Telangana SSC Board question papers for Class 10 Social Science 2017 paper 1 with solutions are solved by subject professionals holding a deep knowledge of the subject. All the solutions are solved perfectly after thorough analysis of the complete syllabus. Students while solving the question papers can refer to the solutions to cross-check their answers and rectify their mistakes. By solving the previous year question papers students can understand the exact question paper pattern.
While preparing for exam students must make it a habit of solving the previous year question papers regularly. Here in this article, we have provided solutions of Telangana Board SSC Class 10 Social Science question papers 2017. Students can access these solutions free of cost which will help them to excel in their Social Science Class 10 exam.
Telangana SSC or Class 10 Social Science Question Paper 2017 Paper 1 with Answers – Free Download
Download Telangana SSC 2017 Social Science Question Paper 1
Download Telangana SSC 2017 Social Science Question Paper 1 With Solutions
Telangana Class 10 Social Science Question Paper 1 With Solution 2017
1. Write down the reason for the low temperature in India in the months of December and January.
Answer: Reason for the low temperature in India in month of December and January:
- Geographically, India is located in the ‘Northern Hemisphere’.
- So, during the final days of December, the sun is situated vertically over the Tropic of Capricorn on the Southern Hemisphere and the rays of the sun are not that strongly directed over India which lies in the Northern Hemisphere.
- In the north part generally, they experience low temperatures.
- This is the reason India experiences lower temperatures during December and January.
- Also, the north of India lays the Himalayas. During winter, the cold airflow from the Himalayas moves towards the south of the Indian Subcontinent resulting in colder temperature.
Observe the given bar graph and answer the questions 2, 3, 4, 5.
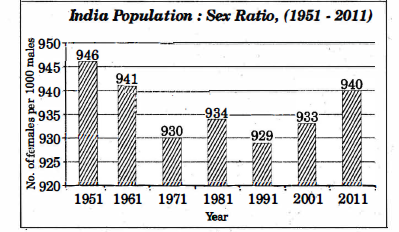
2. What does the above graph tell about?
3. What does the change in sex ratio show when compared with 1991 year to that of 2011
year?
4. What do you mean by sex ratio?
5. Mention the reason behind the low female population in India.
Answer 2:
- Sex ratio was the highest in 1951 and the second in 2011.
- Sex ratio was least in 1971, followed by 1991.
- Measures to improve sex ratio is bearing results as we can see a rise in sex ratio over a span of twenty years from 1991 to 2011.
- Only 1951 and 1961 has better sex ratio than 2011.
Answer 3: From 1991 to 2011 the sex ratio increased from 929 to 940. Although the improvement is not too vast, there is a healthy improvement in the sex ratio, and there is a lot of optimism because the rise in ratio would not have happened if the measures taken to arrest the decline in sex ratio was not working. Hence, we can say that we are moving in the right track, and it needs to be sustained.
Answer 4: Sex ratio is the ratio of males to females in a population. That is, it is the proportion of males in a population.
Answer 5: The reasons behind low female population in India are:
1. The general idea that boys are superior to girls. This leads to more preference of the boy child than the girl.
2. Female infanticide and abortion which lead to the low female population numbers also based on the above reason.
3. Religious and cultural beliefs that exacerbate the belief that boys are better than girls and lead to pride and preservation of family line and name.
Read the map given and answer the questions 6 and 7.
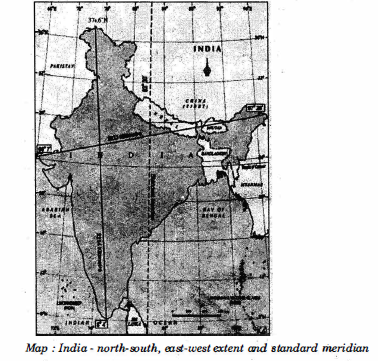
6. Name the latitude that divides India into two parts.
7. On which longitude, is Indian Standard Time based upon?
Answer 6: Tropic of cancer is the imaginary line that divides India into almost two equal parts.
