What is Amoeba?
Amoeba is a unicellular organism that has the ability to change its shape. They are usually found in water bodies such as ponds, lakes and slow-moving rivers. Sometimes, these unicellular organisms can also make their way inside the human body and cause various illnesses.
One of the first reports referencing amoebas dates can be traced back to 18th century. A German naturalist named August Johann Rösel von Rosenhof who discovered a specimen and made detailed illustrations of the same in 1755.
Structure of Amoeba
Typically, most amoebas are characterized by the following features:
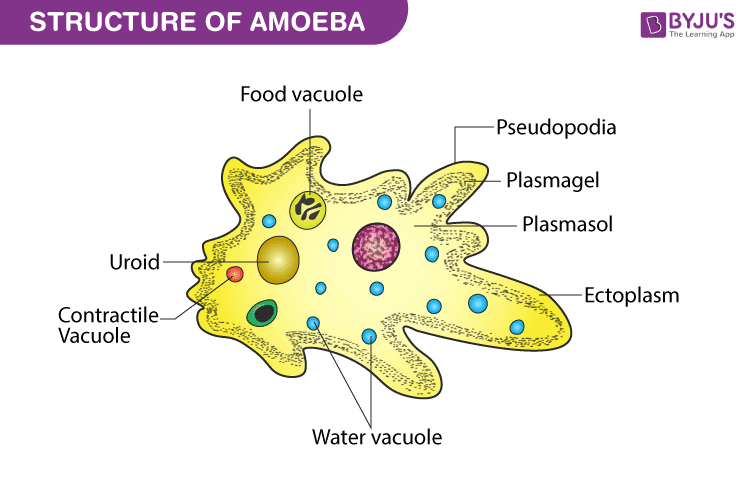
- Movement occurs through the use of pseudopodia, where the cytoplasm pushes the plasma membrane outward or inward, creating blunt, finger-like projections.
- There can be multiple pseudopodia at one particular instance, hence, its shape rapidly changes.
- Structure of amoeba primarily encompasses 3 parts – the cytoplasm, plasma membrane and the nucleus.
- The cytoplasm can be differentiated into 2 layers – the outer ectoplasm and the inner endoplasm
- The plasma membrane is a very thin, double-layered membrane composed of protein and lipid molecules.
- Amoeba also contains other cellular organelles such as a contractile vacuole, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus and fat globules.
- Amoeba consumes food either through the process of phagocytosis or pinocytosis.
- The process of reproduction is through asexual means, such as binary fission.
- The lifespan of a typical amoeba is 2 days, but because it undergoes binary fission, the resultant daughter cells are the same as its parent cell, so technically, amoebas can be termed as immortal.
- When living conditions are not ideal, an amoeba can essentially transform itself into a protective ball, called a microbial cyst. When living conditions become better, it can revert back to its trophozoite stage, where it can start feeding again.
Also Read: Types of Nutrition
Amoeba Classification
Traditionally, amoebas are grouped under the Kingdom Protista as they are neither classified as a plant, animal nor fungus. However, amoebas fall under eukaryotes as they possess a true nucleus.
Though technically not a true amoeba, the Naegleria fowleri, or more commonly called the brain-eating amoeba is an amoeboid organism than can make its way into the human body through the nose. It primarily feeds on neurons, thereby destroying the brain tissue. Unsurprisingly, the fatality rate of this infection is high – 97%.
Learn more in detail about Amoeba, its structure, classification and other related topics at BYJU’S Biology.
