We know that light is a form of energy and can undergo various phenomena like diffraction, reflection, refraction, interference, and polarisation. Refraction is the phenomenon that takes place due to the bending of light when it travels from one medium to another. In this article, let us briefly understand the laws of refraction.
| Table of Contents |
What Is Refraction?
Refraction of Light is a phenomenon wherein light bends and travels from one transparent substance to another. Let’s understand this concept in-depth with an illustration. So, have you ever observed the bottom of a thick glass slab when a printed paper is kept below it? You will find that the printed matter seems to be raised. Similarly, when a pencil is partly immersed in water in a glass tumbler, it appears to be displaced from its original position at the surface. Did you ever think why does it happen? Why can’t it appear to be at the normal position?
Let us understand this with the help of the case of a partially immersed pencil in water. The pencil seems to be displaced from its original position because light reaching our eyes from the portion of the pencil inside the water comes from a different direction. Due to this reason, the pencil and printed matter seem to be displaced from the original position.
What if the water in the tumbler is replaced by kerosene or turpentine? Will the pencil appear to be displaced to the same extent? No, now the pencil will be displaced to some other extent. The extent of displacement is different for a different medium. This shows that light does not travel in the same direction in all mediums. The direction of propagation of light while travelling obliquely changes from one medium to another. This phenomenon is named as refraction of light. We can define refraction as the phenomenon of bending of light when it passes from one substance to another. Rainbow, mirage are a few real-life examples of refraction. Sunrise and sunset are a results of atmospheric refraction. Let us understand it more clearly by the concept of refraction through a rectangular glass slab.
Watch the video and learn more about refraction
Refraction through a Rectangular Glass Slab
Let us understand the phenomenon of refraction of light with the help of an activity.
- Take a white sheet and put a glass slab over the sheet.
- Draw the outline of the slab and mark it as ABCD as shown in the fig.
- Take two pins, say E and F and put them at the edge of A and B.
- Now, look at the images of the pins E and F through the opposite sides. Place two more pins G and H such that G, F and the images of E and F are in the same straight line.
- Remove the pins and the slab carefully.
- Join the points E and F and extend the line up to AB. EF meets at O. In the same manner, join G and H and extend it to the edge of CD. Mark O’ at the point where HG meets CD.
- Now, join O and O’. Also, extend EF till P as shown in the figure.

Refraction of Light
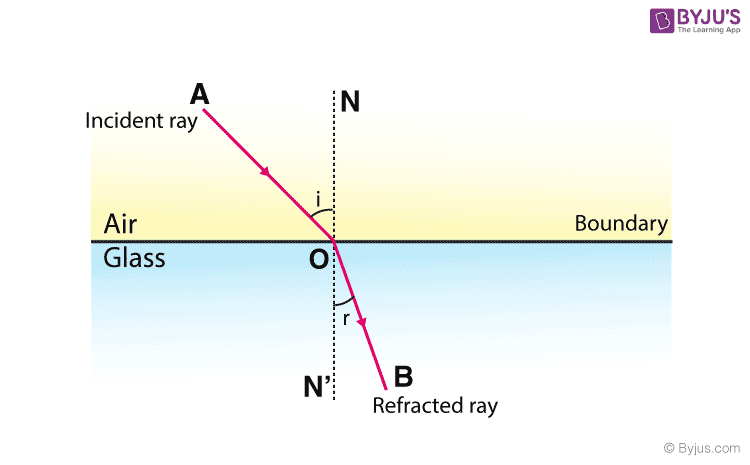
In the above activity, we have observed that light rays change their direction at O and O’ points at the surfaces of two separating transparent media. Make a perpendicular line NN’ to AB at O and another perpendicular line MM’ to CD at O’. At O the light ray enters from a rarer medium to a denser medium i.e. from air to glass. Hence, the light travels towards the normal. While at O’, the ray of light moves from denser to rarer medium. Hence, the light moves away from the normal.
In the given figure EO is the incident ray, O’H is the emergent ray and the OO’ is the refracted ray. In this, we can observe that the emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray. From the above activity, we can say that refraction happens due to a change in the speed of light when light travels from one medium to another.
Laws of Refraction
The laws of refraction govern the behaviour of light as they pass through the interface between two media. It is generally known as Snell’s Law. From the above-depicted activity, we can say that the refraction of light follows two laws:
- The refracted ray, incident ray and the normal at the interface of two transparent media at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
- For the given pair of media, the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of angle refraction is always constant.
Refractive Index:
We know that when light passes obliquely from one medium to another, it changes direction in the second medium. The extent to which change in direction takes place in the given set of a medium is termed as refractive index.
Consider a ray of light passing from medium 1 to medium 2 as shown in fig.
v1= speed of light in medium 1
v2= speed of light in medium 2
The refractive index of medium 2 with respect to 1 can be written as below:
Recommended Videos
Revision: the Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10

NCERT Questions on the topic Refraction of Light Class 10

Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is refraction?
What is the difference between reflection and refraction of light?
Why do the stars twinkle?
What is the refractive index?
What is the refractive index of water?
The below videos help to revise the chapter Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10


Stay tuned with BYJU’S for more such interesting articles. Also, register to “BYJU’S – The Learning App” for loads of interactive, engaging Physics-related videos and an unlimited academic assistance.

Thanks you sir for kind information