Answer 7: For India the central longitude 82°30` E is taken as Standard Meridian which passes near Allahabad. This is the reference for Indian Standard Time (IST) and this is 5½ hours ahead of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
8. Observe the given graph and analyse it.
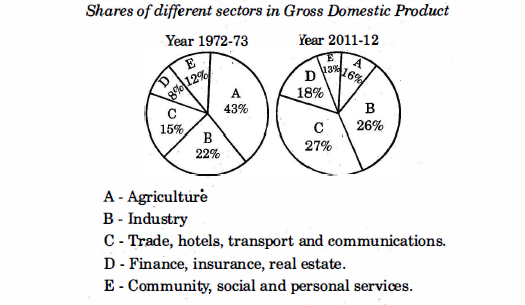
Answer:
- The share of agriculture as a percentage in GDP has reduced massively from 43% in 1972-73 to mere 16% in 2011-12. This shows that Indian economy is no longer heavily dependent on the agriculture sector.
- The contribution of industry in the GDP is more or less the same, it is a mere increase of 4 percentage points spread over 4 decades.
- Trade, hotels, transport and communications has seen a good spike in its contribution to the GDP. It won’t be wrong to conclude that the tourism sector in India saw an upswing in four decades.
- Finance, insurance and real estate sector contribution has increased from 8% in 1972-73 to 18% in 2012-13. It shows that the economy of the country is growing.
9. Give four reasons to the factors that helped Globalisation.
Answer: Four reasons to the factors that helped Globalisation are:
1) Improvement of transportation: This has made possible much faster delivery of goods across long distances at lower cost.
2) Improvement in information and technology: It has played a major role in spreading out production of services across countries. Telecommunication facilities are used to contact one another around the world to access information instantly and to communicate from remote areas.
3) Liberalization: Nations have removed many of the barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment and thus promoted and facilitated globalization.
4) Multilateral trade agreement: To promote foreign trade and free flow of investment.
10. Create any two slogans to prevent Global warming.
Answer: Two slogans to prevent Global warming
- If global warming is a lot, it makes the earth hot
- Nature does not need us but we need nature
11. Identify the importance of environment in the development of a nation.
Answer: Environment is extremely important for the development of a nation, due to various reasons.
- Environment is the source of all natural resources for the survival and sustainable development of a nation.
- Clean Environment provides pure air which is vital for survival of all living beings on earth plus wind energy is a source of renewable energy for a nation.
- Minerals, fossil fuels found in the environment are the main source of all the economic activities in a nation. It provides employment, they are a source of raw materials for various products manufactured in a nation and it is the source of power generation in a nation.
- Raw materials found in a nations’ environment helps it in increasing its revenues by carrying out trade with other countries.
- Water resources of a nation will help it to generate power by building dams. It is a source of livelihood of people since a healthy water resource will help in creating a flourishing fisheries industry.
- Top soil is the major lifeline for growth of plants, trees and agricultural crops. Healthy soil clubbed with best agricultural practices will help in increasing the production of nations food crops, thereby helping a nation meet its food security needs, as well as export excess produce to other nations.
12. Analyse the problems of Urbanisation.
Answer: Urbanization is an indication of the economic growth of a country, it leads to other disastrous effects to the environment and to the people.
- The growth in urbanization causes a haphazard and chaotic growth of people and housing in the urban areas. This unplanned urban sprawl has caused the deficient supply of resources like water, electricity, housing space, education, employment, sanitation, medical resources, transport, etc.
- The major problem of unemployment and lack of facilities leads to poverty that increases social evils like thefts, dacoity, etc.
- Also, the lack of urban space leads to the invasion of the urban and rural areas into the agricultural and forest areas, causing a disruption in the natural habitats.
- The other issues include – increase in slums, overcrowding, increase in urban pollution, disposal of wastes and trash, etc.
