NEET 2023 is approaching, and it is time to do thorough revisions and give your best for the entrance exam. This comprehensive session is based on the Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Atomic Structure for NEET 2023. Topics covered in this series are Bohr’s radius, the energy of radiation emitted, velocity of an electron, quantum number, Balmer series, de Broglie wavelength, and 3d orbital.
Question 1: What is Bohr’s radius of the 4th orbit of He+ in Å?
- 5.23 Å
- 3.23 Å
- 6.23 Å
- 4.23 Å
Answer: d) 4.23 Å
Explanation: rn = a° x n2/Z = .53 Å x (4)2/2 = .53 Å x 16/2 = 4.23 Å
Question 2: The energy of radiation emitted when an electron falls from n = 3 to n = 2 level in a hydrogen atom will be: (RH = 2.18 x 10–18 J atom–1)
- 0.3 x 10–18 J atom–1
- 3 x 10–18 J atom–1
- 0.03 x10–18 J atom–1
- 3 x 10–17 J atom–1
Answer: a) 0.3 x 10–18 J atom–1
Explanation:
ΔE = E [1/n12 − 1/n22 ] x Z2
= 2.18 x 10–18 [1/4 − 1/9] x 12
= 2.18 x 10–18 [(9 − 4)/36] x 1
= 2.18 x 10–18 x 5/36 = 0.3 x 10–18 J atom–1
Question 3: How fast does light travel in vacuum as compared to the velocity of an electron in Bohr’s first orbit of hydrogen atom?
- 13.7 times
- 67 times
- 137 times
- 97 times
Answer: c) 137 times
Explanation:
Vn = V0 x Z/n
⇒ Vn = V0 x 1/1
V1 = 2.18 x 106 ms−1
S = 3 x 108 ms−1
∴ (3×108) / (2.18 x 106) = 300 / 2.18 = 137 times
Question 4: The first emission lines of the hydrogen atomic spectrum in the Balmer series appear at:
- 5R/36 cm–1
- 3R/4 cm–1
- 7R/144 cm–1
- 9R/400 cm–1
Answer: a) 5R/36 cm–1
Explanation: The transition from n1 = 2 to n2 = 3 results in the first emission line in the atomic spectra of hydrogen in the Balmer series.
The wavenumber is given by the expression,
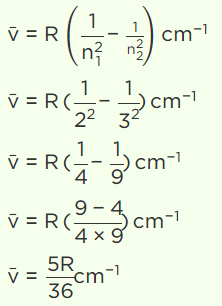
Thus, the first emission lines of the hydrogen atomic spectrum in the Balmer series appear at 5R/36 cm–1
Question 5: Quantum numbers are different quantities used to describe the electrons present in an atom. Each quantum number signifies a property. Identify the quantum number that determines the orientation of the orbital in space.
- Azimuthal quantum number
- Spin quantum number
- Magnetic quantum number
- Principal quantum number
Answer: c) Magnetic quantum number
Explanation: The magnetic quantum number represents the total number of orbitals in a subshell as well as their orientation. The symbol ‘ml‘ is used to represent it. This value represents the projection of the orbital’s angular momentum along a specific axis.
Question 6: Which one of the following about an electron occupying the 1s orbital in a hydrogen atom is incorrect?
(The Bohr radius is represented by a0)
- The total energy of the electron is maximum when it is at a distance a0 from the nucleus.
- The probability density of finding the electron is maximum at the nucleus.
- The electron can be found at a distance of 2a0 from the nucleus.
- The magnitude of the potential energy is double that of its kinetic energy on average.
Answer: a) The total energy of the electron is maximum when it is at a distance a0 from the nucleus.
Explanation: At a0 distance from the nucleus, the probability of finding an electron is maximum, and the total energy of the electron is minimum.
Question 7: What is the de Broglie wavelength of the electron accelerated at 400 V, approximately?
- 1.00 nm
- 0.12 nm
- 0.08 nm
- 0.06 nm
Answer: d) 0.06 nm
Explanation: Short method:
de Broglie wavelength (λ) = (12 − 3) / √V Å
⇒ λ = (12 − 3) / √400 Å
= (12 − 3) / 20 Å
= 0.6 Å
∴ λ = 0.06 nm
Long method:

Question 8: The uncertainty in the position of an electron is equal to its de Broglie wavelength. The minimum percentage error in its measurement of velocity under this circumstance will be approximate:
- 4
- 8
- 2
- 18
Answer: b) 8
Explanation: According to the question, uncertainty in the position of an electron is equal to its de Broglie wavelength.
