Hydrogen has many isotopes and deuterium is one of them. It has a proton and a neutron. Protium is the most common isotope of hydrogen that has no neutrons and one proton. This isotope is heavier than protium since it contains a neutron and therefore it is also called heavy hydrogen.
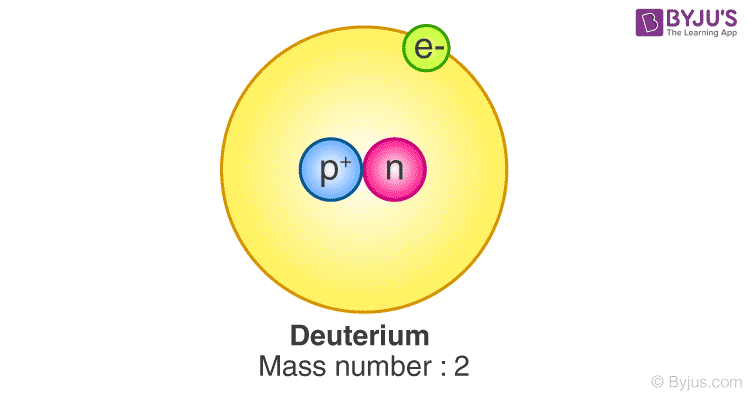
Facts of Deuterium:
- A deuterium nucleus is termed as deuteron or deuton.
- D or 2H is the chemical symbol used for deuterium.
- This isotope of hydrogen in the form of heavy water is present in very small quantities in the oceans, but these are not easy to extract. The production of heavy water begins with the intense energy Girdler sulfide.
- Deuterium has an atomic weight of 2.014.
- Deuterium is a stable atomic species that is found in natural hydrogen compounds to an extent of about 0.0156%. Hence, it is not radioactive.
- Approximately 156.25 ppm of deuterium is present in the oceans which are equal to one atom in 6,400 of hydrogen.
- Deuterium got its name from the Greek word deuterons, meaning “second”. It refers to the two particles i.e. a neutron and a proton that make up the nucleus of a deuterium atom. The term used for the deuterium nucleus is deuteron.
- Harold Urey discovered deuterium in 1931. Samples of heavy water were produced using the new form of hydrogen by Urey and in 1934 he won the Nobel Prize.
Uses of deuterium:
- It is widely used in prototype fusion reactors and has their application in military, industrial and scientific fields.
- In nuclear fusion reactors, it is used as a tracer and it is responsible for slowing down neutrons in heavy water moderated fission reactors.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
How many isotopes are in hydrogen?
Is Protium an isotope of hydrogen?
Which isotope of hydrogen has no neutrons in it?
What is the atomic mass of deuterium?
What are the uses of deuterium?
In nuclear fusion reactors, it is used as a tracer and it is responsible for slowing down neutrons in heavy water moderated fission reactors.

Comments