13. Name the facilities enjoyed by the workers in the organised sector.
Answer: Organised sector covers those enterprises or places of work where the terms of employment are regular and therefore, people have assured work. They are registered by the government and have to follow its rules and regulations which are given in various laws such as the Factories Act, Minimum Wages Act, Shops and Establishments Act etc. It is called the organised sector because it has some formal processes and procedures.
Workers in the organised sector enjoy security of employment. They are expected to work only for a fixed number of hours. If they work more, they have to be paid overtime by the employer. They also get several other benefits from the employers. They get paid leave, payment during holidays, provident fund etc. They are supposed to get medical benefits and under the laws, the employer has to ensure facilities like drinking water and a safe working environment. When they retire, many of these workers get pensions as well. People who work in the government or with companies or large establishments are all in the organised sector.
14. Write down the advantages and disadvantages of the people when they migrate.
OR
Explain the use of water in the river basin of Tungabhadra.
Answer: Advantages of Migration
- Migrants of all skill levels considerably contribute to societies. They spawn creativity, nourish the human spirit and spur economic growth. They bring diversity, provide innovation and bring about economic development and growth in the host societies.
- The primary motivation for migration is economic and at the heart of migration, management is imperative to maximize the development impact of international migration for all.
- India exemplifies the strengths of a large, tolerant, secular, live democracy with a pluralistic society in which people of different faiths, languages, ethnicity and political persuasions co-exist and thrive. Indeed, this milieu is the ‘sine qua non’ of any society that can create conditions for positive migratory movements and labour mobility for the benefit of all.
- This places India in a position to help contribute to the international community’s efforts to develop an appropriate world migration strategy.
Disadvantages of Migration
There are many disadvantages of migration.
- Due to migration there will be an increase in environmental pollution. There will be an increase in water pollution, air pollution, pollution due to lack of sewage treatment plants and disposal of solid wastes.
- There will be rapid increase in unplanned urban areas which will lead to rise in slum colonies.
- There will be tremendous pressure on the physical infrastructure of urban areas.
- Due to migration of men from rural areas to urban areas, leaving behind their wives, it leads to extra mental and physical pressure on women.
- Some of the other social consequences of migration are dejection, anonymity, all these factors can lead people to become involved in anti-social activities.
- Rural migration to urban areas in different states, has caused serious imbalance in the sex ratio in the place of destination and place of origin of migrants.
Answer: Tungabhadra, shared by the three southern states, Karnataka, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh, is a tributary of the larger river system Krishna. It originates in the Western Ghats with a catchment area of 71,417 km2, of which 57,671 km2 are in Karnataka.
The use of water in the river basin of Tungabhadra are:
- In this farmland area 80% of the population depends on agriculture for their livelihoods. Irrigation is provided through canal systems, while in rainfed regions farmers extract groundwater through bore wells. The major crops grown include paddy, jowar, sugarcane, cotton and finger millet.
- The area is ideal for semi-arid crops, the major crops grown demand a lot of water (paddy and sugarcane). Cultivation of such crops throughout the basin has dramatically altered the water sharing balance.
- Increasing trend in the number of small towns and industrial areas has made the competing demands for water more complex. Increased industrialisation and growth of urban areas have improved standards of living. There are 27 functioning large units and 2543 small units in this river basin. They consume a large amount of water per day.
- There has been a mismatch between keeping pace with development activities on various fonts and providing sanitation and drinking water supply for all sections of society, both in small towns and rural areas.
15. How can flexibility in labour laws support the present companies?
OR
How far is ‘Food Security’ required today in India?
Answer: Flexibility in labour laws support the present companies
- Flexibility in labour laws helps companies to get labourers for small periods of time.
- Flexibility in labour laws helps in the increase in unskilled and skilled labour in the companies.
- Flexibility in labour laws helps the smallest company to employ 20 million workers just near to the position of agriculture.
- Flexibility in labour laws helps in securing the jobs of workers.
- Flexibility in labour laws help in giving maximum profit to the companies.
