The derivation of the mirror formula is one of the most common questions asked in various board examinations as well as competitive examinations. A mirror formula can be defined as the formula which gives the relationship between the distance of object ‘u’, the distance of image ‘v’, and the focal length of the mirror ‘f’. The mirror formula is applicable for both, plane mirrors and spherical mirrors (convex and concave mirrors). The mirror formula derivation is provided here so that students can understand the concept of the topic in a better way. The mirror formula is written as:
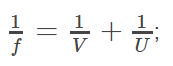
Assumptions for Derivation Of Mirror Formula
The following assumptions are taken in order to derive the mirror formula.
- The distances are being measured from the pole of the mirror.
- According to the convention, the negative sign indicates the distance measured in the direction opposite to the incident ray while the positive sign indicates the distance measured in the direction of the incident ray.
- The distance below the axis is negative whereas the distance above is positive.
Learn about Spherical Mirrors

Mirror Formula Derivation
The derivation of the mirror formula is given below. The diagram given below will help learners to understand the mirror formula derivation more effectively.
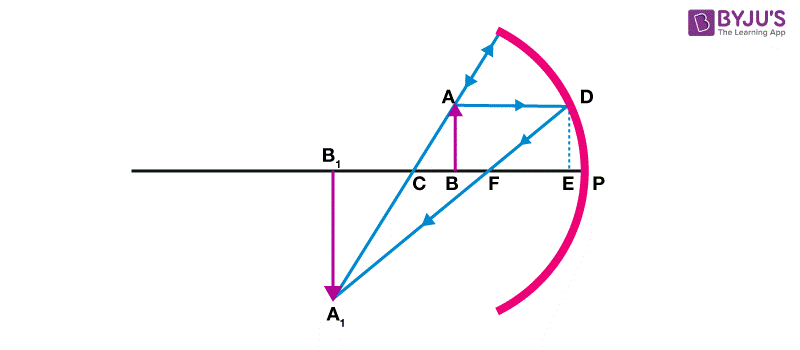
From the figure given above, it is obvious that the object AB is placed at a distance of U from P which is the pole of the mirror. From the diagram we can also say that the image A1B1 is formed at V from the mirror.
Now from the above diagram, it is clear that according to the law of vertically opposite angles the opposite angles are equal. So we can write:




Recommended Videos
Previous year questions in the chapter Light: Reflection and Refraction

Theory and important questions of the chapter Light: Reflection and Refraction

This was the derivation of the mirror formula. Students must understand each step of the mirror formula derivation to get a piece of in-depth knowledge about the topic. Stay tuned with BYJU’S and learn various other derivations of physics formulas.

it good
thanks
Nice explanation ..
This website really helped me a lot in my exams and I also learnt such new things which our teacher had never taught us!
Really great helpful…
deduction for object at F and image at infinity??
When the object is placed at F that is the focal point, there is no formation of an image as the refracted rays neither diverge nor converge at a point. After refraction, the rays are parallel to each other, and therefore, no image is obtained.
Very nice explanation and a very good and easy questions in the quiz.
well explanation. 👍