The process of producing new individuals from their parents is called reproduction. Plant reproduction is the process by which plants produce new individuals or offspring. It is an inherent characteristic of all living organisms to continue or maintain their races by the mechanism of reproduction. Let’s see different modes of reproduction in plants and how it is different from animals.
Table of Contents
Modes of Reproduction in Plants
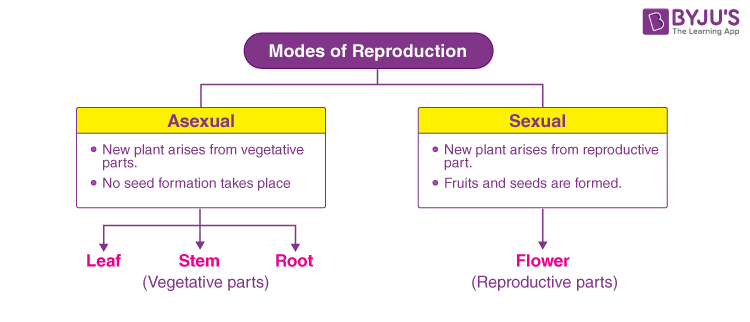
A mode of reproduction determines the genetic constitution of a plant and helps to understand its characteristics. If we look at a plant, we notice that it consists of different parts. The parts of a plant can be categorized as vegetative parts, which include leaves, roots and stem, and reproductive parts, which include flowers. A flower may either possess male parts or female parts or both male and female parts. Flowers perform reproductive functions in plants. When the male parts and the female parts are brought in contact, the gametes fuse to produce fruits that bear seeds. The seeds inside the fruits germinate to produce new plants. However, the vegetative parts of the plants are also capable of giving rise to new plants.
Also Refer: Reproduction In Plants
The modes of plant reproduction can be majorly classified as:
- Asexual mode of reproduction
- Sexual mode of reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
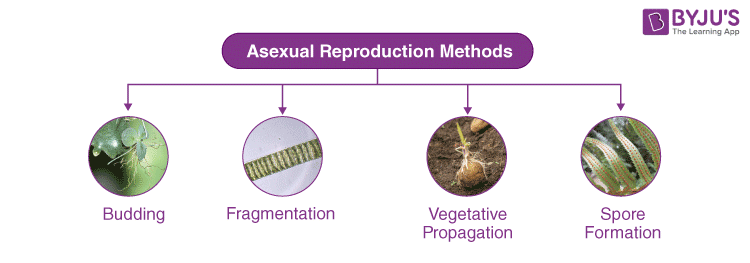
In this mode of reproduction, plants can give rise to new plants without the involvement of male and female reproductive parts. In this mode, plants do not produce fruits and seeds. Asexual reproduction in plants can occur in a variety of forms:
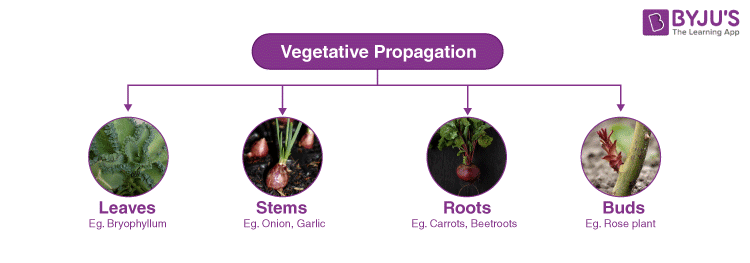
- Vegetative Propagation – New plants are developed from a portion of the main plant’s body. It can be reproduced both naturally as well as by the artificial method of vegetative propagation. For example- Onion bulbs are produced by natural propagation. Rose and banana plants are produced by artificial methods of propagation.
Read More: Vegetative Propagation
- Budding – In this mode of asexual reproduction, new plants grow from an outgrowth or bud in the plant body.
- Fragmentation – New plants are developed from fragments of the parent plant.