Answer: While there might be enough food for the whole population of India, many families and especially children in India don’t have access to food because of financial problems.Food security means affordability, accessibility, availability, of food at all times to all people. The poor households are more vulnerable to food insecurity whenever there is a problem of production or distribution of food crops. In order to provide the Right to food to every citizen of the country, the Parliament of India, enacted a legislation in 2013 known as the National Food Security Act, 2013. Also called the Right to Food Act, this Act seeks to provide subsidized food grains to approximately two thirds of India’s 1.33 billion population.Food security has been a major concern in India. Food security depends on the Public Distribution System (PDS) and government vigilance and action at times, when this security is threatened. UN-India, there are nearly 195 million undernourished people in India, which is a quarter of the world’s hunger burden, around 43% of children in India are chronically undernourished.India ranks 74 out of 113 major countries in terms of food security index.The largest number of food insecure people in India are located in the states of West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh (eastern and south-eastern parts), Orissa, Chattisgarh, parts of Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh. Since the advent of the Green revolution in the early-’70s, the country has avoided famine even during adverse weather conditions. As a variety of crops are grown all over the country, over the course of the last thirty years, India has become self-sufficient in food grains.
16. Read the given paragraph and comment.
In many parts of the country, girl’s education is still given less priority by the parents as compared to boys’ education. While girls may study for a few years, they may not complete their schooling.
Answer: Literacy rate among women is much lesser than the literacy rate of men.
The proportion of girls going for higher studies is much lesser than boys, because parents prefer to spend their resources for boys education instead of girls education. While girls may study for a few years, they may not complete their schooling. Most of the families in rural areas are living in poverty, hence the families prefer to spend their resources on boys’ education. Studies consistently reinforce that girls who face multiple disadvantages such as low family income, living in remote or underserved locations are farthest behind in terms of access to and completion of education. Too often in the case of girls, marriage is seen as a higher priority than education. Once they are married at an early age those girls are not given the opportunity to continue their education, this is one of the main hindrances for continuation of girls education. Lack of proper sanitation facilities in schools is another major hindrance for success of girl child’s education. Lack of nearby education facilities is another major obstacle for girl child’s education, since parents are afraid to send their daughters to schools due to fear of their safety.
OR
Read the given paragraph and interpret.
Labour being the most abundant factor of production, it would be ideal if the new ways of farming used much more labour. Unfortunately, such a thing has not happened. The use of labour on farms is limited. The labour, looking for opportunities is thus migrating to neighbouring villages, towns and cities. Some labour has entered the non-farm sector in the village.
Answer: Farming is the main production activity in the village. Over the years there have been many important changes in the way farming is practiced. These have allowed the farmers to produce more crops from the same amount of land. The new ways of farming need less land, but much more capital. The Green Revolution in the late 1960s introduced the Indian farmer to cultivation of wheat and rice using high yielding varieties (HYVs) of seeds. Compared to the traditional seeds, the HYV seeds promised to produce much greater amounts of grain on a single plant. As a result, the same piece of land would now produce far larger quantities of foodgrains than was possible earlier. Higher yields were possible only from a combination of HYV seeds, irrigation, chemical fertilisers, pesticides, etc. The medium and large farmers are able to use their own savings from production to arrange for capital during the next season. At present, the non-farm sector in the village is not very large. Unfortunately, not all the people engaged in agriculture have sufficient land for cultivation. Cultivation of such plots doesn’t bring adequate income to the farmer family. Out of every 100 workers in the rural areas in India, only 24 are engaged in non-farm activities. As more villages get connected to towns and cities through good roads, transport and telephone, it is possible that the opportunities for non-farm activities in the village would increase in the coming years.
17. Locate the following in the given map of India.
(a) A peninsular river
(b) Mumbai
(c) Himalayan mountains
(d) Circar coast
OR
(a) Vindhya mountains
(b) Chennai
(c) One summer resort
(d) Arunachal Pradesh
Answer: Activity to be done by yourself.










Comments