Table of Contents
What is Anatomy?
Anatomy is a branch of biological science which is concerned with the description of body structures of various living organisms as revealed by dissection.
The word anatomy is derived from the Greek word “anatomē”, where “ana” means “up” and “tome” means “cutting.” Originally, anatomy was first learnt by cutting up corpses, hence the name “anatomy.”
Types of Anatomy
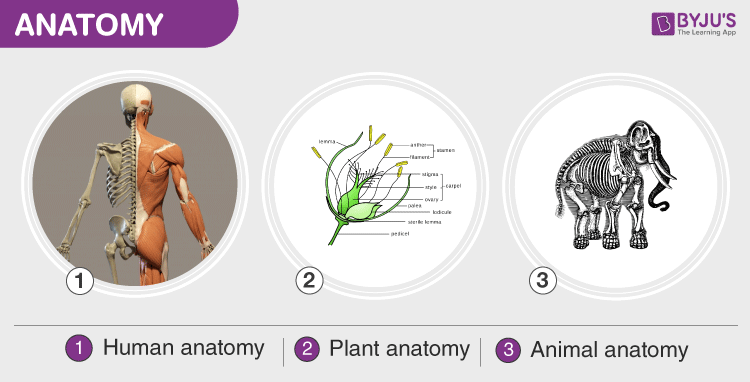
Anatomy could be classified into:
Human Anatomy – Human anatomy involves the study of the physical structure of the human body. It focuses on numerous systems, including circulatory, digestive, endocrine, skeletal, lymphatic, nervous, respiratory, urinary, reproductive and muscular systems.
Plant Anatomy – Also called the phytotomy. It is the study of the internal structure of a plant including the tissues, root system, stem, leaves, flower, fruit and seeds.
Animal Anatomy – Also called the zootomy. It deals with the study of the internal structure of an animal including the cells, tissues, organs, bones and other organs of the animal body.
As mentioned above, Anatomy was primarily learnt through dissection. The word ‘Anatomy’ and ‘dissection’ have virtually the same meaning in Greek and Latin. Besides the fact that both the words have the same source, anatomy has a broad discipline of its own and the word “dissection” is completely removed.
On the other hand, Physiology mainly deals with the functions and processes of the human body. It is distinctly different from anatomy as the latter deals specifically with the structure of the organism.
Anatomy is classified into:
- Microscopic Anatomy (Histology)
- Gross Anatomy (Macroscopic anatomy).
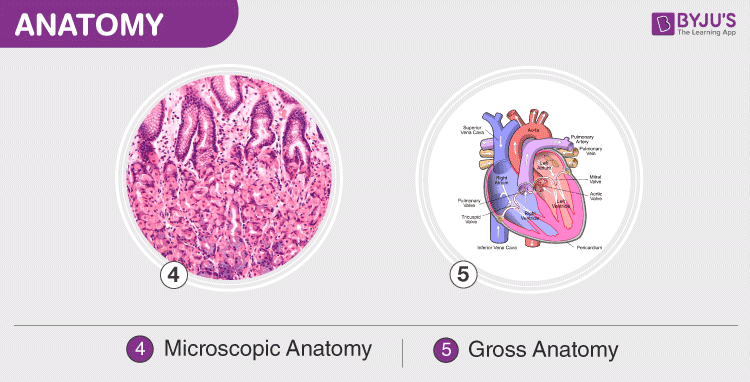
Microscopic Anatomy (Histology)
Also known as histology. Microscopic anatomy is the study of cells and tissues as discerned by a microscope. The individuals who specialize in this study are called histologists. The process involves marking and dividing cells and tissues into sections to be viewed under a microscope. The biological samples are dissected into thin slices so that they could be clearly examined. Stains are added to these dissected samples to enhance visibility and highlight important structures. Microscopic anatomy is useful to examine and compare different types of organisms, their structures and different stages of the cell cycle.
Application of Histology
- Histology slides are often used to explain the microstructures of biological cells and tissues.
- Analysis of tissue samples can reveal crucial information about any underlying infection or disease.
- Very helpful during the postmortems as it can pinpoint the exact cause of death.
- Useful in palaeontology, especially to identify fossils.
- Used in diagnosing certain cancer cells and biopsies.
- Useful in other domains of life science.
Gross Anatomy
Also known as macroscopic anatomy. Gross anatomy is defined as the study of an organism’s structures which are visible to the naked eye. The main objective of Gross anatomy is to obtain complete information about the structural organization of an organism.
Application of Gross Anatomy:
- Gross anatomy is used for studying in detail about the different organs.
- Used in endoscopy, where a tube having a camera at the end is inserted into an organism’s body cavity.
- It is used in Angiography, where an opaque dye is injected into the blood vessels to view the blood circulation within the human body.
- The internal structures and organs of living beings are studied by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and X-rays.
Anatomy – Questions
- What is the difference between Anatomy and Physiology?
Anatomy is the study of the internal structure and organs of living beings. Physiology mainly focuses on the functions and relationships of body parts.
- What are the types of Anatomy?
Microscopic Anatomy and Macroscopic Anatomy are the two main types of Anatomy.
Microscopic Anatomy is the study of the structure of cells, tissue and other microscopic parts of the body which cannot be seen through the naked eye. For example the types of white blood cells, plant and animal tissues, etc.
Macroscopic Anatomy refers to the examination of organs, parts and other structures of living organisms which are visible to the naked eye. For example- All internal and external organs of an individual.
- What is the importance of Anatomy?
In the field of medicine and life science sectors, anatomy plays a vital role as it helps us to learn about the different parts of an organism, including plants, animals and humans, along with their structure and characteristic features.
- Who is called the father of Plant Anatomy?
Nehemiah Grew, an English botanist is known as the father of plant anatomy based on his observations and contributions. He also published many books on plants and his first book Anatomy of plants was published in the year 1682. K.A. Chaudhary is known as ‘Father of Indian plant anatomy.
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about Anatomy and other related topics at BYJU’S Biology.

Comments