Incomplete oxidation of carbohydrates in plants leads to the synthesis of oxalate. Many metal ions when it reacts with oxalate forms insoluble precipitates. Oxalates are also capable of forming coordination compounds. Calcium oxalate is one of the commonly seen examples in oxalates. The primary constituent of the most common kind of oxalate found in the human body is kidney stones.
Properties Of Oxalate
| Chemical formula | C2O4 -2 or (COO)22- |
| Molecular weight | 88.018 g/mol |
| Solubility in Water | 1e+006 mg/L at 25 deg C |
| Chemical names | oxalate
ethanedioate Oxalate Ion Ethanedioic acid, ion(2-) Oxalic Acid Dianion |
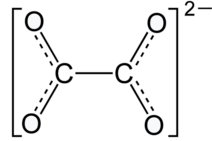
Oxalate Structural Formula
Oxalate is a dianion with structural formula as shown below.
For more information on various chemicals with chemical and structural formula, Refer BYJU’S!!
Comments