The plants that we see today are the result of billions of years of evolution. Today, plants cover almost 30 per cent of the total landmass and account for the 50 per cent of the plant’s productivity (generation of biomass). Plants fulfil many roles in the ecosystem. They are a source of food, nutrition, shelter, maintain the integrity of soil (by preventing erosion) and most importantly, they are the main source for balancing the oxygen level in the atmosphere.

Anatomically, plants are very complex organisms and are classified into various types based on certain defining characteristics. Roots are very important structures that provide a variety of functions, but contrary to popular belief, all plants do not have roots. Roots are absent in plants like mosses and liverworts.
Also Read: Plant Growth and Development
Table of Contents
Read on to explore what are roots, its types and the important functions of roots.
What are Roots?
Roots are the important underground part of all vascular plants. This part of the plant is mainly responsible for anchoring it down into the ground and absorbing the essential mineral elements, nutrients, and water from the soil. It is also used to store food.
However, not all plants have their roots underground, some plants have their roots growing above the ground. These are called aerial roots. Alike underground roots, these aerial roots are also responsible for absorbing nutrients, anchoring and affixing the plant by supporting them to the structures such as nearby walls, rocks, trellises, etc.
Few examples of plants with the aerial roots are–Bonsai, Banyan Tree, Mangroves, etc.
Types of Roots
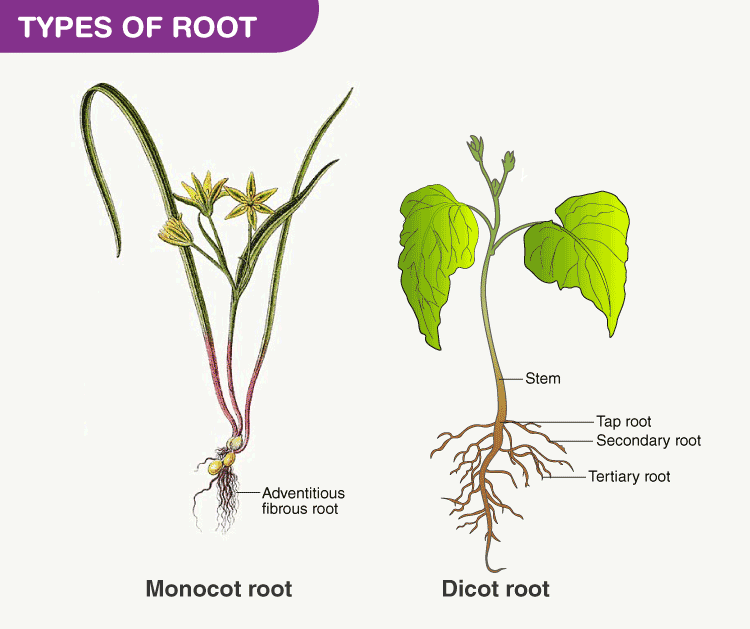
All roots have similar functions, however, their structure varies. Hence, based on these criteria, the root system is classified into two types:
Tap Root System
Taproots have a main central root upon which, small, lateral roots called root hairs are attached. Mustard, carrot, beetroot, parsley, china rose and all dicotyledons are examples of taproot systems.
Do Check: Tap Root Diagram
Fibrous Root System
Fibrous roots, on the other hand, are bushy roots in which thin, moderately branching roots grow from the stem. Rice, wheat, maize, marigold, banana and all monocotyledons are some examples of the fibrous root system.
Also Read: Anatomy of Monocot and Dicot Plants
What Are Adeventitious Roots?
Adventitious roots are a unique category of roots that develop from sources other than the radicle. Primary roots will also be present in plants with this particular sort of root system. The adventitious root system is a characteristic feature of angiosperms and they are modified for various purposes such as respiration, support and food storage.
The main difference between tap roots and adventitious roots is that the former penetrates deep into the soil while the latter does not.
Functions of Root
Following are the important functions of root:
Roots perform various functions that are necessary for the survival of the plants. They are an integral or integrated system that helps the plant in:
Anchoring: Roots are the reason plants remain attached to the ground. They support the plant body, ensuring that it stands erect.
Absorption: Primary function of the roots is to absorb water and dissolved minerals from the soil. This is crucial as it helps in the process of photosynthesis.
Storage: Plants prepare food and store in the form of starch in the leaves, shoots and roots. Prominent examples include carrots, radish, beetroot, etc.
Reproduction: Even though roots are not the reproductive part of plants, they are vegetative parts. In some plants, the roots are a means of reproduction. For instance, new plants arise from creeping horizontal stems called runners (stolons) in jasmine, grass, etc. This type of reproduction is called vegetative propagation.
Ecological Function: They check soil erosion, provide sustenance and also habitat to various organisms.
Explore More: Morphology Of Flowering Plants
Learn more about root system, types of roots, the function of the root, and other related topics @ BYJU’S Biology
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of root systems?
The different types of root systems are:
- Taproots
- Fibrous roots
- Adventitious roots
What is the function of roots?
Roots perform the following functions:
- Roots absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
- They anchor the plant firmly.
- They help in storing food and nutrients.
- Roots transport water and minerals to the plant.
What are the differences between monocot and dicot roots?
The main difference between monocot and dicot root is that the dicot root contains xylem in the middle and phloem surrounding the xylem. Whereas in monocot root, xylem and phloem are arranged circularly.
What are the primary and secondary roots?
Primary roots are the early roots in young plants that consist of taproots, basal roots, and lateral roots. Secondary roots are the side branches of the primary roots.
Name the plants with taproots.
The plants with taproots are:
- Beetroot
- Carrot
- Parsley
- Dandelion
Mention some edible roots.
Some edible roots include:
- Ginger
- Turnip
- Yam tubers
- Cassava tubers
What are fibrous roots?
Fibrous roots are the roots formed by thin, moderately branching roots emerging from the stem. Wheat, rice and corn are some of the examples of fibrous roots.
What are tap roots?
A taproot is a prominent, large, upright and straight root that develops vertically downward. Tap roots are more likely to be present in plants whose leaves contain reticulate venation. For example- Rose and carrot.


Really appreciate this service, it has been much help for me
I really like the videos and all . The mentors here are very good teachers
Very good
It is helpful for video making
Very very very very very very nice
Can plant have multiple variation of root morphology ?
What Is a root