∴ Δx = h / mv
Now, according to uncertainty principle, Δx * Δp = h / 4𝜋
As mentioned in the question, a minimum percent error is required.
So, mΔv * Δx = h / 4𝜋
By putting the value of Δx, we get Δv / v = 1 / 4𝜋
∴ % of error = Δv / v * 100 = 100 / 4𝜋 = 8
Question 9: From the following sets of quantum numbers, which state is possible?
(i) n = 0, l = 0, ml = 1, ms = +1/2
(ii) n = 2, l = 1, ml = 0, ms = –1/2
(iii) n = 2, l = 0, ml = 3, ms = +1/2
(iv) n = 3, l = 1, ml = 0, ms = –1/2
- (i), (ii), (iii)
- (ii) and (iv) are possible
- All are not possible
- All are possible
Answer: b) (ii) and (iv) are possible
Explanation: (i) Because the minimal value of n can only be 1 and not zero, the set of quantum numbers is not possible.
(ii) This set of quantum numbers is possible.
(iii) If the value of l is zero, then the value of ml should also start from zero and not 3.
(iv) This set of quantum numbers is also possible.
Question 10: When the 3d orbital is complete, the new electron will enter the:
- 4p orbital
- 4f orbital
- 4s orbital
- 4d orbital
Answer: a) 4p orbital
Explanation: The 4p orbital is the next shell to be filled after the 3d orbital, according to the Aufbau principle of electron filling in orbitals.
Question 11: What should be the maximum number of lines obtained in the spectrum, if the total number of energy levels is five?
- 10
- 6
- 4
- 2
Answer: a) 10
Explanation: Given, levels (l) = 5, n1 = 1, n2 = 5
∴ Maximum number of lines = ((n2 − n1)(n2 − n1 + 1)) / 2
= (Δn (Δn + 1)) / 2 = (4 x (4 + 1)) / 2 = (4 x 5) / 2 = 10
Question 12: We can distinguish two electrons occupying the same orbital by:
- Principal quantum number
- Azimuthal quantum number
- Magnetic quantum number
- Spin quantum number
Answer: d) spin quantum number
Explanation: The value of a spin quantum number can be either +1/2 or −1/2.
This helps in the differentiation of two electrons occupying the same orbital.
Question 13: In which quantum level does the electron jump in He+ ion to ground state if it is given an energy corresponding to 99% of the ionisation potential of He+ ion?
- 4
- 6
- 8
- 10
Answer: d) 10
Explanation: E ∝ 1/λ ∝ (1/n12 − 1/n22)
Here, ionisation potential = 99% (E), n1 = 1 and n2 = ?
∴ 99/100 = 1/1 − 1/n22
⇒ 1/n22 = 1/100
∴ n2 = 10
Question 14: The value of quantum numbers (n, l, m and s, respectively) for the valence electron of Rb (Rubidium) is:
- 5, 0, 0, +1/2
- 5, 1, 0, +1/2
- 5, 1, 1, +1/2
- None of these
Answer: a) 5, 0, 0, +1/2
Explanation:
E.C of Rubidium is (Z=37) = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s1
The valence electron is in the 5s orbital.
Thus, its 4 quantum numbers are n = 5, l = 0, m = 0, s = +1/2
Question 15: Which statement does not form part of Bohr’s model of hydrogen atom?
- The energy of the orbit is quantised.
- Electrons in orbit nearest to the nucleus have the lowest energy.
- Electrons revolve in different orbits around the nucleus.
- The position and velocity of electrons in orbit cannot be determined simultaneously.
Answer: d) The position and velocity of electrons in orbit cannot be determined simultaneously.
Explanation: Statement (d) is not included in Bohr’s hydrogen atom model.
An electron in an atom, according to Bohr, is placed at a specific distance from the nucleus and revolves around it at a specific velocity. This contradicts Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, which states that the position and velocity of electrons in orbit cannot be known at the same time.
Recommended Video:


Related Links:
- MCQs on Structure of Atom for NEET
- Flashcards for NEET Chemistry – Structure of Atom
- Atomic Structure – Discovery of Subatomic Particles
- Structure of Atom Class 11 Notes
- NEET Chemistry MCQS – Important Questions and answers
- NEET Chemistry 2023 – Important Topics and Preparation Tips
- NEET Chemistry Flashcards
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2023
Comments