Velocity is the rate of change in an object’s position in a specific time range. When the object moves along a straight path, its velocity is termed linear velocity. It is given as the ratio of distance covered to time. It is denoted using V and measured using the S.I unit m/s. It is a vector quantity.
| Table of Contents |
What Is Linear Velocity?
Linear velocity is the measure of “the rate of change of displacement with respect to time when the object moves along a straight path.” It is a vector quantity. The dimension formula of linear velocity is [M]0[L]1[T]-1
Linear and angular velocities are related to the speed of an object based on the perspective chosen. Linear velocity is applied to an object that moves, whereas angular velocity applies to those that turn, such as a wheel, the earth’s revolution or a spinning top.
Linear Velocity Formula
The linear velocity depends on the distance an object travels with respect to the time taken. The linear equation or the linear velocity formula is given by,
v = x/t
Where,
- v = Linear velocity
- x = distance covered
- t = Time taken to cover the distance(x).
Linear Velocity units
Linear velocity is measured using SI unit meter per second or m/s
Angular Velocity to Linear Velocity
Anything that moves or turns in the circular direction has both linear velocity and angular velocity. The angular velocity is the ratio of the angle traversed to the amount of time it takes to traverse that angle.
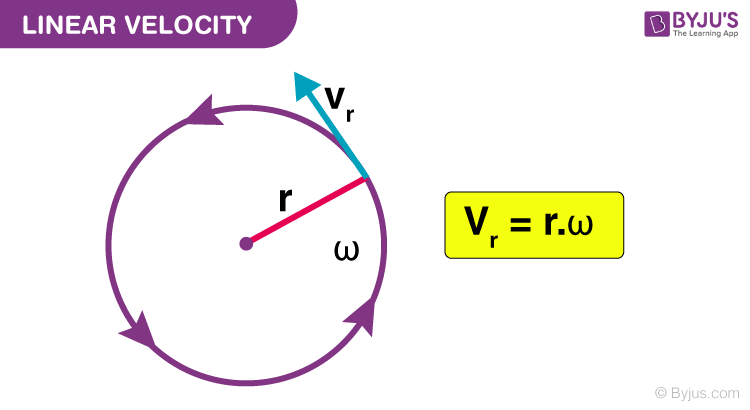
Angular velocity gives an expression of angular displacement over time and can be expressed in radians or degrees. Angular velocity is determined with the above-mentioned equation.
To calculate the linear velocity from angular velocity, you can apply the formula, where –
ω is expressed in radians/time,
r indicates the radius of the path taken.
Read More: Angular Displacement
Constant Linear Velocity
When a body moves with constant speed without changing its direction, it is said to be moving with a constant linear velocity. Linear velocity indicates the direction is not changed, and constant shows that the magnitude remained constant.
Physics Related Topics:
| Velocity of Light |
| Relation between Velocity and Wavelength |
| Relation between Escape Velocity and Orbital Velocity |
| Relation between Group Velocity and Phase Velocity |
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is linear velocity?
How do you determine the magnitude of the linear velocity of point B on a link AB which is relative to point A?
ω*AB
What is a tangential component?
What is a radial component?
What is the dimensional formula of angular momentum?
What does the rate of displacement mean?
What is instantaneous velocity?
How do you determine the direction of the linear velocity of a body moving in a circle?
What is the angle between the linear velocity and the angular velocity of a body moving in a circle?
Define linear velocity.
Write the expression for linear velocity.
v=xt
Write the dimensional formula of linear velocity.
State true or False. “Linear velocity is a scalar quantity.”
Write the type of motion involved in linear velocity.
Write the SI unit of linear velocity.
Name the types of velocities involved in a circular motion.
If an object covers 3 meters in 2 seconds along a straight. Calculate its linear velocity.
A plane is travelling Northeast. If the eastern component of its velocity is 300 m/h, how fast is the plane travelling?
An object is moving in a circular path. How will its linear velocity change if the diameter of the circular path is decreased by one-half?
Watch the video and learn more about laws of motion
Hope you have understood linear velocity, how it is calculated and its formula along with terms and units.
Stay tuned with BYJU’S for more such interesting articles. Also, register to “BYJU’S – The Learning App” for loads of interactive, engaging Physics-related videos and unlimited academic assistance.

Comments