- Apomixis – is the type of asexual reproduction in which seeds are formed, and the embryo is developed without the fusion of male and female gametes. Citrus trees commonly use this method of asexual reproduction by using their seeds.
Also Read: Asexual Reproduction in Plants
Sexual Reproduction
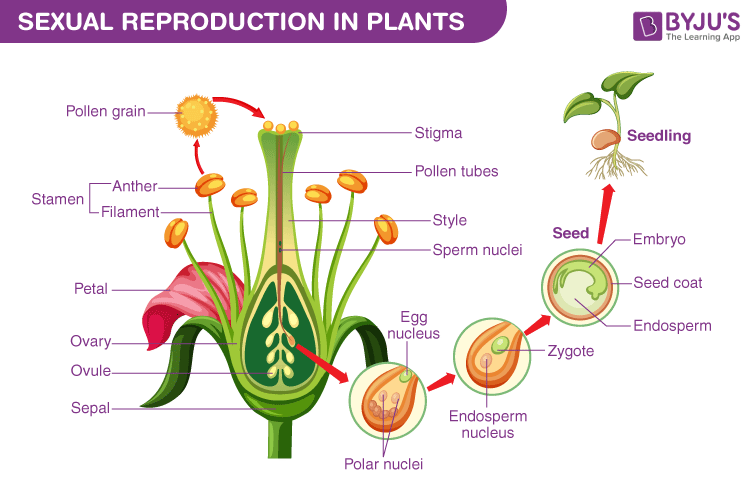
This mode of reproduction involves the production of new plants through embryos developed by the fusion of male and female gametes. In sexual reproduction, a fusion of male and female gametes produces fruits that contain seeds. The seeds give rise to new plants.
A flower is the reproductive part of a plant which can either be unisexual or bisexual. Stamen is the male reproductive part and the pistil is the female reproductive part of a flower.
Sexual reproduction is divided into three stages:
- Pollination
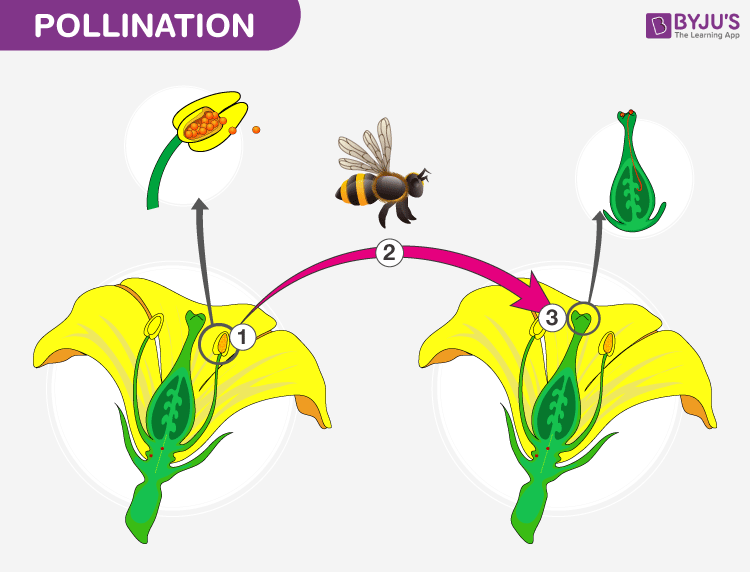
Pollination
A process in which the pollen grains are transferred across the anther to the stigma of the same flower or flowers of different plants. There are two types of pollination- self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Refer More: What Is Pollination
- Zygote formation
After the transfer of pollen grains, the male gamete is transferred down through the style of the pistil to the ovary where the male gamete is fused with the female gamete to form a zygote.
- Fruit and seed formation
After fertilization, a formed zygote is developed into an embryo. The ovary develops into fruit and ovules into seeds.
Also Refer: Sexual Reproduction In Plants
To learn more about plant reproduction, visit BYJU’S.

The byjus app is best for online classes
But i don’t join the class in this app
How can i join the classes in byjus?