Single-Stranded DNA (ssDNA)
Some viruses have ssDNA or single-stranded DNA. It is a single linear strand of nucleic acid sequence. They do not have hydrogen bonds, and are thus less stiff and also less stable. The ssDNA is found abundantly in viruses of extreme conditions and marine environments.
Double-Stranded DNA (dsDNA)
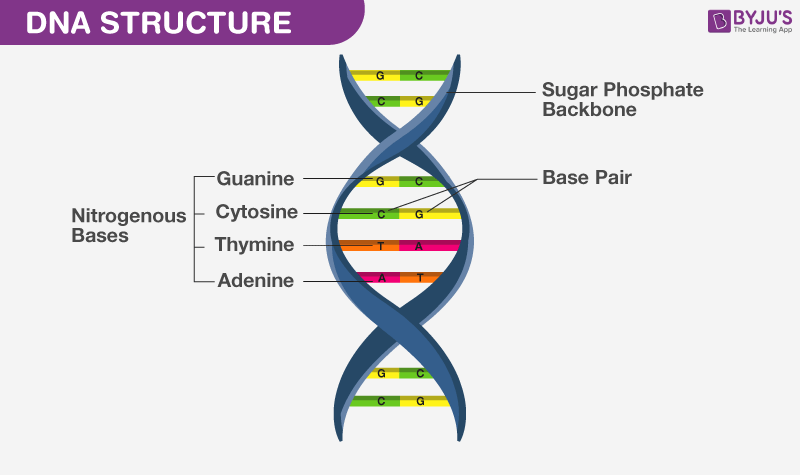
Most DNA molecules have two strands that are bound together by non-covalent (hydrogen) bonds. The strands are intertwined in a helical fashion. The DNA is made of nucleotide sequences. Each nucleotide is composed of a nucleobase (A, T, G, C), deoxyribose sugar and a phosphate group. Also, the percentage of G and C base pairs play a vital role in determining the stability of dsDNA.
The dsDNA can become two ssDNA through a process called melting. This melting occurs at high pH, low salt and high temperature.
Difference between ssDNA and dsDNA
|
ssDNA |
dsDNA |
|---|---|
|
ssDNA is a linear structure that has only one DNA strand. |
dsDNA has two DNA strands bound by hydrogen bonds in a helical fashion. |
|
It is found in a few viruses. |
Most organisms have dsDNA |
|
It is a less stiff and stable structure. |
It is a comparatively stiffer and more stable structure. |
|
The purine: pyrimidine ratio is highly variable. Thus, it does not follow chargaff’s rule. |
The purine: pyrimidine ratio is constant (i.e one). It follows chargaff’s rule. |
Explore: Difference between Purines and Pyrimidines
Frequently Asked Questions on Difference between ssDNA and dsDNA
What are the different DNA conformations?
A double helical DNA can adopt various structures or conformations. This structural change happens so that the specific protein gets attached to the DNA. The three biologically active conformations of dsDNA are A-DNA, Z-DNA, and B-DNA.
What are nucleotides and nucleosides?
A nucleoside is composed of just a nitrogenous base (A, T, G, C) and a sugar molecule. A nucleoside, along with a phosphate group, forms a nucleotide. The DNA is composed of such nucleotide sequences.
What is Chargaff’s rule?
When the ratio of purine (A, G) and pyrimidine (C, T) in a DNA molecule is 1: 1, then it is set to follow chargaff’s rule. The means, the amount of adenine should equal thymine, and the guanine should equal cytosine.
Also Read: Difference between Nucleotide and Nucleoside
Keep exploring BYJU’S Biology for more exciting topics.
Comments