“Binomial nomenclature is the biological system of naming the organisms in which the name is composed of two terms, where, the first term indicates the genus and the second term indicates the species of the organism.”

What is Binomial Nomenclature?
The system of binomial nomenclature was introduced by Carl Linnaeus. Multiple local names make it extremely difficult to identify an organism globally and keep a track of the number of species. Thus, it creates a lot of confusion. To get rid of this confusion, a standard protocol came up. According to it, each and every organism would have one scientific name which would be used by everyone to identify an organism. This process of standardized naming is called as Binomial Nomenclature.
All living species including plants, animals, birds and also some microbes have their own scientific names. For eg.,
- The scientific name of the tiger is presented as Panthera tigris. ‘Panthera’ represents the genus and ‘Tigris’ represents a particular species or specific epithet.
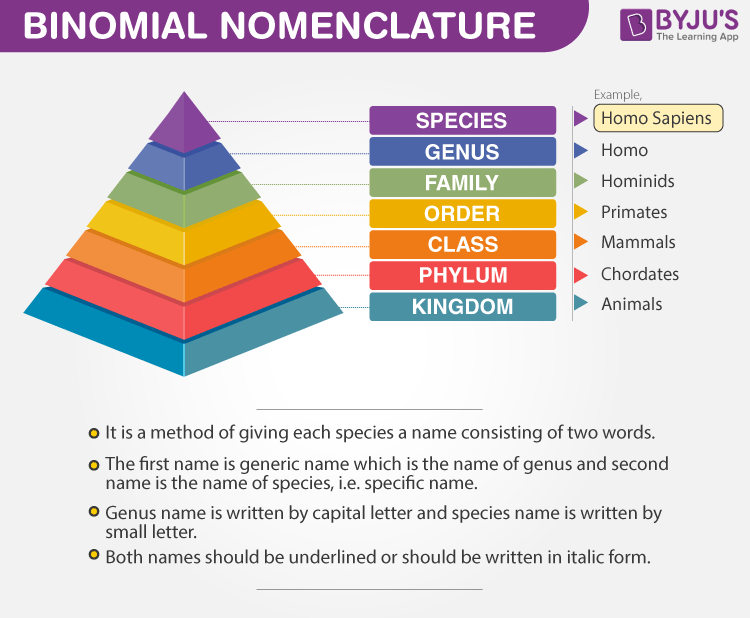
- The scientific name of humans is presented as Homo sapiens. ‘Homo’ represents the genus and ‘sapiens’ represents a particular species.
- The Indian bullfrog is scientifically written as Rana tigrina. ‘Rana’ is the name of the genus and ‘tigrina’ is the name of the specific species.
Also Read: Taxonomy
Rules of Binomial Nomenclature
A Biologist from all over the world follows a uniform set of principles for naming the organisms. There are two international codes which are agreed upon by all the biologists over the entire world for the naming protocol. They are:
- International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN) – Deals with the biological nomenclature for plants.
- International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) – Deals with the biological nomenclature of animals.
These codes make sure that each organism gets a specific name and that name is globally identified.
The naming follows certain conventions. Each scientific name has two parts:
- Generic name
- Specific epithet
The rest of the binomial nomenclature rules for writing the scientific names of organisms include the following:
- All the scientific names of organisms are usually Latin. Hence, they are written in italics.
- There exist two parts of a name. The first word identifies the genus and the second word identifies the species.
- When the names are handwritten, they are underlined or italicized if typed. This is done to specify its Latin origin.
- The name of the genus starts with a capital letter and the name of the species starts with a small letter.
Why is Binomial Nomenclature Important?
As stated previously, there are millions of species of organisms distributed throughout the world. Furthermore, the same organisms are known by different names around the world and this can cause confusion when trying to identify or classify. Hence, binomial nomenclature was seen as a viable solution to this problem.
Drawbacks of Binomial Nomenclature
Some of the basic drawbacks of binomial nomenclature are:
- If two or more names are currently in use, according to the law of priority, the correct name will be the one used first and the others end up being synonyms as validity is the senior synonym. Providing stability in the naming and classification of organisms must be emphasized.
- Also, the names used prior to those included in the “Systema Naturae”, by Linnaeus are not recognized.
Also Read: Biological classification
To learn more about binomial nomenclature, its rules and drawbacks, keep visiting BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S app for further reference.

very informative
Excellent