Iris eye Definition
Iris is the most anterior part of the uvea. It is a thin, contractile and circular disc, centrally perforated by the pupil.
The anterior section of the uvea forms the bulk for the body of iris and as a result, the inflammation of the iris is known eithers as anterior uveitis or iritis. The posterior section of the uvea is known as choroid.
Download the Complete Guide to NEET UG Prep
Download Now
What is Iris?
Iris is a thin, pigmented structure found in the eye that can regulate the amount of light that can enter the retina. Also, it determines the eye colour.
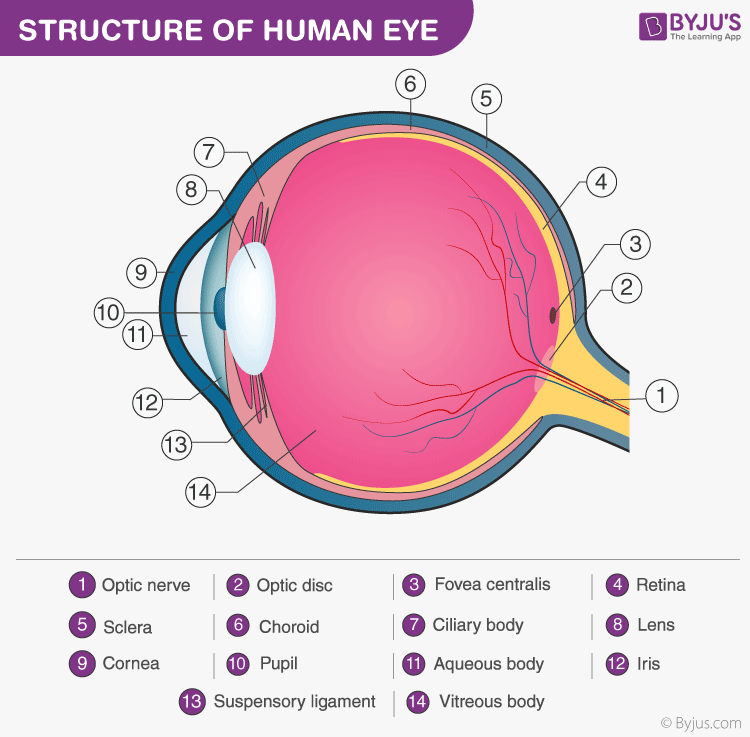
Iris is present in the anterior part of the eye lens. It controls the size and diameter of the pupil and thus regulates the amount of light entering the eye. It is the visible part of the eye. It is pigmented and opaque. Iris’s muscles control the size of the aperture, which is known as the pupil. When the light is bright the iris closes the pupil and lets less light enter the eyes and when the light is dim it opens up the pupil more to allow more light to enter the eye.
The pigmented or vascular layer includes the iris. It is the dark coloured, round structure found under the cornea.
Also Explore:
| What is the function of pupil? |
| What is the sclera of eye? |
Iris Structure and Function
It is present behind the cornea and above the eye lens. It originates from the ciliary body. The thick anterior portion of the choroid layer of the eye, which is known as the ciliary body extends further forming iris. It is a pigmented structure and the colour depends on the amount and nature of the pigment present in it, e.g. brown, grey, green, blue, etc. The quantity of melanin pigment determines the colour of the iris.
The iris is made up of two layers:
- Stroma – the front pigmented fibrovascular layer
- Pigmented epithelial cells – present at the back
The iris surrounds a small aperture called the pupil. The iris contains two sets of muscles. When the circular muscles contract, the size of the pupil decreases and when the radially arranged muscles contract the size of the pupil increases. This is how it works as a diaphragm controlling the size of the aperture and regulates the amount of light entering the pupil. This is under involuntary control.
Thus iris plays a vital role in regulating the amount of light that can enter the retina.
Eye colour
The iris is a strongly pigmented structure that determines eye colour. The typical eye colour can be hazel, brown, grey, blue and green. The most vital pigment that contributes to the iris colour is melanin.
Muscles of the Iris
Iris is a pigmented diaphragm having a central aperture – the pupil. It is placed in front of the lens thus separating the anterior chamber from that of the posterior chamber each having aqueous humor passing through the pupil.
There are two muscles in iris –
- Sphincter pupillae – The constriction of the pupil is provided by the parasympathetic fibres from the oculomotor nerve. It is a circular muscle constricting the pupil in bright light
- Dilator pupillae – The dilation of the pupil is provided by the sympathetic fibres. This muscle of the iris expands the opening upon contraction
This was in brief about Iris. Test your understanding with MCQs on Structure of Eye, only at BYJU’S.
Recommended Video:
Neural Control and Coordination Class 11 Biology | NEET Biology Important Chapters | NEET 2023

Related Articles:
| Sensory Receptors |
| Process of Neural Communication |
| NEET Biology Flashcards – Neural Control and Coordination |
Frequently Asked Questions
What colour is human iris?
The pigmentation of iris in humans differs from black to light brown based on the concentration of melanin in the iris pigment epithelium, the melanin content in the iris stroma and stroma’s cellular density.
What are the two layers of iris?
The two layers of the iris are stroma and pigmented epithelial cells. The stroma is the front pigmented fibrovascular layer beneath which the pigmented epithelial cells are present.
Iris is part of?
What is iridology?
Iridodiagnosis or iridology is a type of alternative medicine technique which examines the colors, patterns and other characterististics of the iris to determine the patient’s systemic health.
What is the radial muscle of the iris?
The radial muscle of the iris or the iris dilator muscle are smooth muscles of the eye which radially run in the iris and hence serve as a dilator.

Comments