, it is devoid of β-ketoacyl-CoA transferase.
Ketogenesis Pathway
Our body normally derives energy from stored carbohydrate by the process of glycogenolysis (glycogen → glucose) or from non-carbohydrate sources such as lactate by the process of gluconeogenesis.
Ketogenesis occurs continuously in a healthy individual, but under certain conditions, when there is an increased concentration of fatty acids or carbohydrate reserves are decreased, ketogenesis happens at a higher rate:
- Under low blood glucose level, e.g. during fasting or starvation
- On exhaustion of carbohydrate reserve, e.g. glycogen
- When there is insufficient insulin, e.g. Type-1 diabetes
All the main body parts such as the brain, skeletal muscles, heart, etc. can utilise the energy formed by ketogenesis.
Insufficient gluconeogenesis results in hypoglycemia and excessive production of ketone bodies resulting in a fatal condition called ketoacidosis.
Also see: Biochemical Pathways
Ketogenesis Steps
The ketogenesis process occurs primarily in the mitochondria of liver cells. Below are the steps in the process of ketogenesis:
- Transfer of fatty acids in mitochondria by carnitine palmitoyltransferase CPT-1
- 𝛽-oxidation of fatty acid to form acetyl CoA
- Acetoacetyl-CoA formation: 2 acetyl CoA form acetoacetyl CoA. The reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme thiolase
- 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) synthesis: the step is catalyzed by HMG-CoA synthase
- Acetoacetate formation: HMG-CoA is broken down to acetoacetate and acetyl-CoA by the action of HMG-CoA lyase
Acetoacetate thus produced forms other ketone bodies, acetone by decarboxylation and D-3-hydroxybutyrate by reduction
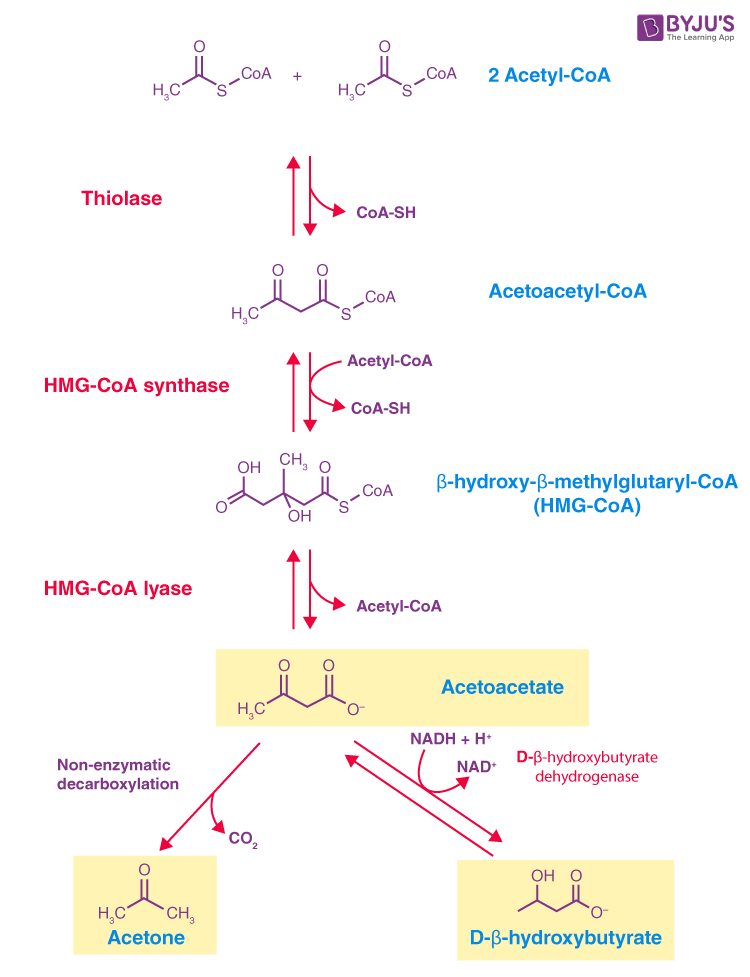
Liver, which produces ketone bodies, primarily in the mitochondria, cannot utilise it due to lack of an enzyme 𝛽-keto-acyl-CoA transferase.
Acetoacetate and D-3-hydroxybutyrate are used by the body to get energy. These ketone bodies are circulated out of the liver cell.
In the extrahepatic tissues, the following reactions occur:
- D-3-hydroxybutyrate is converted back to acetoacetate by 𝛽-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase
- Acetoacetate is converted back to acetyl-CoA by 𝛽-keto-acyl-CoA transferase
- Acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle (TCA or Kreb’s cycle) and produces 22 ATP molecules
- Acetone is excreted out
Ketogenesis process is regulated by Insulin. Hormones such as glucagon, thyroid hormones, catecholamines, cortisol increase ketogenesis rate by stimulating the breakdown of free fatty acids.
Significance of Ketogenesis
- Ketogenesis is used to get energy by the brain, heart and skeletal muscles under fasting condition
- The ketogenic diet (low-carb, fat-rich diet) is used these days to lose weight. The idea is to utilise excess fat stored in the body to get energy, but excess ketone bodies production can lead to various complications and ketoacidosis
- In ketoacidosis condition, the kidneys excrete extra ketone bodies with the water resulting in fluid loss
- Diabetic patients are greatly affected by ketoacidosis because insulin hormone is the main regulator of the process
- Symptoms of ketoacidosis include frequent urination, breath smelling like fruits or acetone, nausea, shortness of breath, fatigue, excessive thirst, etc.
- Level of ketone bodies present in the body can be tested by blood serum or urine sample analysis
Also Read:
Frequently Asked Questions on What is Ketogenesis?
Define ketone bodies.
Ketone bodies are water-soluble molecules; metabolites containing ketone groups which are produced from the fatty acids by the liver. It replaces glucose as the primary fuel of the brain in conditions when there is scarcity of glucose such as during extenuating exercise, fasting for long duration, diabetes etc.
What is Ketogenesis?
It is a biochemical phenomenon, which generates ketone bodies after disintegrating fatty acids and ketogenic amino acids.
What Is The Difference Between Ketosis And Ketogenesis?
Ketosis is the state wherein our body tends to produce ketones at detectable levels, ketogenesis, on the other hand, is a chemical phenomenon, which generates those ketones. Therefore, ketosis is caused as a result of ketogenesis while ketogenesis is initiated from a lack of glucose.
Where Does Ketogenesis Occur?
The process of ketogenesis mainly takes place in the mitochondria of cells of the liver. Here, fatty acids are supplied to mitochondria through carnitine palmitoyltransferase and disintegrated into acetyl CoA via beta-oxidation.

Thanks, I appreciate this a lot
I pray I will gain more knowledge here