As we know matter in everyday life exists in three forms; solids, liquids and gases. In this article, we will examine the interchangeability of the states of matter and examine the conditions required for such a change to occur. Let us learn about the change of state from solid to liquid and also know about the melting point.
| Table of Contents: |
Changing States of Matter
Changes in the state of matter occur through changes in the energy of the substance; mainly thermal energy. The molecules that are supplied with energy i.e. heat, start vibrating vigorously. If even more energy is supplied the molecules eventually gain enough energy to separate out of the sample. We can best understand this concept if we try to apply this practically. Let us now understand conversion from solid to liquid and the concept of melting point.
Conversion from Solid to Liquid
Let’s start with ice cubes. Let’s take some ice cubes and heat it in a beaker. What you notice after a while is that the ice cubes are dissolving in its own liquid. This is what is meant by hyperactive atoms. After gaining sufficient energy, the molecules of ice escape out of the ice cube and into the beaker and in doing so undergo a change in state from solid to liquid. As we keep heating, the ice cubes gradually become smaller and smaller and turn into water. This change of state is referred to as melting and it is a change of state from solid to liquid.
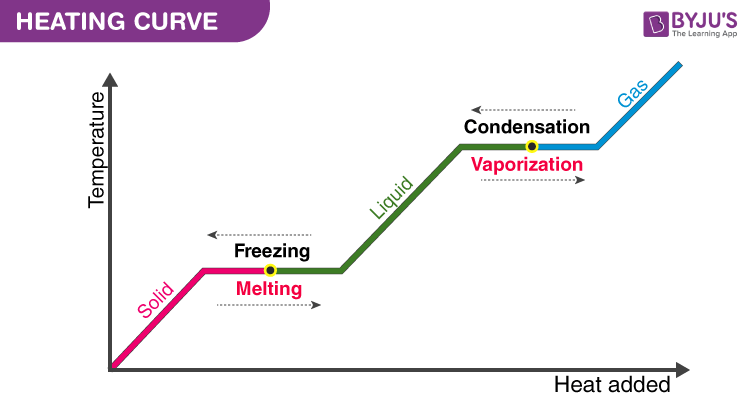
One important thing to remember in case of change of state is that when the change in state is occurring; there will be no increase in temperature even though heat is being supplied. The heat energy is absorbed by the ice changing into water. It is noticed that until all the ice is melted, there is no change in temperature. Both the solid and liquid states of a substance coexist in equilibrium during the change of state. The process of obtaining solid from the liquid is the opposite; remove heat from the sample and it is called fusion or freezing. After learning about changing states of matter, and conversion from solid to liquid, let us now have a look at the melting point.
To know about the changing states of matter in detail, see the video below

What Is Melting Point?
The temperature at which solid and liquid states coexist together is called the Melting point. It is unique to a substance and is dependent on the pressure acting on the body. Greater the pressure, the lower the melting point. The pressure controls the rate of melting by influencing the equilibrium of the solid and liquid states. Snow skating takes advantage of this very phenomenon. By concentrating all the weight of the skater on a thin line, the skater applies considerable pressure on the ice causing the ice below his shoes to melt. This melting ice lubricates the undersides of his skating shoes. This is what allows us to skate on ice. Ice melts while we are on it and refreezes after we are over it. This phenomenon of refreezing is known as Regelation. The melting point of a substance at normal atmospheric temperature is known as the normal melting point of the substance.
To know about the melting and boiling points in detail, see the video below

Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Define melting point?
The temperature at which solid and liquid states coexist together is called the Melting point.
The phenomenon of refreezing is known as?
State true or false: The heat energy is absorbed by the ice changing into water.
In how many states does the matter exist?
Define the normal melting point of the substance.
The melting point of a substance at normal atmospheric temperature is known as the normal melting point of the substance.
Hope you have learned what a melting point is, a change of state from solid to liquid, and changing states of matter. Learn with BYJU’S to get more insights into different states of matter.

Comments