Homologous and analogous structures are often confused and understanding them is of great importance in comprehending the similarities and differences between various organisms.
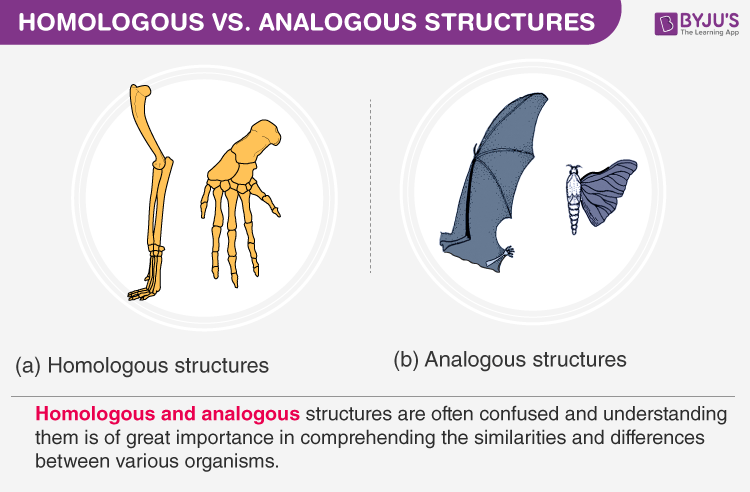
This knowledge helps scientists to make use of other animals to study various human biological processes and drug treatments without extensive and potentially dangerous experimentation on humans. Structures with similar anatomy, morphology, embryology and genetics but dissimilar functions are known as homologous structures. Structures that are superficially similar but anatomical dissimilar doing the same function are known as analogous structures. In this article, we look at the various differences between homologous and analogous structures.
Homologous vs. Analogous Structures
| Homologous Structure | Analogous Structure |
| Similar anatomy | Dissimilar anatomy |
| Dissimilar functions | Similar Functions |
| Inherited from a common ancestor | Not inherited from ancestors |
| Develops in related species | Develops in unrelated species |
| A result of divergent evolution | A result of convergent evolution |
| Developed as a result of the adaptation to a different environment | Developed as a result of the adaptation to a similar environment |
| An arm of a human, the leg of a dog or a flipper of a whale are all homologous structures | From wings in birds, bats and insects to fins in penguins and fishes are all analogous structures |
These were a few differences between analogous and homologous structures. From this, we can conclude that the main difference between homologous and analogous structures is the origin of each species.
Also Read:
| Evidence of Evolution | Anatomy |
| Morphology and Anatomy of Frogs | Evolution |

Difference between homologous character and analogous character with ex?