When a ray of light falls on a surface, then it can undergo one of the following three phenomena reflection, refraction, or absorption. When it falls on a normal surface then most of the light gets absorbed. So mirrors are polished surfaces coated with mercury such that they reflect most of the light falling on them. Now based on the type of reflecting surface we can classify mirrors as concave, convex, or plane mirrors. Here we will be talking about the plane mirror only. So to form an image we require at least two rays from the object which meet or appear to meet at a point. In the case of a plane mirror, here we have used three rays for better clarity in the ray diagram shown below.
| Table of Contents |
Formation of Image by a Plane Mirror
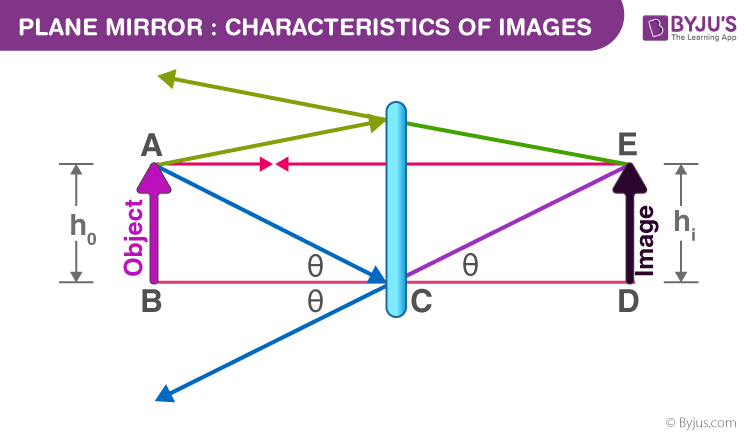
For the ray starting from point A and travelling in a horizontal direction towards point E, the angle of incidence is 0, and hence it retraces its path. Similarly, the ray starting from A and travelling towards point C follows the law of reflection. When these rays are produced backwards, they appear to meet at a point E. Now this image is known as a virtual image. What is the difference between real and virtual images? In a real image, the rays of light actually meet after reflection, while in a virtual image, it appears to meet but do not actually meet. A real image can be obtained on screen but not a virtual image.
Read More: Law of Reflection
Watch the video and learn more about plane mirrors
Following is the table explaining other concepts related to the mirror:
| Concave Mirrors And Convex Mirrors |
| Uses Of Spherical Mirror: Concave And Convex Mirror |
| Mirrors And Reflection |
Characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror :
From the above diagram, the following characteristics of the image can be observed.
- It is virtual
- It is erect and of the same size as the object
- The distance of the object from the plane mirror is the same as the distance of the image from the plane mirror.
- It is laterally inverted.
One of the important characteristics of the image is that it is laterally inverted. It means if you raise your left hand it would appear in the plane mirror that you have raised your right hand.
Watch this video to understand the significance of the mirror formula, which is also applicable to the plane mirror

Laws of Reflection
There are two laws of reflection which are always followed by plane mirror and they are:
- The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are always equal.
- The incident ray, the normal at the point, and the reflected ray, all lie on the same plane.
Properties of an Image Formed by Plane Mirror
- The image obtained is virtual.
- The image is laterally inverted.
- The image is erect.
- The size of the image is the same as the size of the object.
- The distance between the image obtained from the mirror is the same as the distance between the object from the mirror.
Watch the video and revise all the important concepts in the chapter Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 |
The below video helps to revise the topic reflection in the chapter Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 |
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is the magnification of the images formed by the plane mirror?
Can a plane mirror form a real image?
If a ray falls normally on a plane mirror, what is the angle of incidence?
What is the focal length of a plane mirror?
If a man stands 1m away from the plane mirror, what is the distance of the man from his image?
Watch the video below to learn about the reflection on a plane mirror

Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn about the application of the different types of mirrors, spherical mirrors, lenses, etc.

I see your point, and you are correct that a plane mirror itself does not have a physical depth to create an image within it.
In the case of a plane mirror, the image is formed by the reflection of light rays. When an object, such as the man, stands in front of the mirror, light rays from the object reflect off the mirror’s surface. These reflected rays appear to originate from behind the mirror, creating the illusion of an image.
To clarify, when we say that the distance between the man and his image is 1 metre, we are referring to the distance between the man and the mirror itself. The image formed is a virtual image that appears to be located behind the mirror, but it doesn’t physically exist within the mirror.
So, to summarize, the distance between the man and his image in a plane mirror is equal to the actual distance between the man and the mirror, as the image is formed by the reflection of light rays and does not have a physical depth within the mirror itself.