Fruits are an important and characteristic element of plants (angiosperms). But what actually constitutes a fruit? Is a tomato considered a fruit or a vegetable? How is it formed in a plant? Let us take a look at the different parts, types and uses of a fruit.
A flower is a reproductive unit and the fruits are the outcome of reproduction.
Table of Contents
What is a Fruit?
Fruits are seed-bearing structures. It develops from a ripe ovary. They are a rich source of vitamins, minerals and fibres. Grapes, bananas, papaya, watermelon are some of the fruits consumed by humans. They are the main source of a balanced diet.
Let us have a detailed look at the parts, uses and types of fruits.
Parts of a Fruit
A fruit comprises the following parts:
- Pericarp
- Seeds
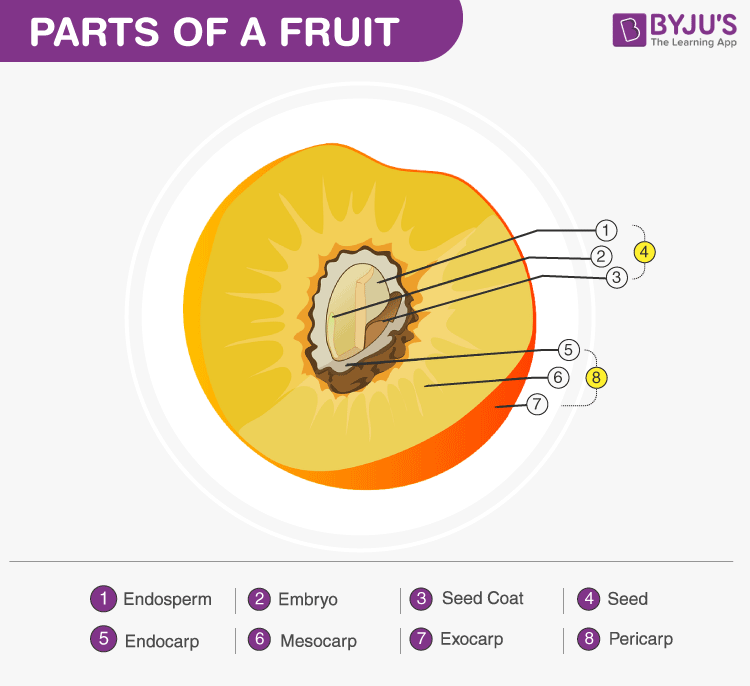
Pericarp
The pericarp is the wall of the ovary that develops as the wall of the fruits. The pericarp of the fruits might be fleshy as in guava, mango, etc. or might be dry as in mustard, walnut, etc. The pericarp is further differentiated into three layers, namely:
- Epicarp: Outermost layer, forms the peel.
- Mesocarp: Middle layer, fleshy, edible portion of the fruits
- Endocarp: Innermost layer, the inner rough portion where the seed is accommodated
Seeds
Seeds are ripened fertilized ovules. It is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering.
Also Read: Significance of seeds and fruit formation
Types of Fruits
Based on the number of ovaries and the number of flowers involved in the fruit formation, fruits are classified into three major groups namely:
Simple Fruits
These fruits develop from a single matured ovary in a single flower. Apple, banana, cherry pear, plum, tomato are few examples of simple fruits. The simple fruits are classified into the following categories:
- Drupes: These are also known as stone fruits since it contains a very hard seed inside the simple fruits. For eg., plum, cherry, peach.
- Berries: These type of fruits have a single seed in the center and are very juicy. For eg., grapes, blueberries.
- Pomes: Such fruits bloom from trees. For eg., apple, papaya
- Hesperidium and Pepos: They are slightly similar to the berries and include fruits such as watermelon, citrus fruits.
Aggregate Fruits
These fruits develop from a number of matured ovaries formed in a single flower. Individual ovaries are called “fruitlets.” Blackberry, raspberry, strawberry are few examples of aggregate fruits.
Composite Fruits
These fruits develop from a complete inflorescence. these are also known as multiple fruits. Composite fruits are of two types:
- Sorosis: These are found in mulberry, jackfruits and pineapple. They develop from catkin, spikes and spadix type of inflorescence.
- Syconus: This develops from hypanthodium type of inflorescence.
Also Read: Fruit and seeds formation without Fertilization
Uses of Fruits
Fruits are rich in vitamins and minerals which are essential for a healthy human body. For instance, we know that oranges are rich in vitamin C. Vitamin C is vital to neutralize any free radicals in our body. Also, acids in citrus fruits are very effective in skin whitening and exfoliation. Besides consumption, these citrus acids can help to get rid of mineral deposits and grease on cooking utensils.
Fibre-rich fruits like raspberries are very good for digestion. The protein in papaya, called papain, can help the breakdown of proteins, and therefore aid digestion. It also reduces acidity levels and eases indigestion.
Palm dates have a low glycemic index and hence, they are very useful in blood sugar regulation. Furthermore, it is high in dietary fibre and is very helpful for digestion.
Grapes have a chemical called Reservatrol that functions similar to aspirin, giving it the properties of an analgesic (painkillers).
Also Read: Parthenocarpy
To learn more about fruits, types of fruits, their parts, uses or other related topics with video lessons, visit BYJU’S.

thanks alot for the cool concept
Great job! Try to include the meaning for the seed parts though.