Everything in Earth’s system is placed into one of the four subsystems: land, water, living things, or air. The subsystems are known as “spheres.” Specifically, they are known as the geosphere (land), hydrosphere (water), biosphere (living things) and atmosphere (air). Environmentalists use this system to classify and study the organic and inorganic materials found on the Earth. In this article, we discuss these four spheres in detail.
| Table of Contents |
The Geosphere
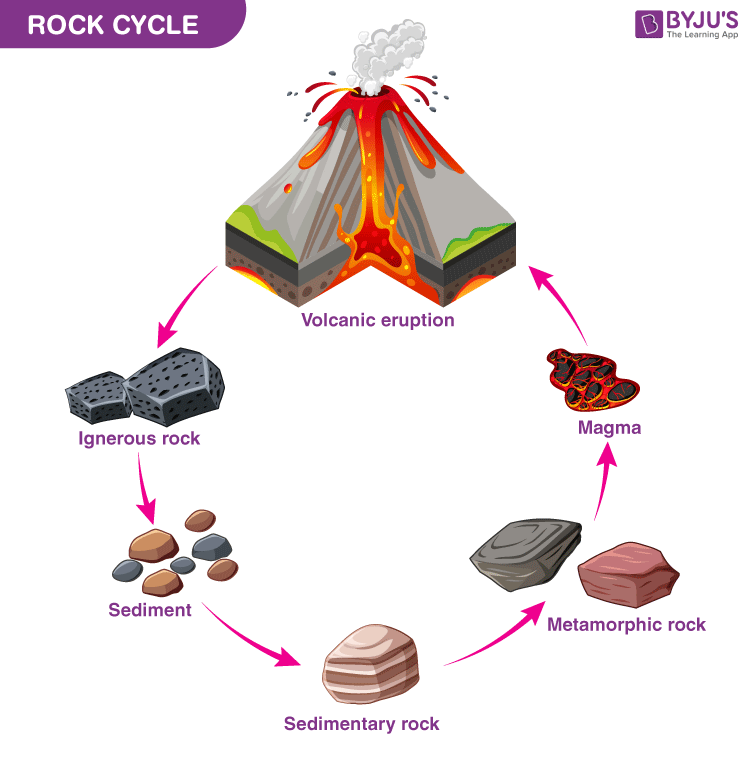
The geosphere includes all the elements that form the crust and core of the Earth. Rocks and sand particles ranging from drylands to those found at the bottom of the ocean are examples of the geosphere. Examples also involve minerals, lava, molten magma and mountains. The geosphere undergoes constant processes that modify other spheres. One of the examples is the rock cycle.
The Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere includes all the water parts of the planet. It includes water on the surface, subsurface and water vapour in the atmosphere. It undergoes infinite processes every day. The water cycle is one way to understand what is the importance of the hydrosphere, its functions and how it supports other spheres.

The Biosphere

- The hydrosphere replenishes plants and animals with water and moisture.
- The geosphere renders a solid surface for the plants and animals to inhabit. It also provides heat from beneath the earth.
- The atmosphere screens the sun’s UV radiation and helps us receive just enough of the sun’s heat.
A theory known as the ecosystem better explains the interaction of the biosphere with the other spheres.
The Atmosphere

The atmosphere comes in layers and the illustration below shows the different layers of the atmosphere. The troposphere is the layer closest to Earth. Humans, animals and plants live in this layer. Birds and aeroplanes also fly in this layer of the atmosphere. In the layers above the troposphere, the air becomes thinner. Beyond the exosphere is space.
How do the Earth’s Spheres Interact with Each Other?

1. Hydrosphere and Atmosphere
The evaporation that occurs in the hydrosphere forms the medium for cloud and rain formation in the atmosphere. The atmosphere brings back this water to the hydrosphere in the form of rain.
2. Hydrosphere and Geosphere
Hydrosphere provides the necessary moisture required to weather and erode rocks in the geosphere. The geosphere, in turn, allows the ice to melt and the water bodies to flow back into the oceans.
3. Atmosphere and Geosphere
The atmosphere provides the required heat and energy for the breakdown and erosion of rock in the geosphere. The geosphere, in turn, reflects the sun’s energy to the atmosphere.
4. Biosphere and Hydrosphere, Atmosphere and Geosphere
The biosphere receives sunlight and gases from the atmosphere. It collects water from the hydrosphere and a living medium from the geosphere.
All four spheres can often be found in a single location. For example, the soil may contain minerals from the geosphere, moisture within the soil from the hydrosphere, insects and plants from the biosphere inhabiting the soil and pockets of air present between the soil pieces. From this, we can conclude that the complete system is what makes life as we know it.
Suggested Reading
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
How are the spheres of Earth interrelated?
What are the names of layers in the atmosphere?
What would happen if the Earth’s spheres do not interact with each other?
What is the purpose of Earth’s sphere?
How do volcanoes affect all four sphere while erupting?
Watch the video to learn more about air and atmosphere

If you wish to learn more Physics concepts with the help of interactive video lessons, download BYJU’S – The Learning App.

Superb!