Table of Contents
Chlorophyll is a green pigment present in plants. It is responsible for the green colour of young stems and leaves. Let’s learn about the structure of chlorophyll in this article.
Chlorophyll
The word chlorophyll is derived from the Greek word khloros (green) and phyllon (leaves). Chlorophyll is a green pigment that acts as a photoreceptor. It is a pigment that absorbs light energy and aids in the photosynthesis. Chlorophyll exists in many forms, such as chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, etc.
The chlorophyll absorbs light energy of red and blue wavelengths. Whereas, the green light is not absorbed and is reflected back. Thus, the leaves appear green.
Also Read: Biological Pigments in Plants
Chloroplast
The chlorophyll pigment is found in cell organelle called chloroplasts. These chloroplasts act as a site of the photosynthesis process in both plants and blue-green algae.
Usually, the chloroplasts align along the walls of the mesophyll. This helps them to receive optimum sunlight. The chloroplast has different parts like grana, stroma, lamellae and thylakoids. The chlorophyll pigment is enclosed in the thylakoids of the chloroplast.
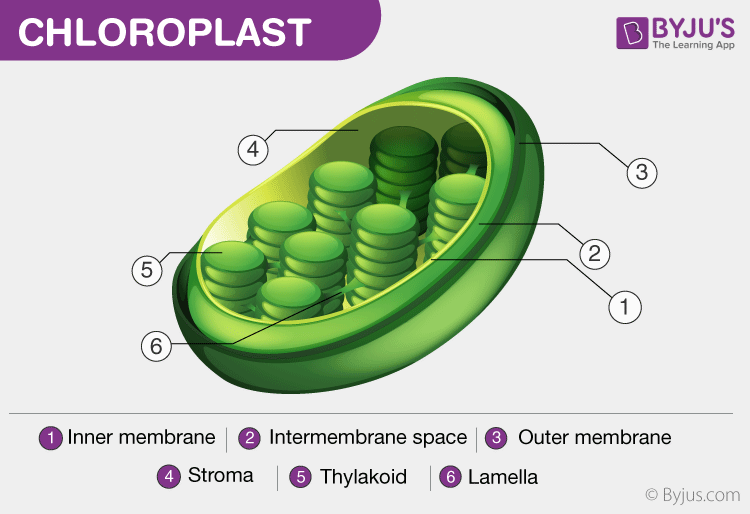
Also see: Chloroplast
Structure of Chlorophyll
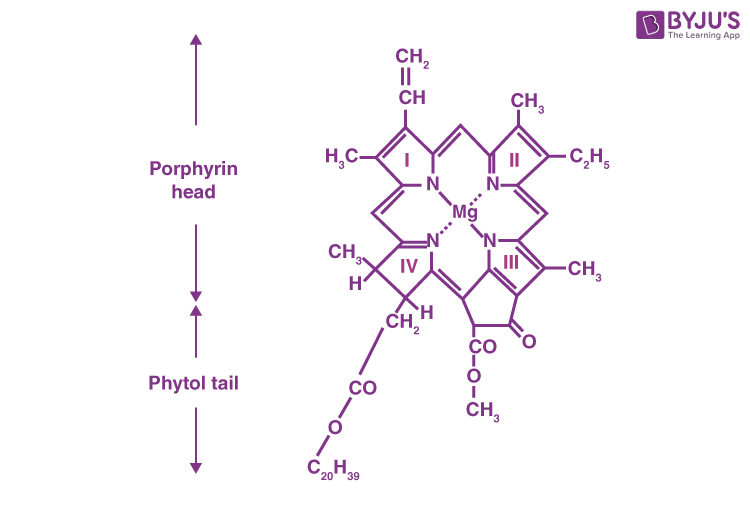
- Chlorophyll is a derivative of porphyrin. The central chemical structure of chlorophyll has a magnesium atom.
- Also, four nitrogen atoms are found around the magnesium. There is a pyrrole ring structure with four carbons and nitrogen.
- A hydrocarbon end is also seen.
- The four pyrrole rings with nitrogen and magnesium are together termed the porphyrin head.
- The hydrocarbon end is the phytol tail.
More to Read: Difference between Chlorophyll and Chloroplast
Frequently Asked Questions
What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is a photochemical process by which green plants prepare their own food. The chlorophyll absorbs sunlight, and this light, along with water and CO2, is transformed into energy molecules (glucose). Oxygen is also a by-product of photosynthesis.
How many types of pigments are involved in photosynthesis?
There are different types of pigments present in the leaves. This includes chlorophyll a (blue-green pigment), chlorophyll b (yellow-green), xanthophylls (yellow) and carotenoids (yellow-orange). Also, chlorophyll a is the chief pigment that helps in maximum photosynthesis. The other pigments are termed accessory pigments. These accessory pigments absorb light energy and transfer it to chlorophyll a.
Do cyanobacteria have chlorophyll?
Cyanobacteria are photoautotrophic organisms. They contain different varieties of chlorophyll pigment. They also trap sunlight to undergo photosynthesis. Various chlorophyll pigments like chlorophyll a, b, and even carotenoids are found in them.
What is the chemical formula of chlorophyll?
The chemical formula of chlorophyll is C55H72O5N4Mg.
What is the chemical structure of chlorophyll?
Also, four nitrogen atoms are found around the magnesium. There is a pyrrole ring structure with four carbons and nitrogen.
What is chlorophyll?

Keep exploring BYJU’S Biology for more exciting topics.

Comments